Surface in-situ processing method of metal lithium negative electrode and application
An in-situ treatment, metal lithium technology, applied in battery electrodes, electrical components, electrochemical generators, etc., can solve the uneven distribution of electric field on the surface of metal lithium, the formation of uneven lithium deposition, the formation of lithium dendrites, and the uneven microscopic surface of metal lithium. problems such as leveling, to achieve the effect of being suitable for large-scale production, solving continuous cracking and self-repairing, and simple preparation method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1, Preparation of Lithium Phosphate SEI Film on Metal Lithium Negative Electrode Surface
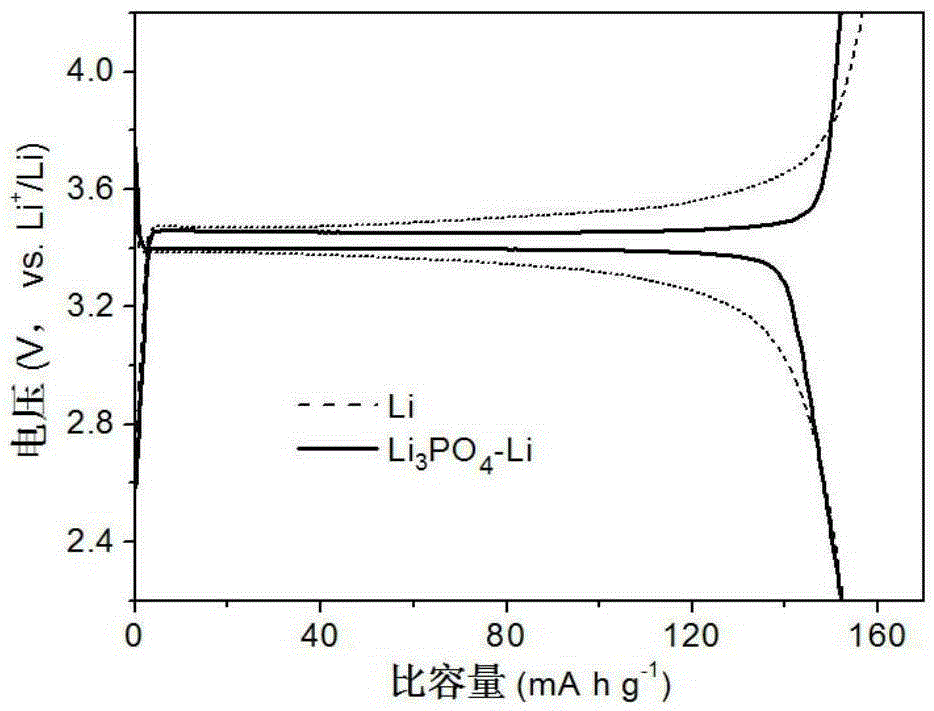
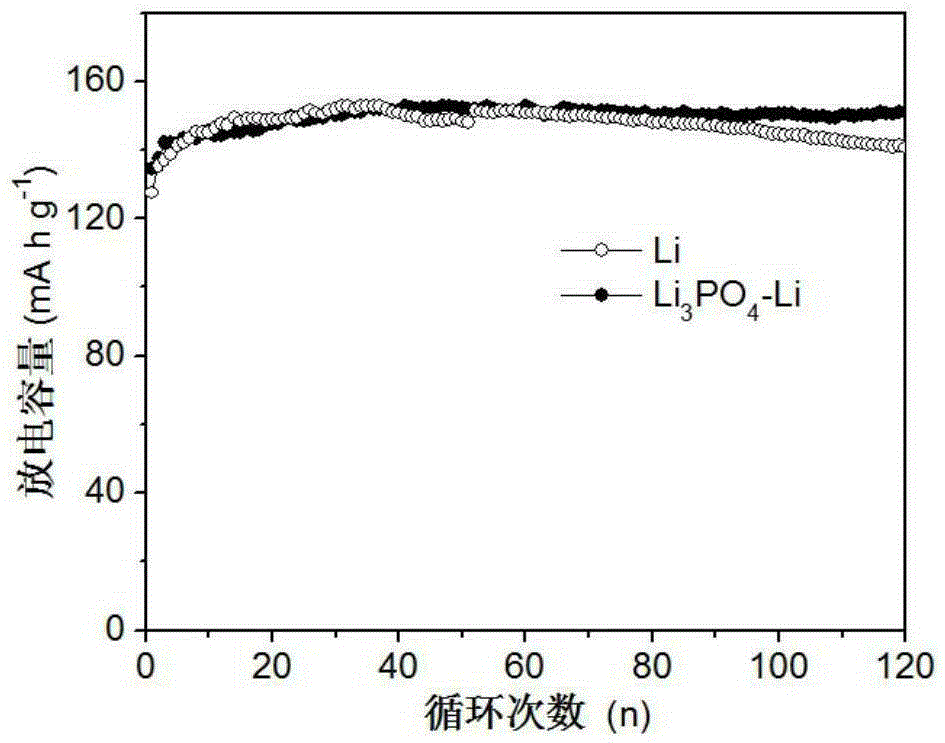
[0034] In a high-purity argon atmosphere, immerse the polished lithium sheet in a DMSO treatment solution containing 0.04M phosphoric acid and react for 2 minutes at a reaction temperature of 25°C. After the lithium sheet is taken out, the excess treatment solution on the surface can be wiped off to obtain the present invention. Metal lithium anode containing lithium phosphate SEI film.
[0035] The morphology and structure of lithium phosphate SEI films were observed by cold field emission scanning electron microscopy (SEM). It can be seen that the surface is rough, and EDXMapping shows that P, O, and C elements are evenly distributed on the surface of the lithium negative electrode. It can be seen from the cross-sectional view of the SEM that the thickness of the lithium phosphate SEI film is about 150 nm. XPS proves that its surface is lithium phosphate and a small am...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2, Preparation of Lithium Phosphate SEI Film on Metal Lithium Negative Electrode Surface
[0037] Other conditions are the same as in Example 1, except that the concentration of the phosphoric acid treatment solution is changed to 0.1M. The morphology and structure of the lithium phosphate SEI film were observed by SEM. It can be seen that the surface is relatively smooth, but the cracking phenomenon is relatively serious. EDXMapping shows that P, O, and C elements are evenly distributed on the surface of the lithium negative electrode. It can be seen from the cross-sectional view of the SEM that the thickness of the lithium phosphate SEI film is about 500 nm. XPS proves that its surface is lithium phosphate and a small amount of organic matter.
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3, Preparation of Lithium Phosphate SEI Film on Metal Lithium Negative Electrode Surface
[0039]Other conditions are the same as in Example 1, except that the concentration of the phosphoric acid treatment solution is changed to 0.005M. The morphology and structure of the lithium phosphate SEI film were observed by SEM. It can be seen that the surface is still rough, and EDXMapping shows that P, O, and C elements are evenly distributed on the surface of the lithium negative electrode. It can be seen from the cross-sectional view of the SEM that the thickness of the lithium phosphate SEI film is about 20 nm. XPS proves that its surface is lithium phosphate and a small amount of organic matter.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com