Method for increase production of aromatic hydrocarbon raw material by use of inferior heavy aromatics
A technology for heavy aromatic hydrocarbons and heavy aromatic hydrocarbons, which is applied in the fields of high-purity benzene, C9 monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and C10 monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon mixtures, xylene, and toluene, can solve the problem of low purity of aromatic hydrocarbon products and utilization rate of inferior heavy aromatic hydrocarbon raw materials. Problems such as low yield and low yield of monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
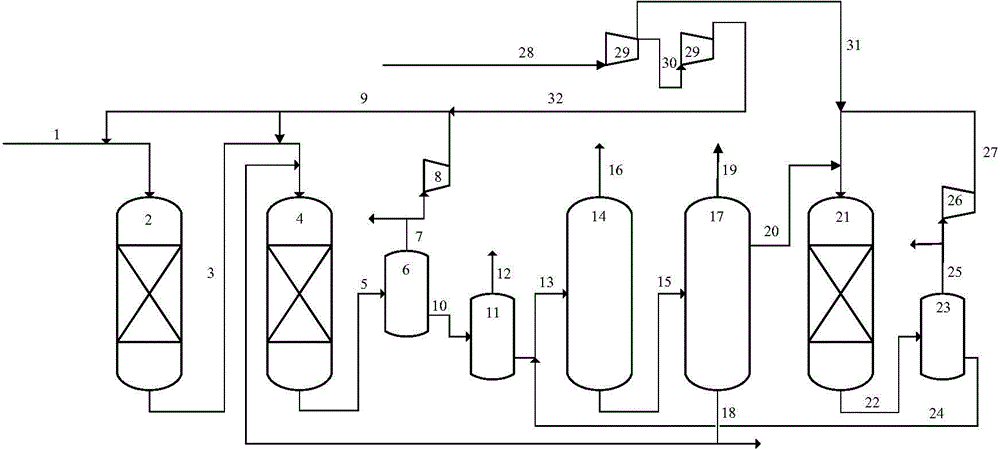
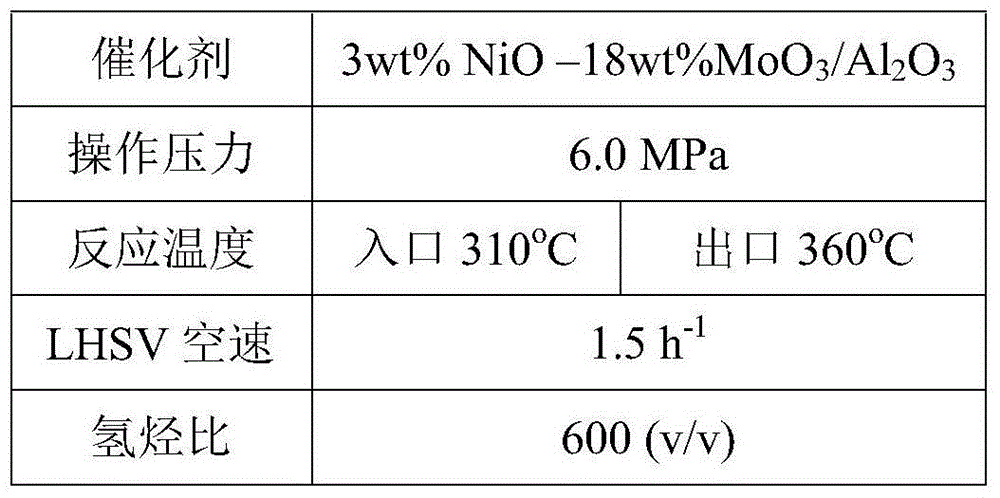
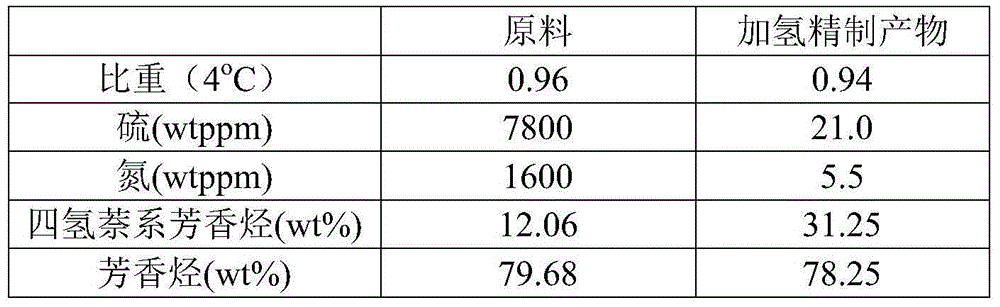
[0016] After mixing inferior heavy aromatics with a boiling point of 180-370°C and 6.0 MPa hydrogen, they enter the hydrotreating reactor to remove sulfur and nitrogen, and saturate part of the condensed ring aromatics until one aromatic ring remains. Table 1 lists the catalysts used and Reaction conditions. Table 2 lists the sulfur and nitrogen content, density, aromatic compound content, tetralin aromatic hydrocarbon content, and fraction distribution of raw materials and hydrorefined products. The nitrogen content of the hydrorefined product is less than 20 ppm.
[0017] Table 1
[0018]
[0019] Table 2
[0020]
[0021]
Embodiment 2
[0023] After the hydrorefined product is mixed with 6.0MPa hydrogen, it enters the selective hydrocracking reactor, where the selective hydrogenation ring-opening reaction and dealkylation reaction of tetrahydronaphthalene aromatics and polycyclic aromatics occur. Table 3 lists the catalysts and reaction conditions used. Selective hydrocracking reaction products are cut into light fractions below 70°C, light aromatic fractions at 70-145°C, heavy aromatic fractions at 145-200°C and heavy fractions greater than 200°C in series fractionation towers. The light fraction below 70°C is discharged to the outside; 70% of the heavy fraction is recycled to the selective hydrocracking reactor, and 30% of the heavy fraction is discharged to the outside; the 70-145°C light aromatic fraction is discharged as a product; the 145-200°C fraction sent downstream. Table 4 lists the composition of light aromatic components, mainly benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and xylene, and also contains a smal...
Embodiment 3
[0030] After mixing the heavy aromatics fraction at 145-200°C with 3.0MPa hydrogen, it enters the heavy aromatics lightening reactor, where C9 aromatics, C10 and above aromatics undergo alkylation transfer and side chain dealkylation reactions. Table 5 lists the heavy aromatics lightening catalysts and reaction conditions used. The lightened products of heavy aromatics are returned to the fractionation system after oil and gas separation.
[0031] table 5
[0032]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com