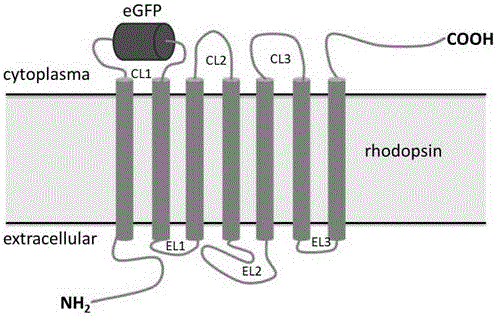
G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) in-vivo tracking method and application
A technology for coupling receptors and G proteins, applied in chemical instruments and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, preparations for in vivo experiments, etc., can solve the problems of G protein transduction function and phosphorylation efficiency reduction, gap, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
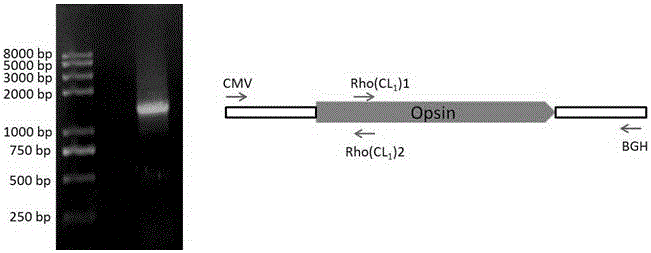
[0031] Example 1: Construction of rhodopsin K66M mutant by segmented PCR method
[0032] The purpose of constructing the rhodopsinK66M mutant is twofold, one is to detect whether K66 of rhodopsin is a key residue and whether it can be inserted into eGFP; the other is to introduce a unique Nde I restriction site in rhodopsin to facilitate the insertion of eGFP . The present invention utilizes segmental PCR method to construct rhodopsinK66M mutant, main steps are as follows:
[0033] 1) Using the existing pcDNA4 / TO-rhodopsin plasmid in the laboratory as a template, use the pcDNA4 / TO plasmid general upstream primer CMV and downstream primer Rho(CL1)2 (including the mutation site) to amplify Fragment 1 with a size of about 390bp . The primers used are as follows:
[0034] CMV: 5'-CGCAAATGGGCGGTAGGCGTG-3'
[0035] Rho(CL1)2: 5'CGTGCGCAGCTT CATATG CTGGACGGT-3' (Nde I)
[0036] 2) Using the existing pcDNA4 / TO-rhodopsin plasmid in the laboratory as a template, use the pcDNA4 / TO...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2: rhodopsin CL1 -eGFP gene construct
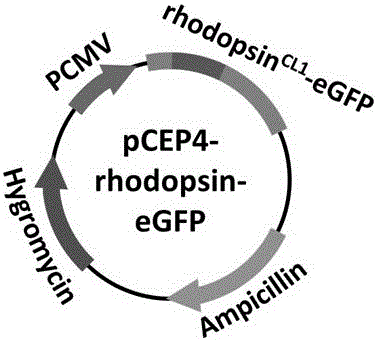
[0056] rhodopsin CL1 - The idea of eGFP gene construction is to insert the eGFP gene into pCEP4-rhodopsinK66M to obtain pCEP4-rhodopsin CL1 -eGFP (see figure 2 ).
[0057] Specific steps are as follows:
[0058] 1) Replace the rhodopsinK66M gene fragment from the pCEP4 plasmid to the pBAD24 plasmid: first, pCEP4-rhodopsinK66M and pBAD24 plasmids were digested with BamH I and Hind III, and then the rhodopsinK66M fragment was ligated with the double digested pBAD24 plasmid with T4 ligase Up, the pBAD24-rhodopsinK66M plasmid was obtained.
[0059] 2) Use primers eGFP1 and eGFP2 to amplify the eGFP fragment (about 720bp) with NdeI restriction sites at both ends from the pcDNA3.1-3'-eGFP plasmid, and recover the PCR product from the gel.
[0060] Upstream primer eGFP1: 5'-GGAATTC CATATG GTGAGCAAGGGCGAGGAG-3' (Nde I)
[0061] Downstream primer eGFP2: 5'-CCCTTAAG CATATG CTTGTACAGCTCGTCCAT-3' (Nde I)
[0062] 3) The...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Example 3: pCEP4-rhodopsin CL1 -Expression detection of eGFP in HEK293S cells
[0077] pCEP4-rhodopsin CL1 - The detection of eGFP expression in HEK293S cells mainly includes two aspects, one is to check rhodopsin through Western Blot results CL1 -Expression level and glycosylation processing of eGFP (reference Figure 5 ), the second is to detect rhodopsin by fluorescence microscopy CL1 -Whether eGFP can normally emit green fluorescence and whether it accumulates in cells, etc. (refer to Figure 6 ). The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0078] 1) Plasmid preparation: Prepare the plasmid with a plasmid extraction kit, and select a plasmid concentration of not less than 200ng / μl, A 260 / A 280 High-purity pCEP4-rhodopsin between 1.9 and 2.0 CL1 - eGFP plasmid. The same method was used to prepare pCEP4-rhodopsinWT and pCEP4-rhodopsinK66M plasmids as controls.
[0079] 2) Cell preparation: select HEK293S that has been passaged at least twice after thawin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com