Preparation and application of several common plant extracts
A plant extract and plant technology, applied in the preparation and application of several common plant extracts, can solve the problems of no lack of active groups, difficult purification, low metabolism, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] 1) Experimental principle
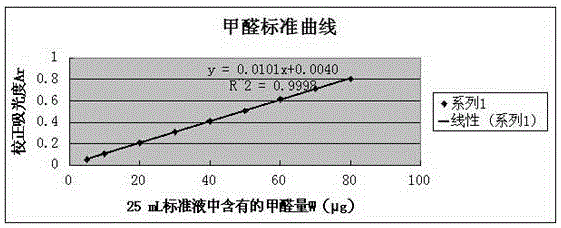
[0038] Formaldehyde in the air reacts with acetylacetone to form a yellow complex, which is colorimetrically quantified at 414 nm with a spectrophotometer. 2) Preparation of standard curve
[0039] (1) Prepare formaldehyde standard use solution: ρ=10ug / mL, absorb 4.28mL formaldehyde standard stock solution, and dilute it into a 500mL volumetric flask with water.
[0040] (2) Preparation of acetylacetone reagent: Dissolve 50g of ammonium acetate, 6mL of glacial acetic acid and 0.5mL of acetylacetone in 100mL of water.
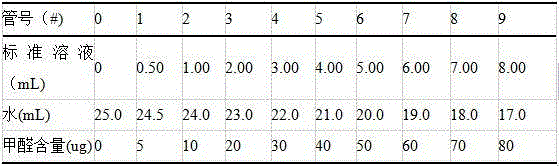
[0041] (3) Take 10 25mL volumetric flasks, number them respectively, and press figure 1 Sequence of adding samples:
[0042]Add 5.0mL acetylacetone reagent to each of the standard tube and the sample tube, stopper, mix well, place in a water bath at 60°C±1°C for 15min, take it out, and cool it to room temperature with tap water. Use the "0" tube as a blank, and use a 30nm cuvette for color comparison at a wavelength of 414...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Choose a 500mL brown bottle as the airtight compartment, stick the filter paper prepared in advance on the bottle cap; then pre-load the extract to be tested, then use a pipette gun to drop 20uL of formaldehyde on the filter paper of the bottle cap, and quickly cover it Cover, and seal the bottle cap with plastic wrap, absorb under normal pressure for a period of time, take out the extract to be tested, and measure the concentration of formaldehyde contained therein.
[0046] Example 3:
Embodiment 3
[0048] 1) Preparation of Humulus japonicus extract
[0049] Take 50g of fresh Humulus leaves and crush them, add 1000mL of 70% ethanol to soak overnight, extract with ultrasonic wave for 1h, centrifugally filter (10min1000r / min), and filter the filtrate through a 0.45μm microfiltration membrane. The filtrate was collected in a 500mL brown bottle and stored in a refrigerator for later use. The measured pH was 6.75.
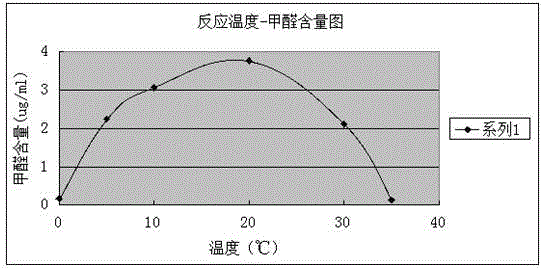
[0050] 2) Effect of reaction temperature on formaldehyde adsorption effect
[0051] Take 100mL of the above-mentioned Humulus japonicus extract, according to the device in Example 2, use a pipette gun to inject 20mL of formaldehyde into the filter paper that has been glued on the bottle cap in advance, and place them at 0°C, 5°C, 10°C, and 20°C respectively. , 30°C, and 35°C for 30 minutes; use the same pH value and volume of 70% ethanol as a blank control under the same conditions.
[0052] Sample determination: take four 50mL volumetric flasks, numbered 1-4 res...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com