Method for detecting Echinococcus multilocularis from fox excrement
A technology of Echinococcus multilocularis and fox, applied in the field of identification of Echinococcus multilocularis pathogens, can solve the problems of low sensitivity and specificity, danger of infecting people and the surrounding environment, and achieve high accuracy and low cost Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] 1 Collection of Tibetan fox feces samples: Tibetan fox feces samples were collected from the home range of 7 radio-tracked Tibetan foxes (Yunbogou, Erdoma Township, Shiqu County, Sichuan Province (N 33°10′, E 97 °39′)), all samples were stored in 70% ethanol, and for safety reasons, they were frozen at -80°C for more than 3 weeks before the experiment.
[0026] 2 Enrichment of feces eggs: Take 2g of feces and put them in a 150ml beaker, add 100ml of deionized water. Water bath at 80°C for 10 minutes, mince with scissors, and mix well. Filter the turbid liquid with a 100-mesh filter, store the filtrate in a 50ml test tube, pour the filtrate on the double-layer sterilized gauze laid flat on the plate, squeeze the gauze several times, let the turbid liquid seep out, and collect it In a 50ml test tube. Centrifuge at 3600g for 30min, discard the supernatant.
[0027] 3. Fragmentation of worm egg embryo membrane: add 600ul ASL, mix it with the precipitate with a pipette ti...
Embodiment 2
[0032] We designed a nested PCR method to screen for the presence of Echinococcus multilocularis genetic material in fox feces. The outer primers were the general primers (F1, R1) used to amplify the partial sequence of mitochondrial DNA cytochrome oxidase I subunit gene (COI), with a length of 874bp. The inner primer was designed with Primer Premier 5.0 software, and the product length was 243bp.
Embodiment 3
[0033] Effect evaluation of embodiment 3 nested PCR
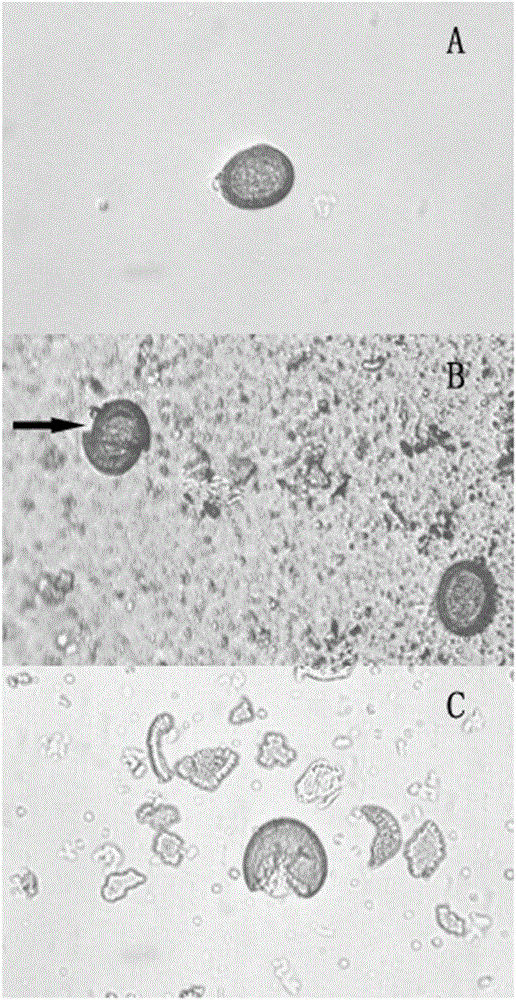
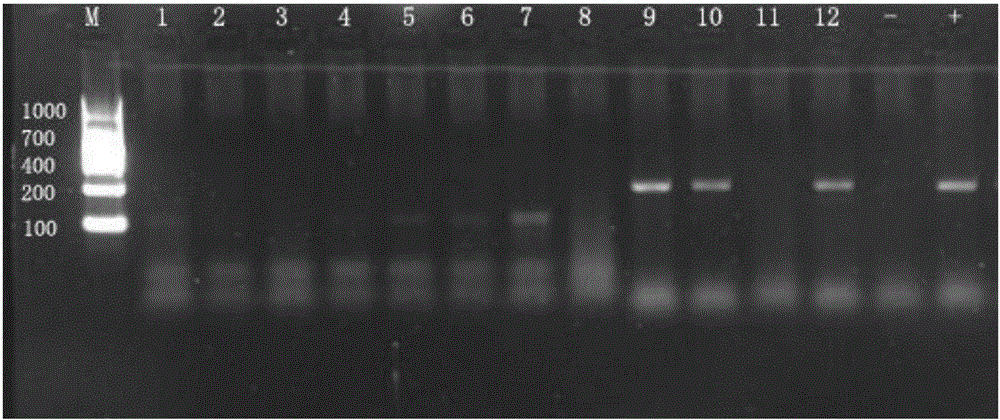
[0034] We randomly selected 72 samples from a total of 184 stool samples collected in 2010 to evaluate the established fecal DNA nested PCR diagnostic method. Among them, the DNA of 48 samples was successfully extracted, and after species identification, all of them came from Tibetan foxes. After enrichment and crushing of tapeworm eggs in fecal samples ( figure 1 ), we used nested PCR and Xiao(Xiao N, Nakao M, Qiu JM, Budke CM, Giraudoux P, Craig PS, Ito A(2006a) Short Report: Dual infection of animal hosts with different species of Echinococcus in the eastern Qinghai -Tibetan Plateau region of China.Am J Trop Med Hyg,75:292-294.) Two methods of PCR-RFLP were established to screen the Em genetic material in fox feces, and found that the detection results of the two methods were significantly different <0.001, Wilcoxon sign test for paired samples). Among the 48 stool samples, nested PCR detected 9 (19%) samples infected...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com