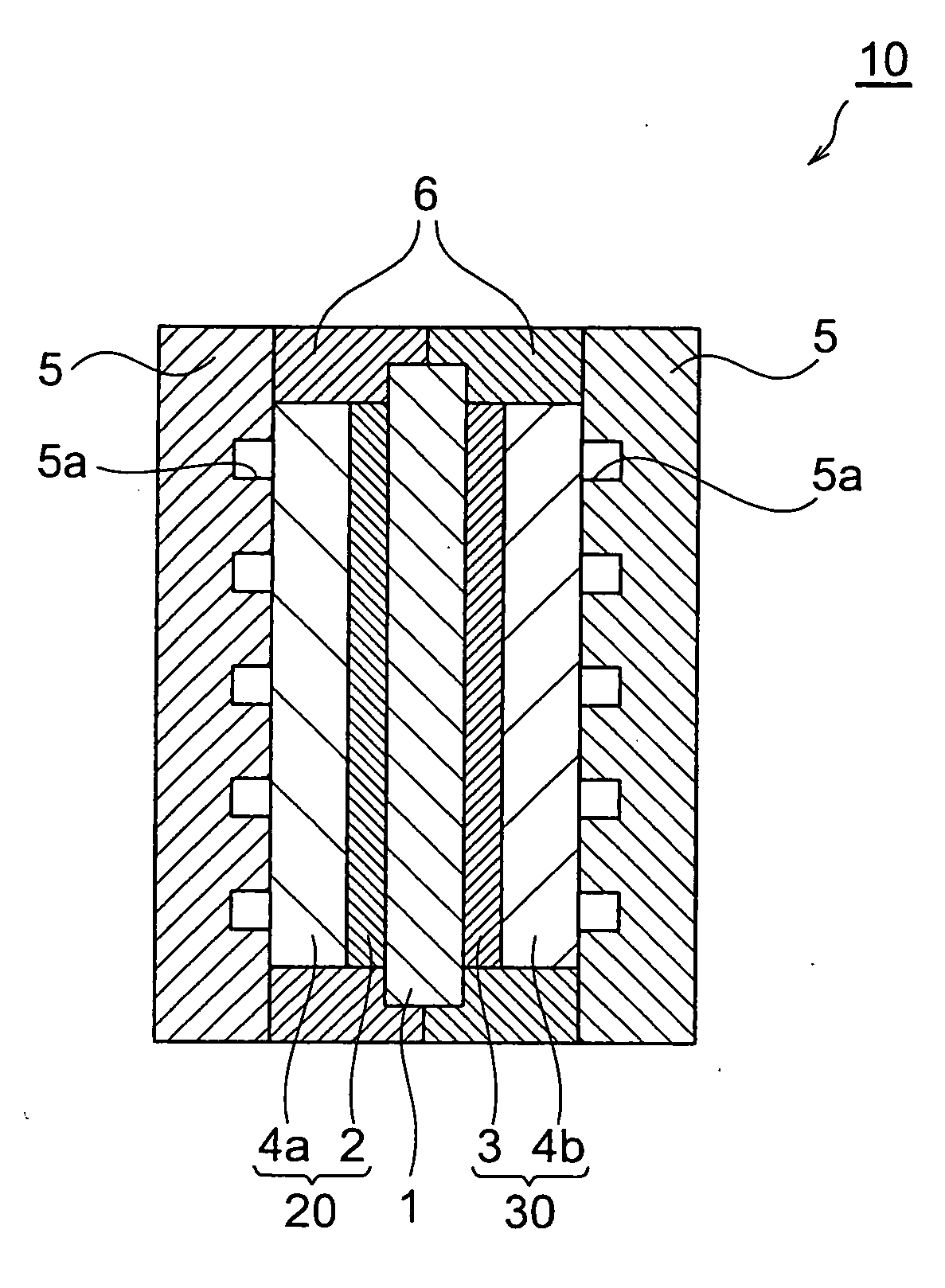
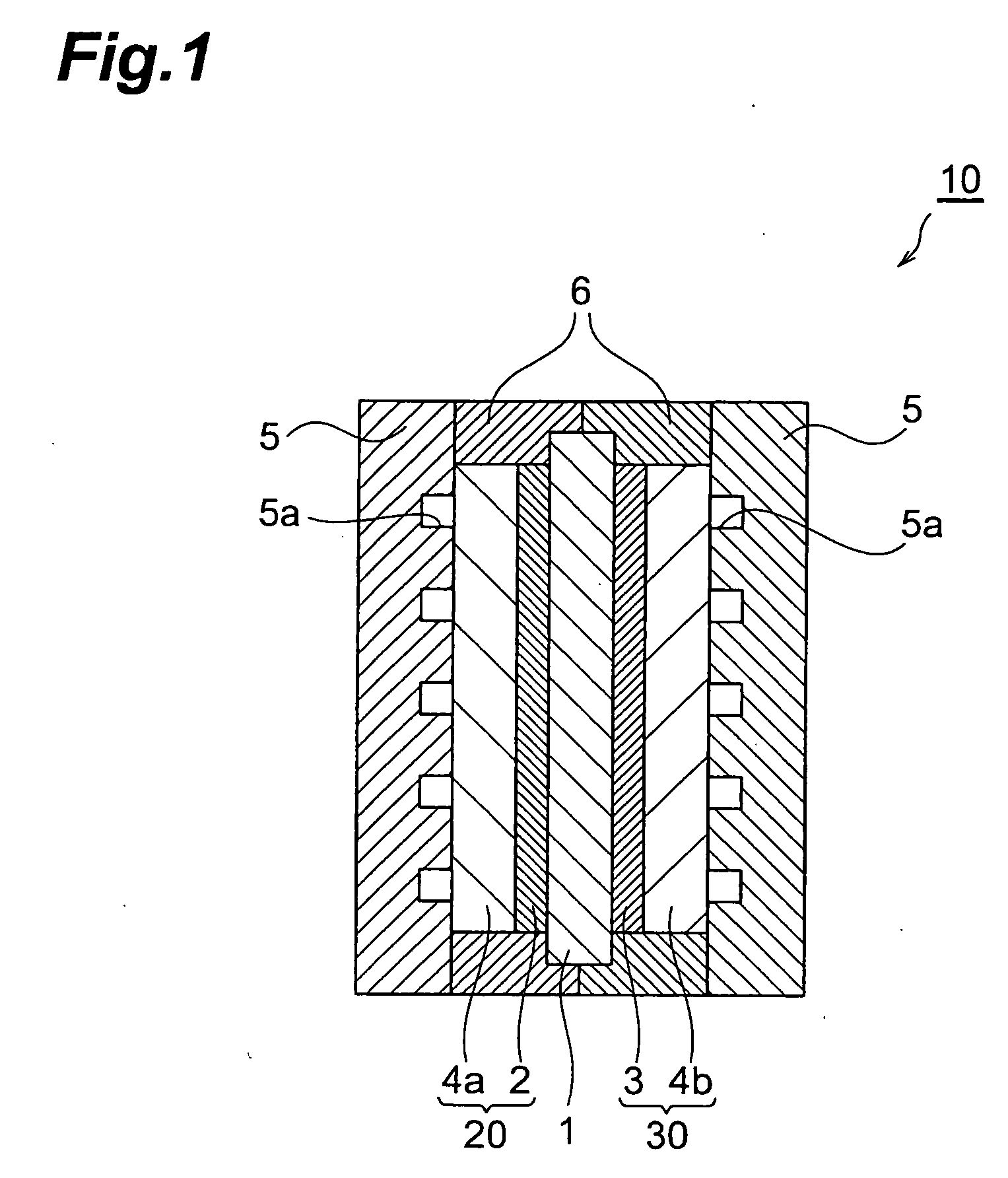
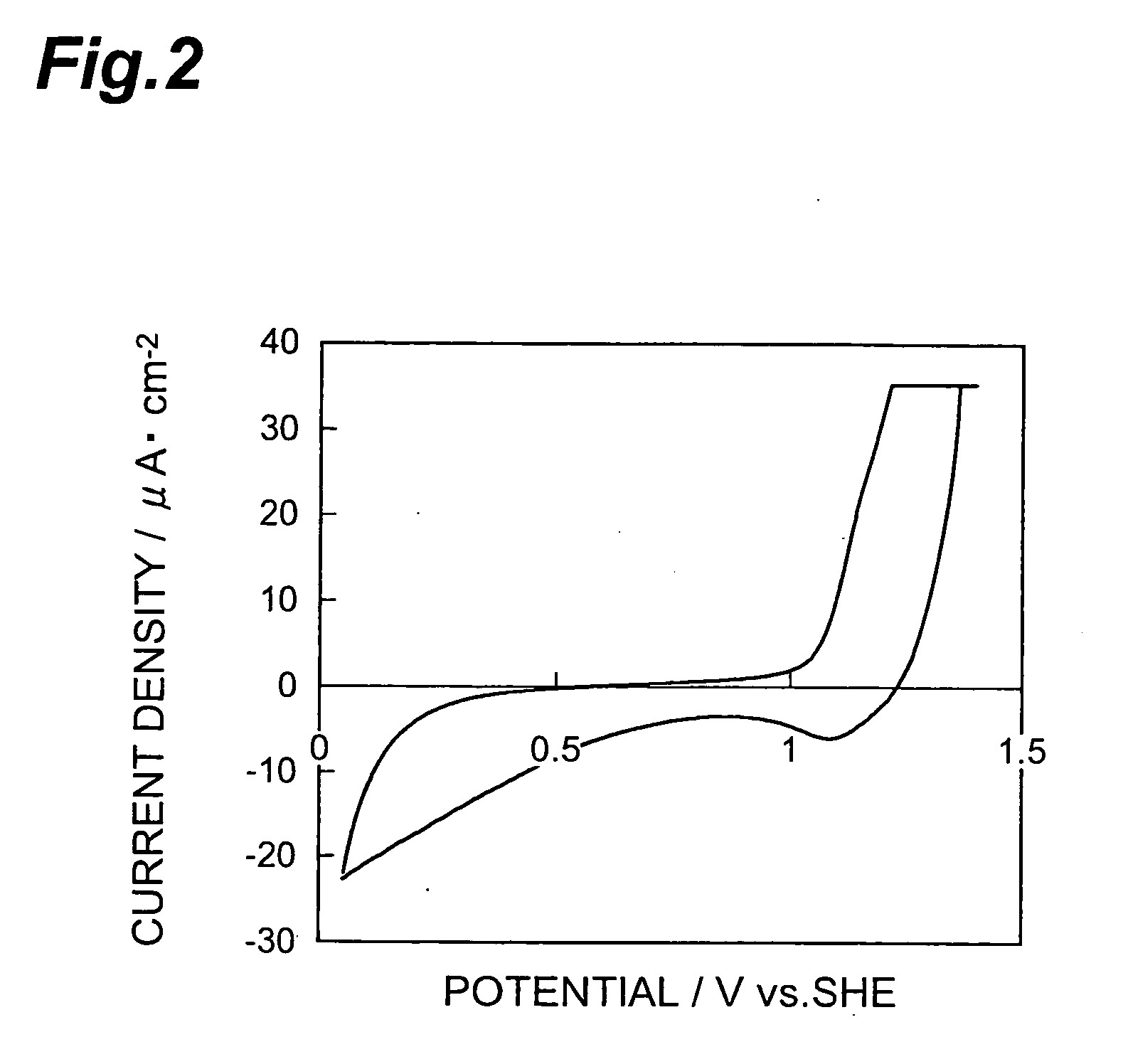
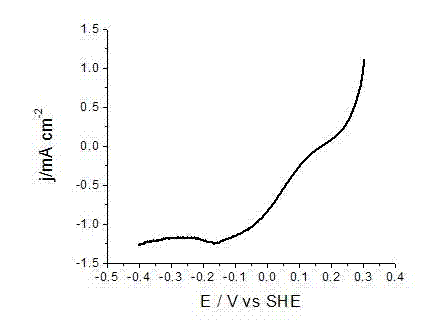
Patents
Literature
76 results about "Standard hydrogen electrode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The standard hydrogen electrode (abbreviated SHE), is a redox electrode which forms the basis of the thermodynamic scale of oxidation-reduction potentials. Its absolute electrode potential is estimated to be 4.44 ± 0.02 V at 25 °C, but to form a basis for comparison with all other electrode reactions, hydrogen's standard electrode potential (E⁰) is declared to be zero volts at any temperature. Potentials of any other electrodes are compared with that of the standard hydrogen electrode at the same temperature.
Compositions and methods for tantalum CMP
InactiveUS20060030158A1Pigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesOxidation-Reduction AgentHeteroatom
A composition suitable for tantalum chemical-mechanical polishing (CMP) comprises an abrasive, an organic oxidizer, and a liquid carrier therefor. The organic oxidizer has a standard redox potential (E0) of not more than about 0.5 V relative to a standard hydrogen electrode. The oxidized form comprises at least one pi-conjugated ring, which includes at least one heteroatom directly attached to the ring. The heteroatom can be a N, O, S or a combination thereof. In a method embodiment, a CMP composition comprising an abrasive, and organic oxidizer having an E0 of not more than about 0.7 V relative to a standard hydrogen electrode, and a liquid carrier therefor, is utilized to polish a tantalum-containing surface of a substrate, by abrading the surface of the substrate with the composition, preferably with the aid of a polishing pad.
Owner:CMC MATERIALS INC
Storage stable autodepositable dispersions of epoxy resins and processes therefor and therewith
InactiveUS6096806AIncreased particle refinementSolvent extractionIon-exchanger regenerationStandard hydrogen electrodePolymer chemistry
PCT No. PCT / US96 / 12540 Sec. 371 Date Feb. 17, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Feb. 17, 1998 PCT Filed Aug. 7, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 07163 PCT Pub. Date Feb. 27, 1997Epoxy resins, particularly those based on bisphenol A, can constitute the principal film forming polymer component of a storage stable autodepositable composition wherein the particle size distribution of all the film forming polymers in the composition satisfies certain criteria of size distribution, and an accelerator component which is an acid, oxidizing agent or complexing agent is present in amount sufficient to provide an oxidation-reduction potential at least 100 mV more oxidizing than a standard hydrogen electrode. Such dispersions can conveniently be prepared using a two stage process in which a solution of the film forming polymers is emulsified into water to form a preliminary dispersion and this preliminary dispersion is subjected to at least one particle size refinement stage in which the preliminary dispersion is forced through a narrow aperture.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
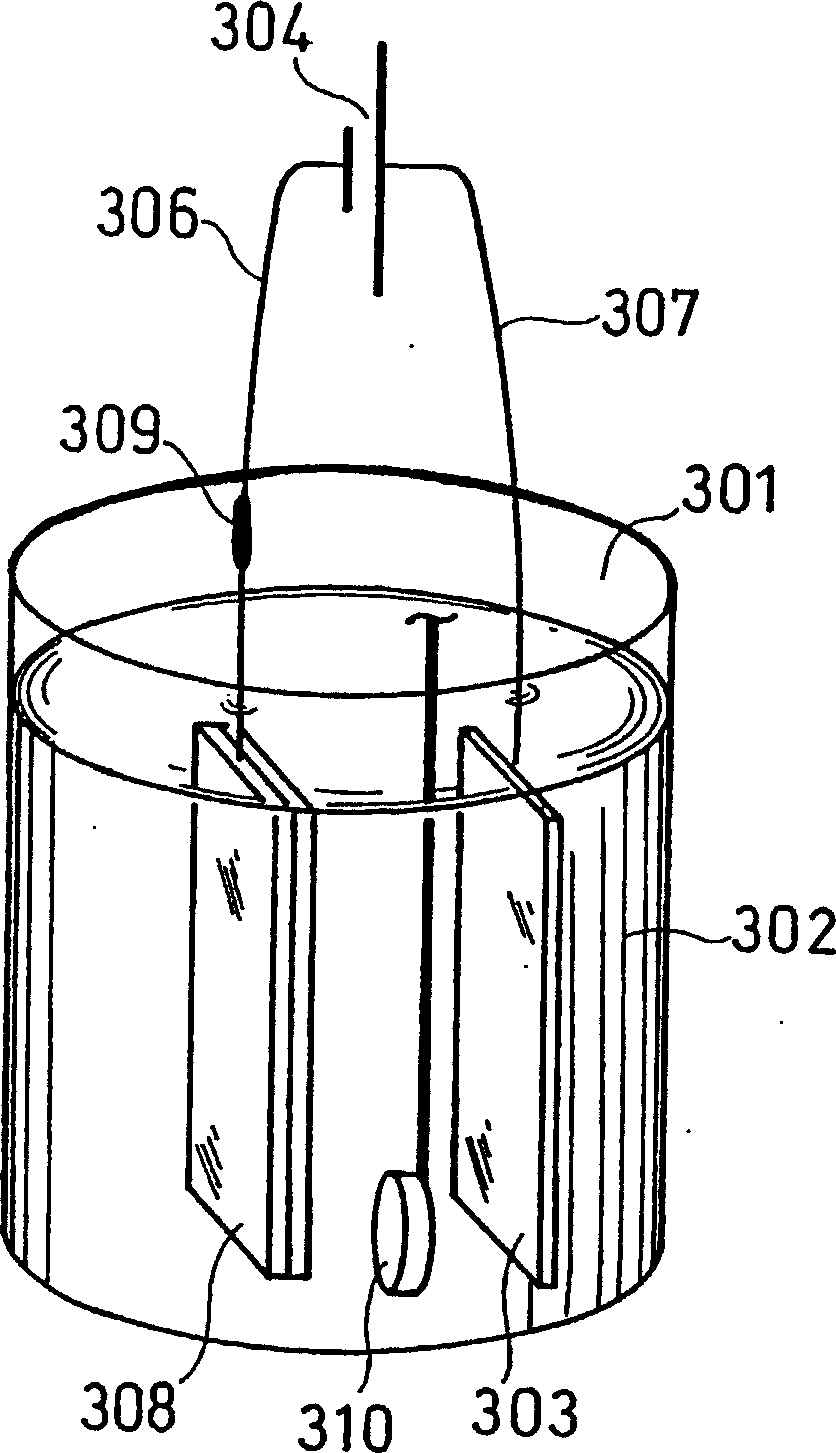
Thin films for controlled protein interaction
A medium for isolating or releasing an electrostatically charged component from or into an aqueous composition. The medium has a polyelectrolyte film on at least one surface of an article wherein the polyelectrolyte film is characterized by an interpenetrating network of a predominantly positively charged polymer and a predominantly negatively charged polymer. The predominantly positively charged polymer, the predominantly negatively charged polymer or both contain (i) a pH sensitive imidazole repeat unit having a pKa between 3 and 9, or (ii) a redox sensitive repeat unit selected from the group consisting of quaternized bipyridine repeat units, coordinated metal repeat units, pyrrole repeat units, aniline repeat units, thiophene repeat units and combinations thereof having a redox potential between +1.2 volts and −1.2 volts versus a standard hydrogen electrode.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Electro-optic display with controlled electrochemical reactions
ActiveUS20150015932A1Reduce residual voltageNon-linear opticsOptical elementsElectrochemical responseRedox
An electro-optic display has a viewing surface through which a user views the display, a bistable, non-electrochromic electro-optic medium, and at least one electrode arranged to apply an electric field to the electro-optic medium, the display. The display comprises at least 10 micromoles per square meter of the viewing surface of at least one redox compound having an oxidation potential more negative that about 150 mV with respect to a standard hydrogen electrode, as measured at pH 8.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Compositions and methods for cmp of semiconductor materials
InactiveUS20070181535A1Other chemical processesDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor materialsCompound (substance)
The invention provides a composition for chemical-mechanical polishing, The composition comprises an abrasive, a first metal rate polishing modifier agent, a second metal rate polishing modifier agent, and a liquid carrier. In one embodiment, the first metal rate polishing modifier agent has a standard reduction potential less than 0.34 V relative to a standard hydrogen electrode, and the second metal rate polishing modifier agent has a standard reduction potential greater than 0.34 V relative to a standard hydrogen electrode. In other embodiments, the first and second metal rate polishing modifier agents are different oxidizing agents.
Owner:CMC MATERIALS INC
Semiconductor device and light-emitting device, and manufactuirng method thereof
InactiveUS20120061652A1Improve reliabilityReduce in quantitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialStandard hydrogen electrode
In a semiconductor device including an organic layer containing a light-emitting substance between a first electrode connected to a source or drain electrode layer of an enhancement-type transistor that has a channel formation region using an oxide semiconductor and a second electrode overlapped with the first electrode, an active, electrically conductive material which produces a hydrogen ion or a hydrogen molecule by reducing an impurity including a hydrogen atom (e.g., moisture) is excluded from the second electrode. The semiconductor device including an oxide semiconductor is formed using especially an inert, electrically conductive material which hardly causes production a hydrogen ion or a hydrogen molecule by reacting with water. Specifically, the semiconductor device is formed using any of a metal, an alloy of metals, and a metal oxide each having a higher oxidation-reduction potential than the standard hydrogen electrode.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Magnetoresistive head with spin valve film magnetic sensor element
InactiveUS6970332B2Improve corrosion resistanceRaise the ratioNanoinformaticsRecord information storageMagnetic reluctanceNon magnetic
An improvement in the corrosion resistance of a magnetoresistive head is aimed for, and a high magnetoresistivity ratio is maintained. In a magnetoresistive head equipped with, as a magnetic sensor element for detecting magnetic signals while in contact with a magnetic recording medium, a spin-valve film, which has a structure where an anti-ferromagnetic layer, a pinned layer in which the direction of magnetization is pinned in a predetermined direction by an exchange-coupling magnetic field at work between itself and the anti-ferromagnetic layer, a free layer in which the direction of magnetization changes in accordance with an external magnetic field, and a non-magnetic layer for magnetically isolating the pinned layer and the free layer are layered, the corrosion potential of the spin-valve film relative to a standard hydrogen electrode measured while immersed in a NaCl solution of a concentration of 0.1 mol / L is specified at +0.4 [V vs. SHE] or above.
Owner:SONY CORP
Water body chemical oxygen demand electrochemical measuring method
ActiveCN101105472AImprove corrosion resistanceHigh mechanical strengthMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansChemical oxygen demandOxygen
The invention relates to an electrochemistry measuring water chemical oxygen demand method; a working electrode, a counter electrode and a reference electrode are provided in a sodium sulfate electrolyte solution or a sodium nitrate electrolyte solution; constant potential is maintained; the chemistry oxygen demand value of a water sample is measured by measuring the response current generated by an oxidation organic substance. The invention is characterized in that the working electrode adopts microcrystal boron adulterated with diamond or nano-crystal boron adulterated with diamond; the PH value of the electrolyte solution is 1-7; the voltage exerted in the electrolyte solution is 2.24-2.28 V if the reference electrode is a standard hydrogen electrode. The invention has the advantages of environmental friendly, high accurate COD determination, wide measuring range, easy operation and small time consumption; the invention can be used to rapid test of COD in the samples of municipal sewage and industrial sewage.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Compositions and methods for tantalum CMP
A composition suitable for tantalum chemical-mechanical polishing (CMP) comprises an abrasive, an organic oxidizer, and a liquid carrier therefor. The organic oxidizer has a standard redox potential (E0) of not more than about 0.5 V relative to a standard hydrogen electrode. The oxidized form comprises at least one pi-conjugated ring, which includes at least one heteroatom directly attached to the ring. The heteroatom can be a N, O, S or a combination thereof. In a method embodiment, a CMP composition comprising an abrasive, and organic oxidizer having an E0 of not more than about 0.7 V relative to a standard hydrogen electrode, and a liquid carrier therefor, is utilized to polish a tantalum-containing surface of a substrate, by abrading the surface of the substrate with the composition, preferably with the aid of a polishing pad.
Owner:CMC MATERIALS LLC
Cooking method for pulp
InactiveUS20020088576A1Pulping with acid salts/anhydridesPulping with inorganic basesKappa numberCellulose
A lignocellulose material is cooked by means of an alkaline cooking liquor containing polysulfides in the presence of a quinone-hydroquinone compound, of which the oxidation-reduction potential in the form present during the cooking, which potential is a value calculated as a standard oxidation-reduction potential (Ea) with a hydrogen ion activity of 1, is within a range of from 0.12 to 0.25V to the standard hydrogen electrode potential. It is thereby possible to cook the lignocellulose material with a low Kappa number and in good yield and at the same time, to reduce the amount of the chemical solution used and to reduce the load on a recovery boiler.
Owner:KAWASAKI KASEI CHEMICALS LTD +1
Preparation method of vanadium doping molybdenum disulfide nanoflower with defects and electrocatalysis application thereof
The invention provides a preparation method of vanadium doping molybdenum disulfide nanoflower with defects and electrocatalysis application thereof. Firstly, a molybdenum and sulfur pre-reaction solution is prepared, and the reaction solution is heated to synthesize defective molybdenum disulfide nano-powder; then hydrothermal reaction is carried out on the defective molybdenum disulfide nano-powder and vanadium source compound to synthesize vanadium doping molybdenum disulfide spherical nano-powder; under the protection of inert gases, annealing treatment is carried out to obtain vanadium doping molybdenum disulfide nanoflower-shaped nano-powder. Vanadium doping molybdenum disulfide with defects is applied to electrocatalysis hydrogen generation reaction (HER), the catalytic performanceis excellent, the overpotential is as low as -0.160V (relative standard hydrogen electrode), and the Tafel slope is as low as 46mV / dec.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Polypyrrole electrolytic synthesis method
ActiveCN1995462AGood electrocatalytic oxidation propertiesReduce manufacturing costElectrolysis componentsElectrolytic organic productionElectrolysisSynthesis methods
The invention discloses an electrolyzing synthesizing method of polypyrrole, which comprises the following steps: dissolving pyrrole monomer in the Bronsted acid typed ionic liquid; placing in the electrolyser with working electrode, auxiliary electrode and reference electrode; selecting working electrode from stainless steel electrode or platinum electrode or nickel electrode or glass-carbon electrode; selecting the auxiliary electrode from platinum electrode or graphite electrode with large area; selecting reference electrode from Ag / AgCl electrode or saturated calomel electrode or large area of platinum electrode or standard hydrogen electrode.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Organic EL element, method for fabricating the same and organic EL display device
InactiveUS20060182996A1Weaken energySuppression problemSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceOptoelectronics
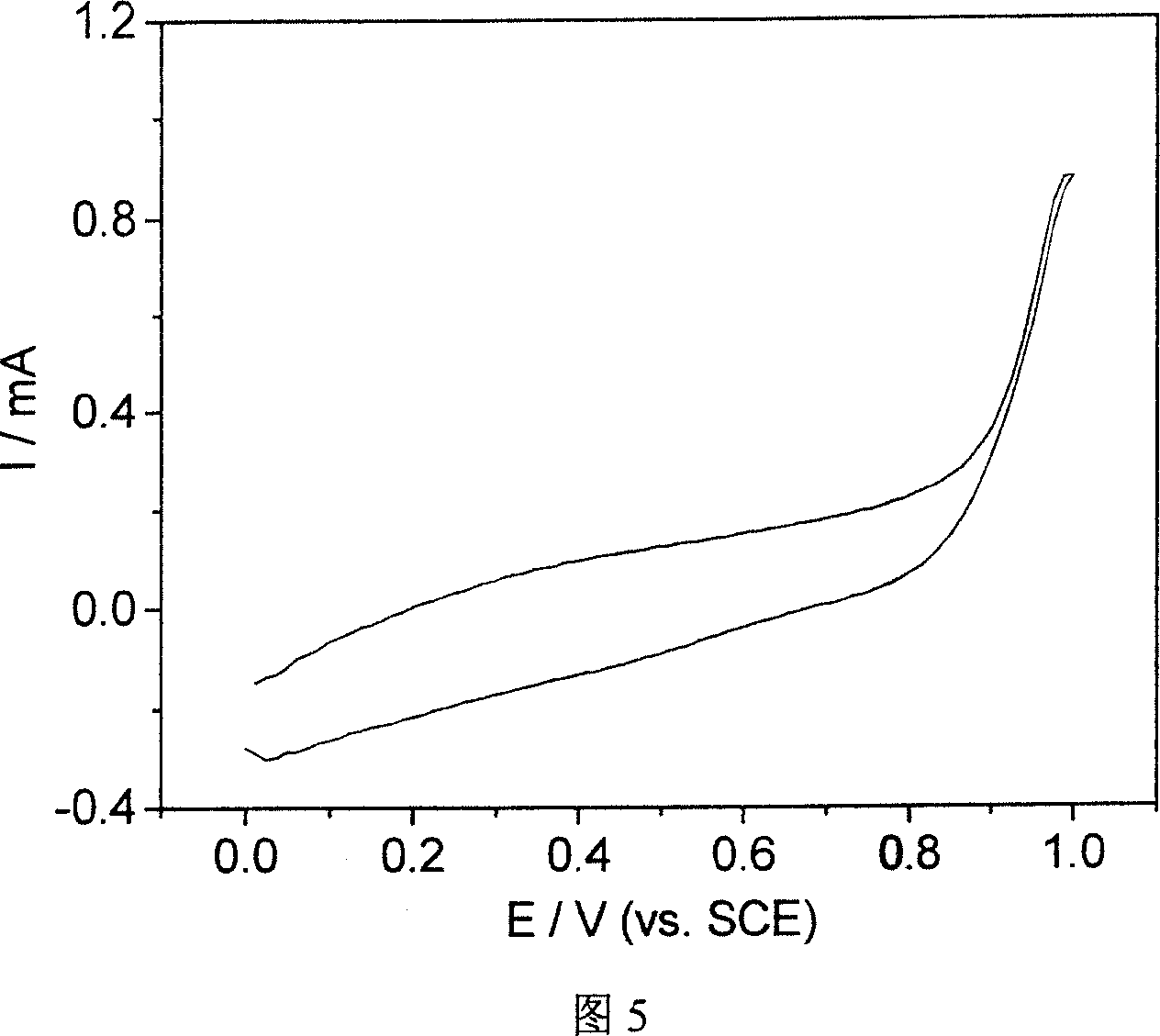
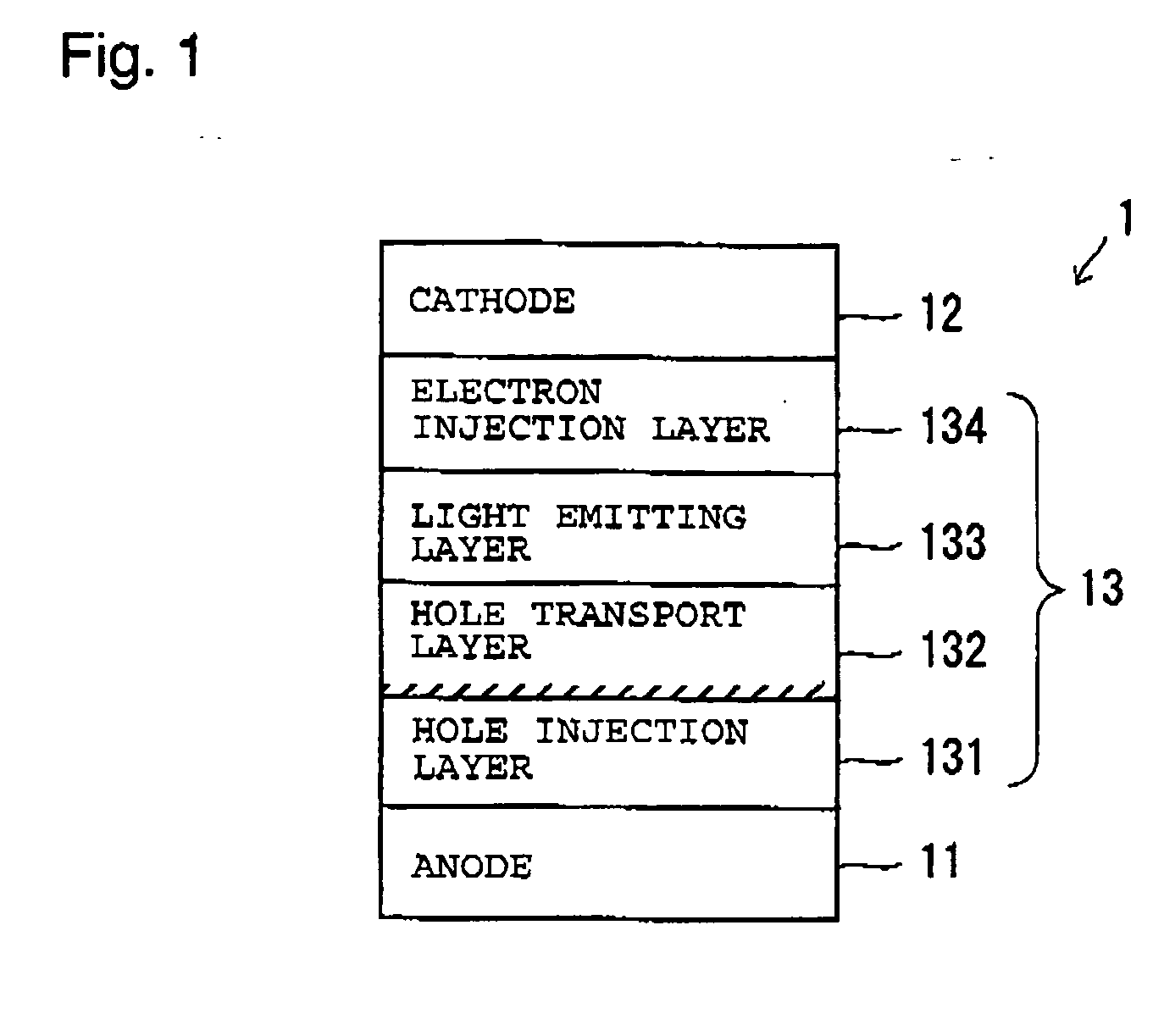
An organic EL element is provided which is capable of restraining chrominance non-uniformity caused by a film thickness distribution of an applied film, of having good display quality, of reducing the driving voltage, and of having interlayer short-circuit endurance. The organic EL element according to one mode of the present invention comprises an anode 11, a cathode 12, and an organic EL layer 13. The organic EL layer comprises a hole injection layer 131 and a hole transport layer 132. The hole injection layer includes organic-thin-film-forming-molecules and dopants oxidizing the organic-thin-film-forming-molecules, the dopants having a reduction potential of 0.5 to 0.85 V with respect to a standard hydrogen electrode, and the hole transport layer having an ionization potential of 8.5×10−19 J (5.3 eV) or below.
Owner:OPTREX CORP
Preparation and electrocatalytic application of inverse-spinel type cobalt ferrite nano-powder with oxygen vacancy
The invention provides preparation and electrocatalytic application of inverse-spinel type cobalt ferrite nano-powder with oxygen vacancy. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing an alkaline cobalt iron aqueous solution and carrying out heating reaction to obtain cobalt ferrite nano-powder; secondly, introducing the oxygen vacancy into the obtained cobalt ferrite by using a normal temperature reduction method; finally, obtaining the cobalt ferrite nano-powder with the oxygen vacancy. The cobalt ferrite nano-powder with the oxygen vacancy has excellent catalyticproperties when being applied to electrocatalytic oxygen-producing reaction (OER), the overpotential drops to 0.330V (relative standard hydrogen electrode) and the Tafel slope is as low as 44 mV / dec.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Iron and nitrogen-doped carbon nanosphere preparation method and oxygen reduction application
InactiveCN108039500AGood anti-methanol effectLarge specific surface areaCell electrodesMicrosphereHigh pressure
The invention provides an iron and nitrogen-doped carbon nanosphere preparation method and application of the nanosphere in oxygen reduction. The dopamine hydrochloride is used for synthesizing a nitrogen source supply object polydopamine under alkaline condition, and then the surface of ferriferrous oxide nanosphere is coated by the polydopamine; the ferriferrous oxide nanosphere coated by the polydopamine is subjected to a reaction with glucose in a high pressure reaction vessel, and under nitrogen condition, high temperature calcining is carried out to obtain the iron and nitrogen-doped carbon nanosphere. The synthesis of the iron and nitrogen-doped carbon nanosphere takes glucose as a raw material, and the ferriferrous oxide nanosphere coated by the polydopamine is taken as a corrosiontemplate and the nitrogen source. The nitrogen-doped carbon nanosphere used in a electrocatalysis oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) has good effect and good endurance, an initial potential relative standard hydrogen electrode of reduction oxygen is 0.949 V, the efficiency after endurance test can still reach more than 85%, after addition of methanol, the usage efficiency can still reach 94%, and the nitrogen-doped carbon nanosphere has good anti-methanol effect.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Preparation method of sulfur-doped nickel phosphide nano powder and application in electrolysis of water
The invention provides sulfur-doped nickel phosphide nano powder and an application in electrolysis of water. A method of preparing the sulfur-doped nickel phosphide nano powder comprises the following steps: (1) performing pretreatment on a nickel-containing aqueous solution, adjusting pH of the solution, adding an alkali regulating agent to prepare an alkaline pre-reaction solution, performing areaction under heating, after the reaction is completed, performing washing, performing centrifugation, and performing collection to obtain nickel source precursor powder; (2) performing calcinationtreatment on the nickel source precursor and a phosphating reagent according to a ratio under the protection of an inert gas to obtain nickel phosphide; and (3) performing calcination treatment on thenickel phosphide and a sulfur source under the protection of an inert gas, and performing collection to obtain the black sulphur-doped nickel phosphide powder. The sulfur-doped nickel phosphide provided by the invention has excellent catalytic performance when used for electrocatalysis of an oxygen evolution reaction (OER), has overpotential as low as 0.294 V (relative to a standard hydrogen electrode) and a Tafel slope as low as 58 mV / dec.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Preparation method of curved surface electrode catalyst layer
ActiveCN102403516ALarge electrochemically active areaImprove performanceCell electrodesPre treatmentStandard hydrogen electrode
The invention provides a preparation method of a curved surface electrode catalyst layer, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1, preprocessing an electrode matrix; 2, carrying out electrochemical deposition on a catalyst: inserting the preprocessed electrode matrix into an electrochemical deposition pool, loading an electroplating bath containing catalyst cations in the electrochemical deposition pool, forming a three-electrode system with a reference electrode and a counter electrode with the electrode matrix as a working electrode, controlling the potential of the working electrode to be -0.7-0.5V relative to a standard hydrogen electrode for carrying out electrochemical deposition until the loading capacity of the catalyst on the electrode matrix reaches a preset loading capacity, then taking the electrode matrix out, rinsing with deionized water for drying in air for later use; 3, dipping in a perfluorinated sulfonic acid resin solution; 4, repeating the step 2 and the step 3 until the loading capacity of the catalyst on the electrode matrix reaches the set loading capacity of the catalyst, entering the step 5; and 5, activating an electrode.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method and apparatus for releasing metal-resin joint
A method for separating a metal-resin joint including the steps of: (1) immersing an article including a metal-resin joint with a counter electrode in an alkaline solution; and (2) applying a voltage over a certain time period between the metal portion of the joint and the counter electrode such that the potential of the metal portion is lower than that of a standard hydrogen electrode.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Preparation method and electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction applications of vanadium-doped ferrous sulfide
ActiveCN110201683AGood effectPhysical/chemical process catalystsElectrodesVulcanizationVanadium doping
In the prior art, ammonia (NH3) as the important raw material industry, agriculture and pharmacy plays an important role in human life and development, and the huge industrial ammonia production process and the release of a large amount of carbon dioxide greatly increase the greenhouse effect, such that the production of ammonia through electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction under mild conditions isthe research focus worldwide. Based on the problem in the prior art, the present invention provides a preparation method and electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction applications of vanadium-doped ferroussulfide nanometer powder, wherein the preparation method comprises: adding an iron source reagent and a vanadium source reagent to a special solvent to prepare a pre-reaction liquid, heating the pre-reaction liquid to obtain iron-vanadium precursor nanometer powder, and carrying out a vulcanization reaction on the iron-vanadium precursor nanometer powder to finally obtain the vanadium-doped ferrous sulfide nanometer powder. According to the present invention, the vanadium-doped ferrous sulfide nanometer powder has excellent activity in the field of production of ammonia through electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction (NRR), the yield of ammonia at -0.1 V (relative standard hydrogen electrode) is up to 106.3 [mu]g h<-1>mg<-1>cat, and the Faraday efficiency achieves 9.5%.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Thin films for controlled protein interaction
ActiveUS8481017B2Water/sewage treatmentSynthetic polymeric active ingredientsPolymer scienceStandard hydrogen electrode
A medium for isolating or releasing an electrostatically charged component from or into an aqueous composition. The medium has a polyelectrolyte film on at least one surface of an article wherein the polyelectrolyte film is characterized by an interpenetrating network of a predominantly positively charged polymer and a predominantly negatively charged polymer. The predominantly positively charged polymer, the predominantly negatively charged polymer or both contain (i) a pH sensitive imidazole repeat unit having a pKa between 3 and 9, or (ii) a redox sensitive repeat unit selected from the group consisting of quaternized bipyridine repeat units, coordinated metal repeat units, pyrrole repeat units, aniline repeat units, thiophene repeat units and combinations thereof having a redox potential between +1.2 volts and −1.2 volts versus a standard hydrogen electrode.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Fuel cell cathode manufacturing method and fuel cell manufacturing method
ActiveUS20070167313A1High densityIncrease energy densityFinal product manufacturePrimary cellsElectrode potentialFuel cells
The method of manufacturing a cathode for a fuel cell in accordance with the present invention is a method of manufacturing a cathode for a fuel cell equipped with a catalyst layer containing a catalyst, and includes a potential providing step of providing a precursor layer containing the catalyst with a potential higher than 1.3 V with reference to a standard hydrogen electrode, so as to form the catalyst layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Carbon, silver-copper and polyaniline composite electro-catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction of fuel cell and preparation method and application of electro-catalyst
InactiveCN102784665AIncrease current densityHigh onset potentialOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCell electrodesPolyaniline compositeSolvent
A preparation method of a carbon, silver-copper and polyaniline composite electro-catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction of a fuel cell includes using ethanol as solution and a reducing agent; simultaneously depositing silver nanoparticles and copper nanoparticles on carbon particles by a hydrothermal method to form a carbon-supported silver-copper bimetal nanometer catalyst; and then decorating the particle surface of the catalyst by polyaniline by a chemical method to obtain the carbon, silver-copper and polyaniline composite electro-catalyst. Anhydrous ethanol and Nafion solution are added into the carbon, silver-copper and polyaniline composite electro-catalyst to prepare a corresponding carbon, silver-copper and polyaniline composite electro-catalyst electrode. The carbon, silver-copper and polyaniline composite electro-catalyst is high in electro-catalytic activity in oxygen reduction reaction, oxygen reduction reaction initial potential is 0.160V [vs SHE (versus a standard hydrogen electrode)], and current density is 1.50mAcm<-2> at -0.15V (vs SHE). In addition, the preparation method is simple, the structure of the electro-catalyst is stable, usage of silver which is precious metal is greatly reduced, and the electro-catalyst is widely applied to fuel cells.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation and application of monatomic platinum catalyst based on MXene quantum dots
PendingCN112264062ACatalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystFaraday efficiency
The invention provides preparation and application of a monatomic platinum catalyst based on MXene quantum dots. MXene quantum dots are used as a carrier, and a certain amount of chloroplatinic acid and molten salt are added to obtain a mixed solution; the mixed solution is stirred, frozen and dried, high-temperature calcination on the obtained solid powder under the protection of an inert atmosphere is carried out, and acid pickling, washing and drying are then carried out to obtain the novel monatomic platinum catalyst taking the MXene quantum dots as the carrier. The catalyst has very highcatalytic activity on electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction reaction, the ammonia yield under -0.2 V (relative to a standard hydrogen electrode) reaches up to 80.3 mug h<-1> mg<-1> cat., the Faraday efficiency reaches 7.3%, and the catalyst is a potential electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction catalyst material.
Owner:LANZHOU JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for removal of Mn from cobalt sulfate solutions
ActiveUS20050120828A1Less by-productsSimple and reliable processRhenium compoundsManganese compoundsStandard hydrogen electrodeOxidation reduction
The present invention provides a method for the removal of substantially all the amount of Mn contained in cobalt containing solution thereby to obtain purified cobalt solution with Mn content of 10 ppm or less and specifically a method for removing Mn from cobalt sulfate solution comprising the steps of adjusting pH of the solution within the range of 3-6 and then adding the NaOCl to the solution to obtain an oxidation-reduction potential in the range of 1100 to 1300 mV, with respect to standard hydrogen electrode (SHE); and removing Mn precipitate from thus treated solution.
Owner:SEIDO CHEM IND
Oxygen carrier system, artificial oxygen carrier, and reducing agent
InactiveUS20050025757A1Oxygen binding ability of hemoglobin is easily recoveredReduce methemoglobinPeptide/protein ingredientsHydroxy compound active ingredientsElectrode potentialStandard electrode potential
An oxygen carrier system includes an artificial oxygen carrier including hemoglobin vesicles encapsulating hemoglobin and an intermediate electron mediator having a standard electrode potential of 0.05 V to 0.56 V (vs. the standard hydrogen electrode) in the vesicles, and a reducing agent which is added to an external aqueous phase of the hemoglobin vesicle to reduce methemoglobin when the hemoglobin encapsulated in the hemoglobin vesicle is oxidized to the methemoglobin. The reducing agent has, as an active component, at least one compound selected from the group consisting of a thiol compound and a reducing sugar.
Owner:OXYGENIX CO LTD
Preparation method and electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction application of ultrathin nanosheet vanadium-doped nickel sulfide nanopowder
InactiveCN110124694AGood effectPhysical/chemical process catalystsElectrodesVulcanizationVanadium doping
The invention provides a preparation method and an electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction application of an ultrathin nanosheet vanadium-doped nickel sulfide nanopowder. The preparation method comprisesthe following steps: a vanadium source and a nickel source are added to a reaction solution to prepare a pre-reaction solution, the pre-reaction solution is heated and reacted for a certain period oftime, and then is cooled, and the obtained reaction product is washed, centrifuged, vacuum-dried and collected to obtain a vanadium-nickel precursor nanopowder; the vanadium-nickel precursor nanopowder is subjected to a vulcanization reaction through a solvothermal process to obtain a vanadium-doped nickel sulfide intermediate nanopowder; and the vanadium-doped nickel sulfide intermediate nanopowder is placed in a tubular furnace, and is annealed under the protection of an inert gas to obtain the ultrathin nanosheet vanadium-doped nickel sulfide nanopowder. The ultrathin vanadium-doped nickelsulfide has an excellent catalytic property in the field of electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction (NRR), the ammonia yield at -0.2 V (relative to a standard hydrogen electrode) is as high as 63.2 [mu]gh<-1> mg <-1> cat, and the Faraday's efficiency reaches 8.3%.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Cooking method for pulp
A lignocellulose material is cooked by means of an alkaline cooking liquor containing polysulfides in the presence of a quinone-hydroquinone compound, of which the oxidation-reduction potential in the form present during the cooking, which potential is a value calculated as a standard oxidation-reduction potential (Ea) with a hydrogen ion activity of 1, is within a range of from 0.12 to 0.25V to the standard hydrogen electrode potential. It is thereby possible to cook the lignocellulose material with a low Kappa number and in good yield and at the same time, to reduce the amount of the chemical solution used and to reduce the load on a recovery boiler.
Owner:KAWASAKI KASEI CHEMICALS LTD +1
Preparation method and electrocatalytic application of phosphorus with defects doped CoFe2O4 nanometer powder
The invention provides a preparation method and electrocatalytic applicationof a phosphorus with defects doped aCoFe2O4 nanometer powder. First, a cobalt - iron prereaction solution is prepared by adding a certain proportion of cobalt and iron sources in a reaction solution, and the CoFe2O4 nanometer powder is collected after heating the prereaction solution for a certain time;and then, the CoFe2O4 nanometer powder is processed for a period of time under the action of a reducing agent to obtain the CoFe2O4 nanometer powder with vacancy defects,secondly, phosphating treatment of the CoFe2O4 nanometer powder with the vacancy defects is carried out,phosphorus atoms are introduced and finally the phosphorus with defects doped a CoFe2O4 nanometer powder is obtained. Specifically, the phosphoruswith the defects doped theCoFe2O4 nanometer powdershows excellent catalytic activity in electrocatalytic oxygen production reaction (OER), an overpotential is 0.287 V (relative to a standard hydrogenelectrode), a tafel slope is down to 56 mV / dec,and charge transfer resistance is reduced to 47ohm.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Preparation of nano-flaky iron-doped nickel phosphide and nitrogen reduction reaction (NRR) application
InactiveCN109876835AImprove efficiencyGood effectMaterial nanotechnologyCatalyst activation/preparationElectrolysisFaraday efficiency
In view of the heavy demand for ammonia and the harsh reaction condition and low conversion rate of a Haber-Bosch process, simple preparation of the ammonia becomes a major problem of development of the present world, and therefore, the study of achieving nitrogen reduction ammonia through electrolysis of an electrolyte with saturated nitrogen at the normal temperature and normal pressure is paidmuch attention. The invention provides a preparation method of nano-flaky iron-doped nickel phosphide nano-powder and application of the nano-flaky iron-doped nickel phosphide nano-powder to a nitrogen reduction reaction (NRR). The preparation method comprises the steps: firstly, a specific proportion of iron source reagent and nickel source reagent are added into a reaction solution, a heating reaction is conducted, and iron-nickel precursor nano-powder is obtained; and then the iron-nickel precursor nano-powder is placed into a tube furnace at the specific nitrogen flow rate to be subjectedto a phosphorization reaction, and finally the nano-flaky iron-doped nickel phosphide nano-powder is obtained. The nano-flaky iron-doped nickel phosphide nano-powder shows excellent catalytic activityin the field of the NRR, the ammonia yield under minus 0.3 V (relative to a standard hydrogen electrode) reaches up to 70.6 [mu]g h<-1> mg<cat.><-1>, and the Faradic efficiency reaches 6.5%.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Oxygen carrier system, artificial oxygen carrier, and reducing agent
InactiveUS6967020B2Oxygen binding ability of hemoglobin is easily recoveredReduce methemoglobinHydroxy compound active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsExocytic vesicleFerri-haemoglobin
An oxygen carrier system includes an artificial oxygen carrier including hemoglobin vesicles encapsulating hemoglobin and an intermediate electron mediator having a standard electrode potential of 0.05 V to 0.56 V (vs. the standard hydrogen electrode) in the vesicles, and a reducing agent which is added to an external aqueous phase of the hemoglobin vesicle to reduce methemoglobin when the hemoglobin encapsulated in the hemoglobin vesicle is oxidized to the methemoglobin. The reducing agent has, as an active component, at least one compound selected from the group consisting of a thiol compound and a reducing sugar.
Owner:OXYGENIX CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com