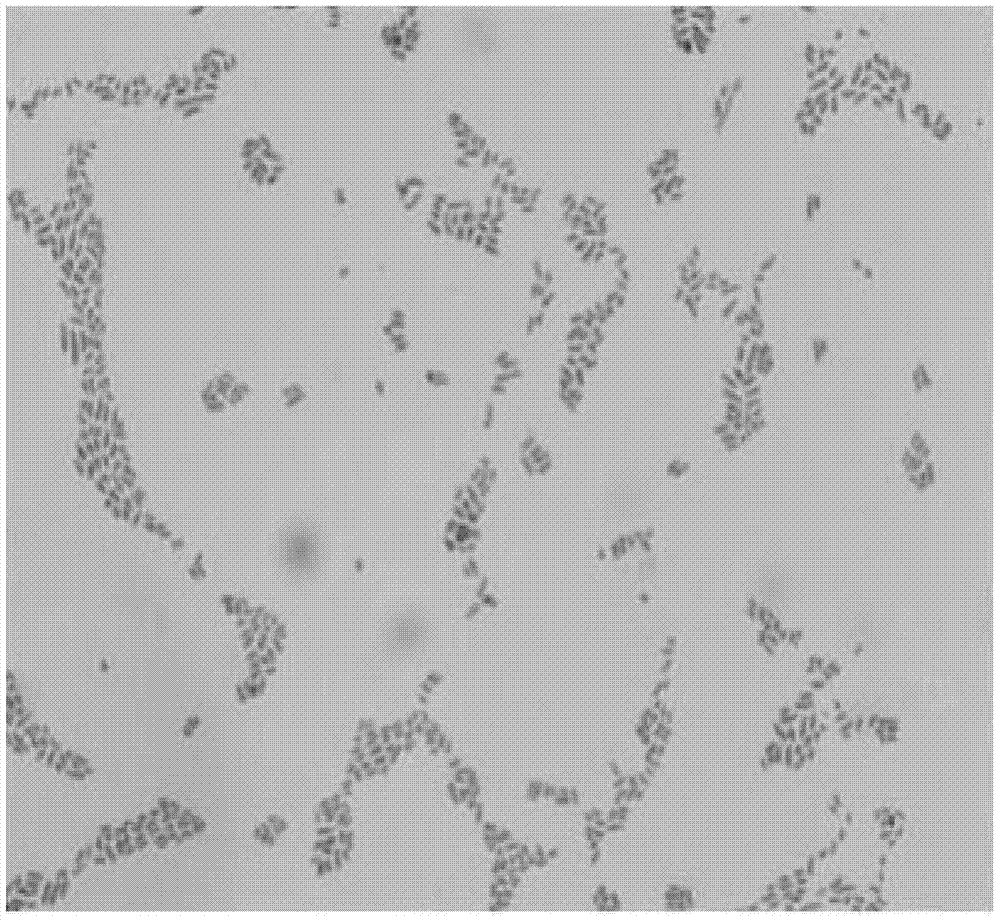
A kind of Pallidus tritici capable of degrading lincomycin
A technology of Paleobacterium pallidum and lincomycin, applied in the field of microorganisms, to achieve the effects of eliminating adverse effects, efficient treatment methods, and saving resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Example 1 Screening of Pallidinus tritici strains.
[0021] Step 1: Collect 10 g of sludge from the vicinity of an antibiotic enterprise in Shijiazhuang, inoculate it into 100 mL of inorganic salt medium containing 20 mg of lincomycin, and culture it on a shaker at 30° C. and 200 rpm. Transfer once every 7 days after the start of culture, and transfer to a medium containing lincomycin at a higher concentration with a 10% (V / V) inoculum during transfer, and the drug concentration of lincomycin in turn 20mg / L, 40mg / L, 80mg / L, 160mg / L, and so on, to 640mg / L, to obtain different concentrations of enriched culture solution containing bacteria.
[0022] Wherein, the composition and the proportioning ratio of the inorganic salt culture medium among the present invention are (g / L): K 2 HPO 4 1.6g, KH 2 PO 4 0.4g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.2g, CaCl 2 2H 2 O 0.025g, FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O 0.0023, NH 4 NO 3 0.5g, 18.0g agar, adjust the pH value to 7.0 with 1mol / L HCL or NaOH, and aut...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2 Screening of the Ochrobactrum tritici strain of the present invention and its degradation effect on lincomycin.
[0030] Step 1: Take 10g of sludge and put it in a sterilized 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, add 100mL of lincomycin hydrochloride solution with a concentration of 2000mg / L, and culture on a shaker at 30°C with a rotation speed of 200r / min. After the culture starts, transfer once every 7 days, inoculate into fresh lincomycin hydrochloride solution acclimation medium with 10% inoculum during transfer, and gradually increase the content of lincomycin hydrochloride. Detect the degradation rate of lincomycin hydrochloride, and select the best group for the isolation of strains.
[0031] Step 2: the bacterial suspension (1 × 108 cells / mL) were inserted into 100 mL of inorganic salt medium containing 20 mg / L lincomycin, and three parallels were taken, and the inorganic salt medium containing no bacteria but containing the same concentration of lincomycin was use...
Embodiment 3
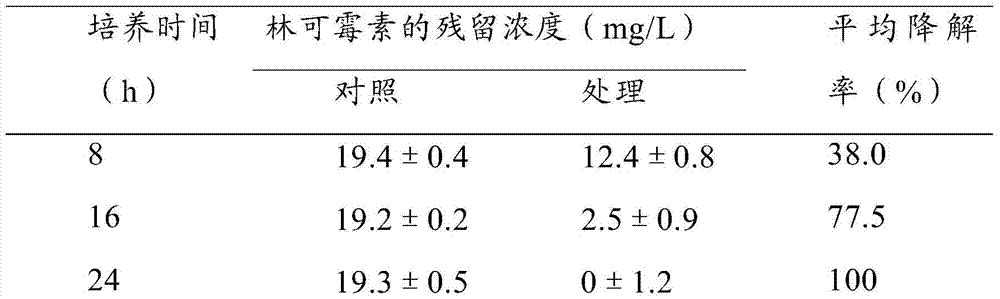
[0036] Example 3: Degradation of lincomycin in the bacteria residue by the strain of P. tritici.
[0037] Pass lincomycin waste wet hyphae through a 0.2 mm sieve, and sterilize at 121°C for 30 minutes. Weigh 10 g of sterilized waste mycelium, put it into 100 mL of water, add 5 g (dry weight) of Pallidinus tritici thalline that has been cultivated for 48 hours to the waste wet mycelium solution, and set up 3 groups of parallel experiments to add bacteria The fermented culture broth of P. tritici without adding P. tritici was used as a control, and samples were taken after 16, 32, 48, and 60 hours of treatment, and the residual amount of lincomycin was detected by high performance liquid chromatography. The results show that the degradation rate of the strain to lincomycin can reach 100% after being cultivated for 48 hours.
[0038] Table 2 Degradation effect of Pallidalbacterium tritici strains on lincomycin in bacteria residue
[0039]
[0040] As can be seen from the abo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com