Method for utilizing sensitive silkworm embryos to detect genetic toxic substances in environment
A technology for genotoxicity and environment detection, applied in the field of genotoxicity, can solve problems such as cell death, tissue and organ damage, developmental delay, etc., and achieve the effect of single detection sample and simple method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1, obtain sensitive silkworm embryo, carry out the following steps successively:
[0031] 1), the preparation of active silkworm eggs:
[0032] The activated silkworm eggs stored in the cold storage are taken out, or the silkworm eggs produced by the female moths (female adults) after mating of the silkworm are refrigerated or immediately pickled to obtain active silkworm eggs;
[0033] Remarks: This step 1) is a conventional technique; how to judge the activity can be tested according to the silkworm breeding technical regulations in the fourth part of "DB33T217.4-2007", when the embryo can be further developed after the greening is satisfied The condition is active.
[0034] 2), the acquisition of sensitive silkworm embryos:
[0035] The above-mentioned active silkworm eggs are accelerated to the terminal stage of reversal according to the simple method of accelerating greening. 2 , to obtain the target environment sensitive silkworm embryo;
[0036] Re...
Embodiment 2
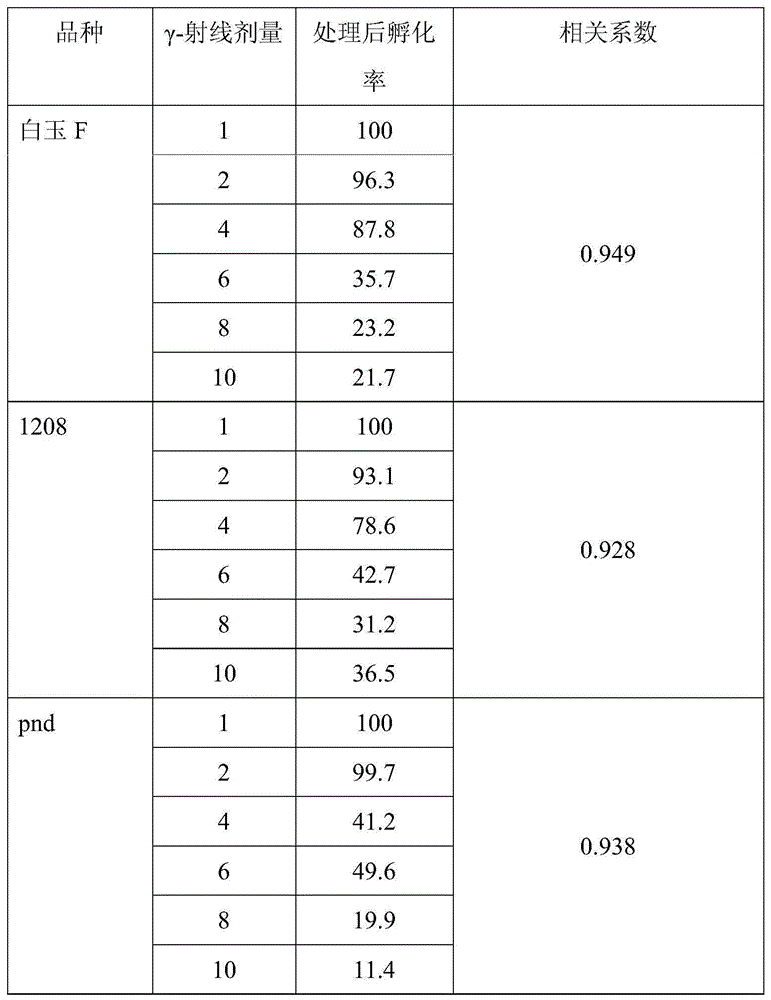
[0037] Embodiment 2, utilize sensitive silkworm embryo to detect gamma-ray:
[0038] The environmentally sensitive silkworm embryos obtained in Example 1 above were irradiated with different doses of γ-rays (1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 Gy) at room temperature. After irradiation treatment, continue to accelerate greening protection according to the simple greening method until hatching. After hatching, investigate the number of hatched eggs and the number of non-hatched eggs on the first day and the second day, and calculate according to hatching rate = number of hatched individuals / total number of treated individuals Two-day hatch rate (practical hatch rate). Remarks: The number of hatched individuals above refers to the number of hatched eggs on the first day + the number of hatched eggs on the second day.
[0039] Environmentally sensitive silkworm embryos are sensitive to radiation, etc. Radiation irradiates environmentally sensitive silkworm embryos. After irradiation, the embryo d...
Embodiment 3
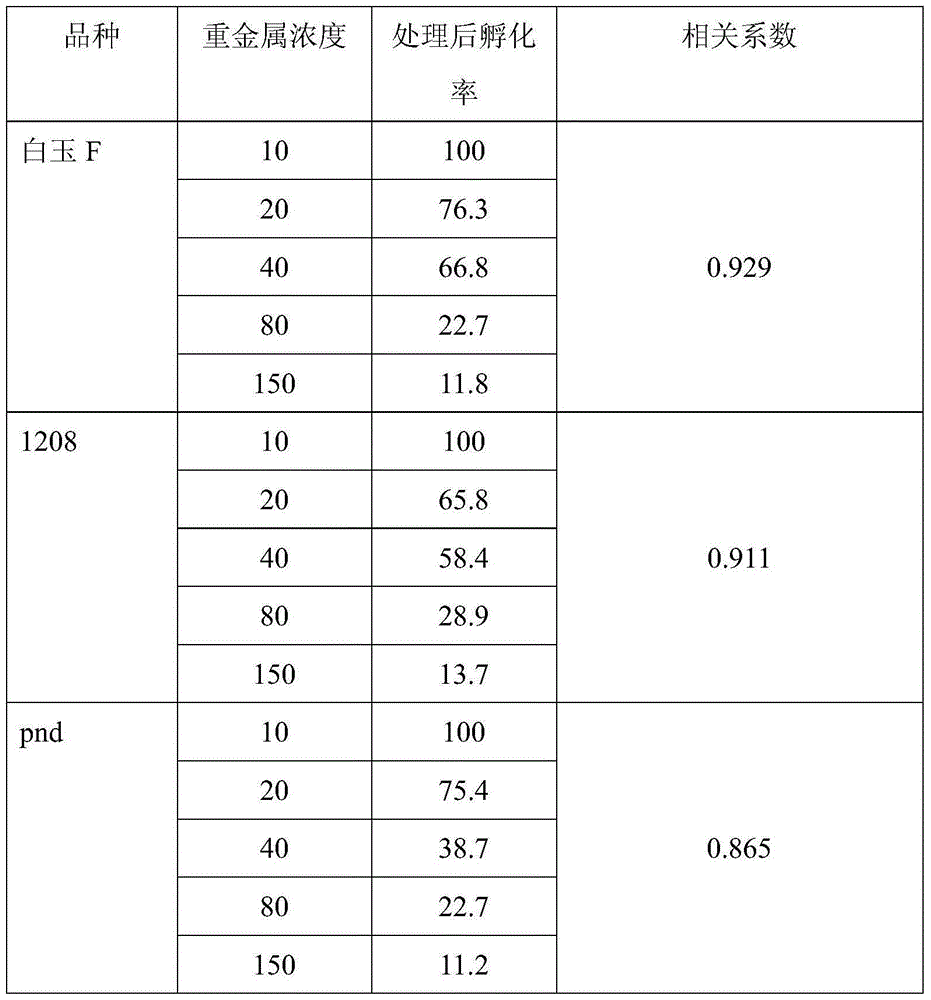
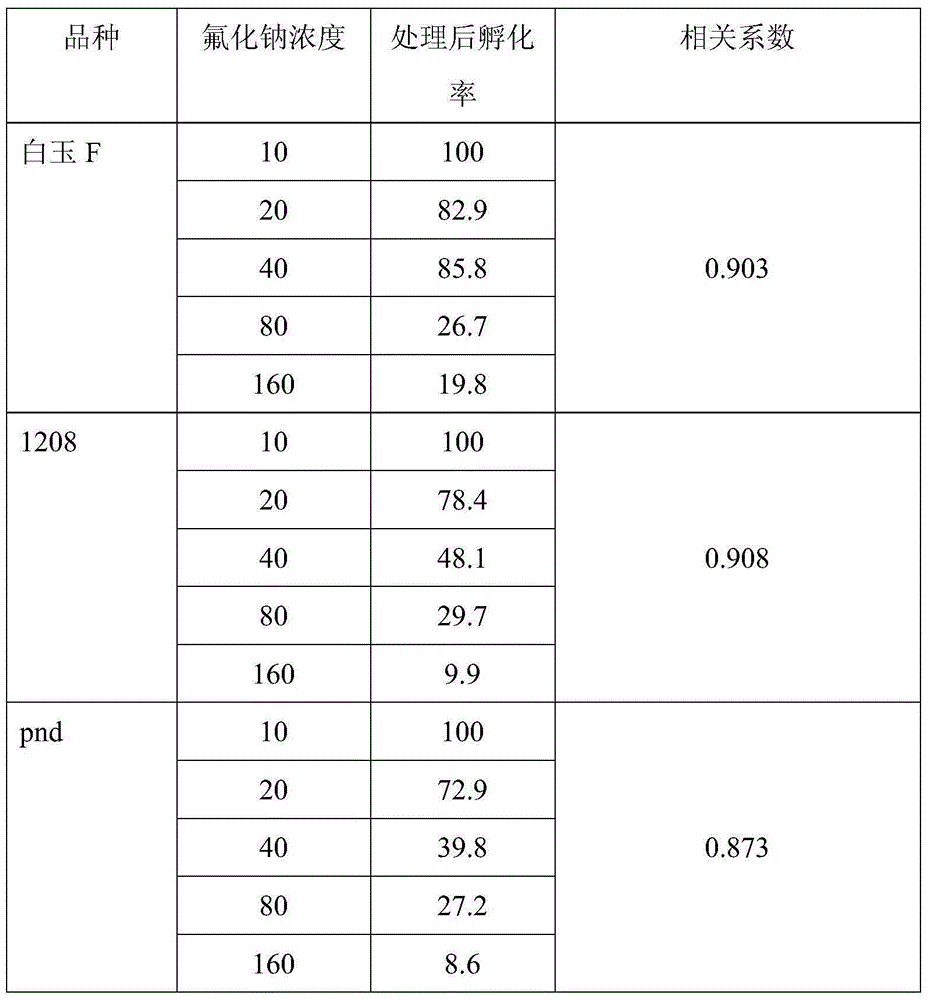
[0042] Embodiment 3, utilize environment sensitive silkworm embryo to detect heavy metal:
[0043] The environmental sensitivity silkworm embryo that above-mentioned embodiment 1 obtains carries out different concentrations of heavy metal CdCl at room temperature 2 Sample dipping (concentrations are 10, 20, 40, 80, 150ppm respectively), the dipping treatment time is 30min, after the dipping treatment, the greening method is accelerated and protected until hatching, and the hatched eggs on the first day and the second day are investigated after hatching Number of eggs and non-hatching eggs, calculate the hatching rate (practical hatching rate) on the second day by hatching rate=hatching individual number / total treatment individual number.
[0044] Environmental Sensitivity Bombyx mori embryos are sensitive to pollutants such as heavy metals, and heavy metal treatment affects embryo development and hatching rate. Therefore, the calculated hatchability is the same as that of hea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com