Macrofungi specimen preparation method
A technology of specimen making and fungi, applied in the fields of botany equipment and methods, teaching models, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as environmental pollution of specimen preservation and storage, and achieve the effect of solving environmental pollution and inhibiting the growth of microorganisms.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
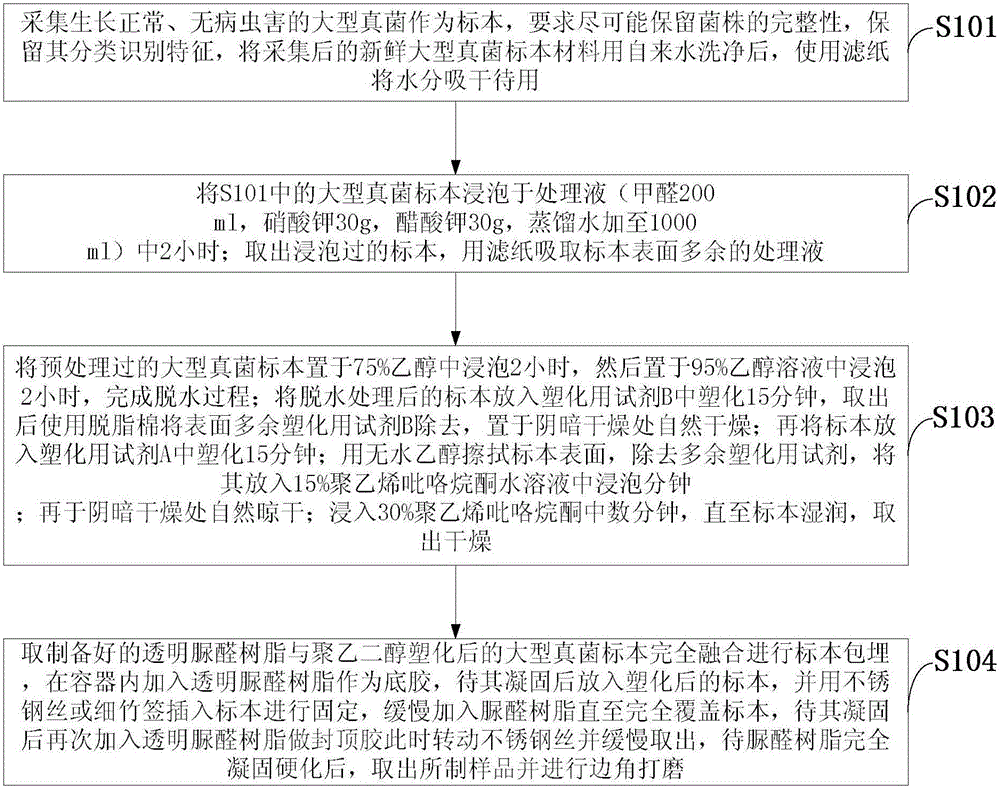
[0016] S101: Collect Pleurotus ferulae with normal growth and no pests and diseases as specimens. It is required to preserve the integrity of the strain as much as possible and keep its classification and identification characteristics. After the collected fresh Pleurotus ferulae is washed with tap water, use filter paper to dry the water stand-by;
[0017] S102: Soak the Pleurotus ferulae specimen in S101 in the treatment solution (200ml of formaldehyde, 30g of potassium nitrate, 30g of potassium acetate, and add distilled water to 1000ml) for 2 hours; take out the soaked specimen, and absorb the excess treatment solution on the surface of the specimen with filter paper ;
[0018] S103: Soak the pretreated Pleurotus ferulae specimen in 75% ethanol for 2 hours, and then soak in 95% ethanol solution for 2 hours to complete the dehydration process; put the dehydrated specimen into plasticizing reagent B Plasticize in medium for 15 minutes, remove excess plasticizing reagent B o...
Embodiment 2
[0033] S105: Collect Agaricus blazei with normal growth and no pests and diseases as specimens. It is required to preserve the integrity of the strain as much as possible and keep its classification and identification characteristics. After the collected fresh Agaricus blazei are washed with tap water, use filter paper to dry the water and set aside ;
[0034] S106: Soak the Agaricus blazei specimen in S101 in the treatment solution (200ml of formaldehyde, 30g of potassium nitrate, 30g of potassium acetate, and add distilled water to 1000ml) for 2 hours; take out the soaked specimen, and absorb the excess treatment solution on the surface of the specimen with filter paper;
[0035]S107: Soak the pretreated Agaricus blazei specimen in 75% ethanol for 2 hours, and then soak in 95% ethanol solution for 2 hours to complete the dehydration process; put the dehydrated specimen into plasticizing reagent B Plasticize for 15 minutes, remove excess plasticizing reagent B on the surface ...
Embodiment 3
[0050] S109: Collect tea tree mushrooms that grow normally and are free from diseases and insect pests as specimens. It is required to preserve the integrity of the strain as much as possible and keep its classification and identification characteristics. After the collected fresh tea tree mushrooms are washed with tap water, use filter paper to dry the water and set aside ;
[0051] S110: Soak the tea tree mushroom specimen in S101 in the treatment solution (200ml of formaldehyde, 30g of potassium nitrate, 30g of potassium acetate, and add distilled water to 1000ml) for 2 hours; take out the soaked specimen, and absorb the excess treatment solution on the surface of the specimen with filter paper;
[0052] S111: Soak the pretreated tea tree mushroom specimen in 75% ethanol for 2 hours, then soak in 95% ethanol solution for 2 hours to complete the dehydration process; put the dehydrated specimen into plasticizing reagent B Plasticize for 15 minutes, remove excess plasticizing ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com