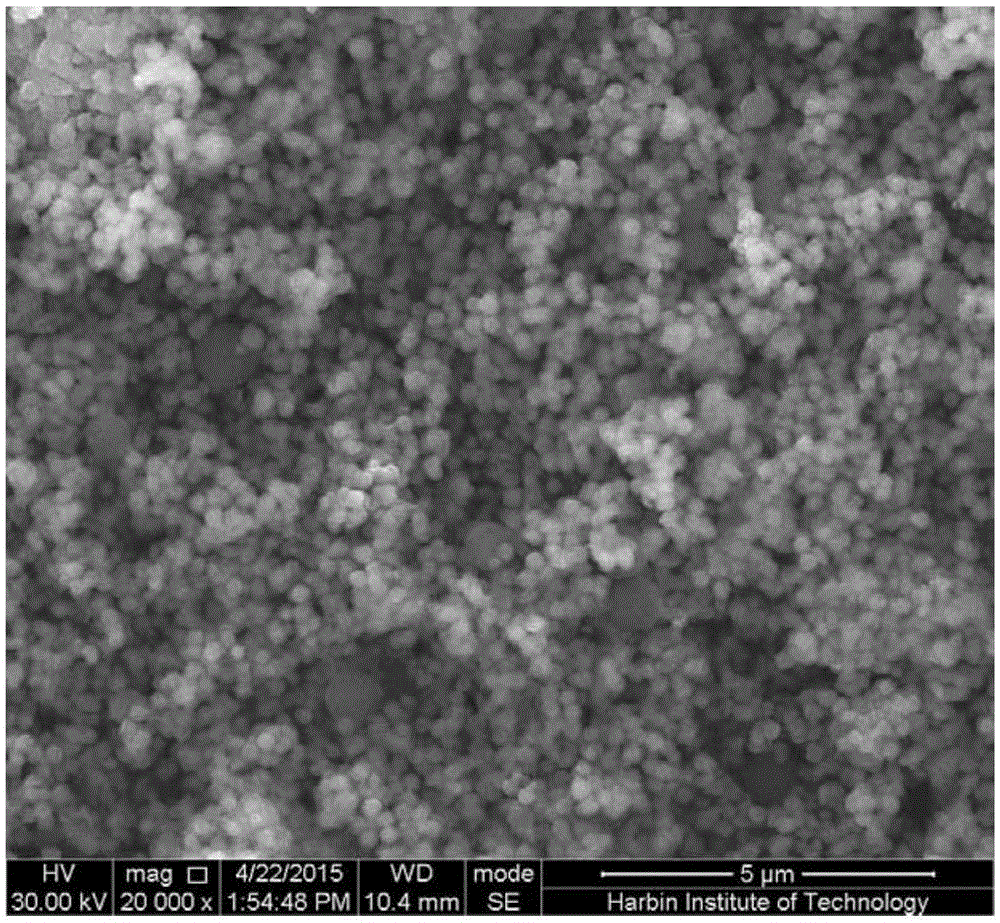
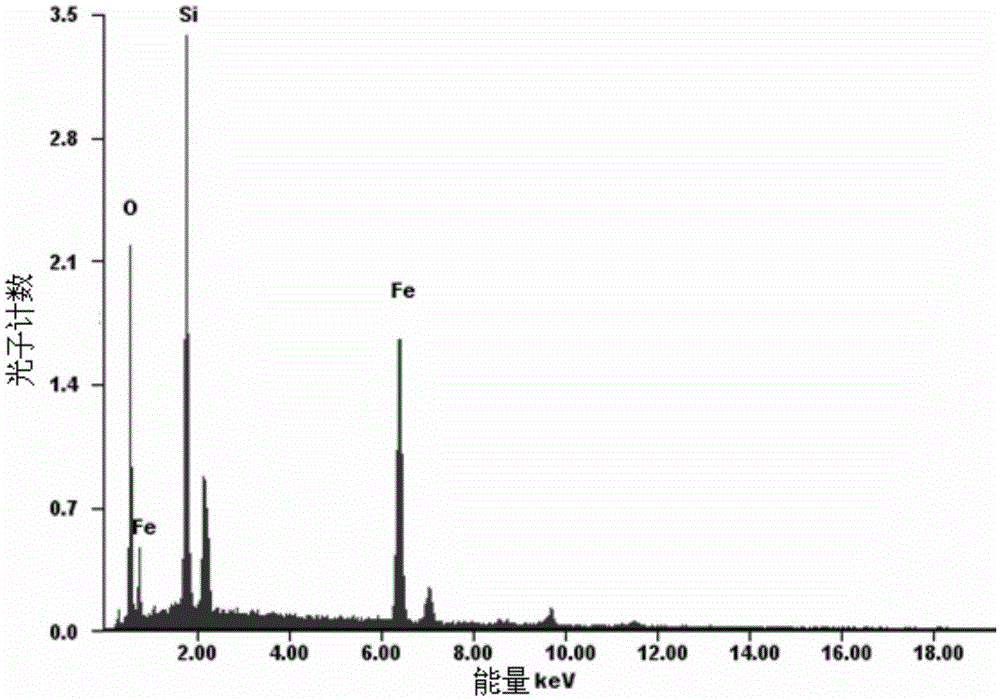
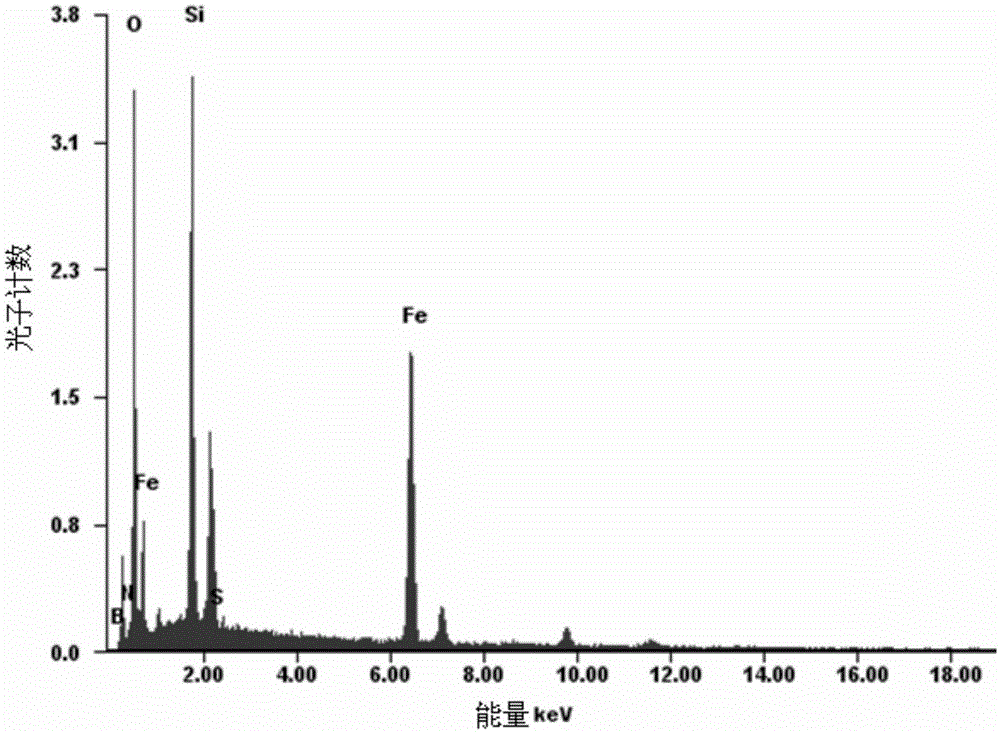
Method for preparing glucose difunctional monomer magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer
A technology of magnetic molecular imprinting and bifunctional monomers, which is applied in the field of preparing glucose molecularly imprinted polymers, and can solve the problems that glucose molecularly imprinted polymers have not been reported.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0036] Embodiment 1: A method for preparing a glucose bifunctional monomer magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer according to this embodiment is carried out in the following steps:
[0037] 1. Preparation of aqueous superparamagnetic Fe 3 o 4 Nanoparticles: FeCl 3 ·6H 2 Dissolve O in ethylene glycol, ultrasonically treat until no solid exists, then add anhydrous sodium acetate, stir at a stirring speed of 200r / min~400r / min for 25min~35min, transfer to a stainless steel reaction kettle, and React for 11h-13h under the conditions of 180-220°C and stirring speed of 80r / min-120r / min, stop the reaction, perform magnetic separation and sedimentation with NdFeB magnets, pour out the upper liquid, and wash the obtained solid matter Treatment, the washing treatment is: first wash the solid matter with 95% ethanol for 3 times, and then wash the solid matter with deionized water for 3 times to obtain Fe 3 o 4 magnetic nanoparticles;
[0038] The FeCl 3 ·6H 2 The ratio of the mas...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0057] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the FeCl described in step one 3 ·6H 2 The ratio of the quality of O to the volume of ethylene glycol is 13.5g: 500mL; the FeCl described in step one 3 ·6H 2 The mass ratio of O to anhydrous sodium acetate is 13.5:36. Other steps and parameters are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0058] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: the volume ratio of hydrochloric acid described in step two and ethylene glycol described in step one is 1.2:5; The volume ratio of trisodium citrate to the ethylene glycol described in step 1 is 1.2:5. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Saturated adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com