A multi-index detection microfluidic chip for quantitative shunting
A microfluidic chip and quantitative shunting technology, which is applied to laboratory containers, laboratory utensils, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of accurate analysis of adverse reaction results, efficient adverse reactions, sample waste and pollution, etc. , to achieve the effects of accurate analysis, simple structure, and convenient waste liquid treatment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Embodiment 1: Multi-index microfluidic chip structure
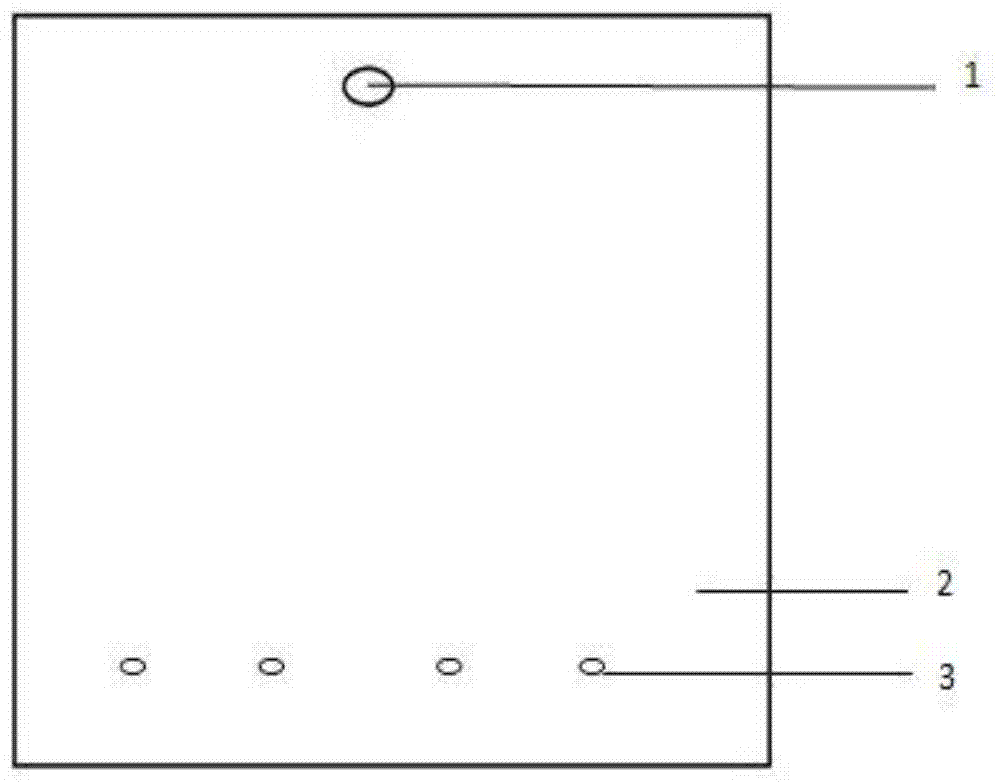
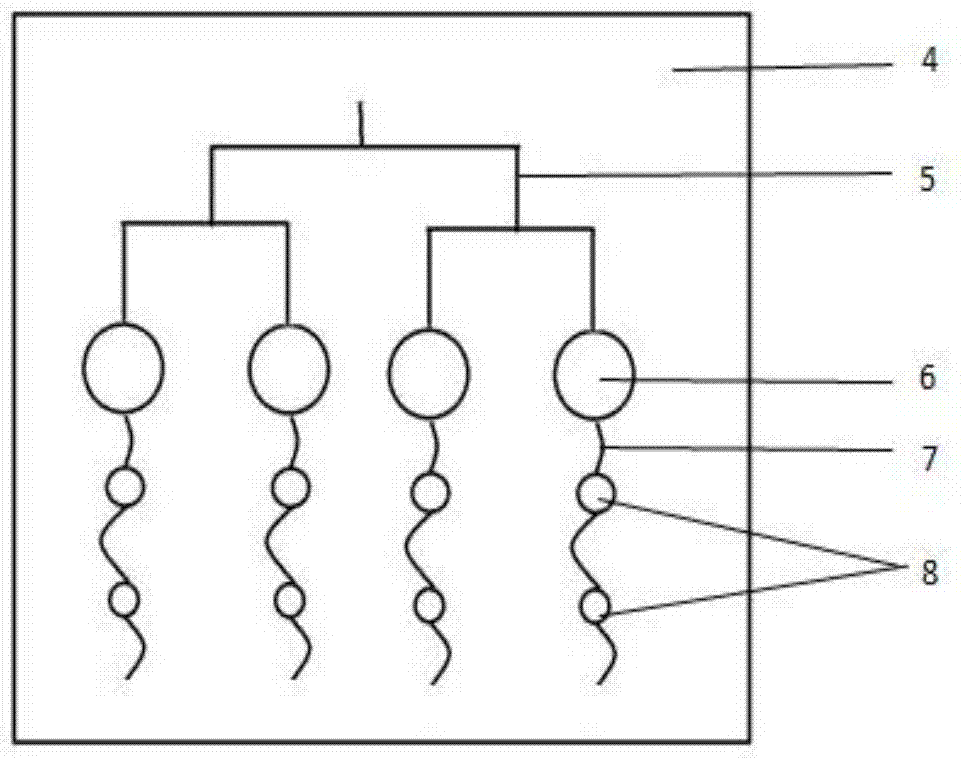
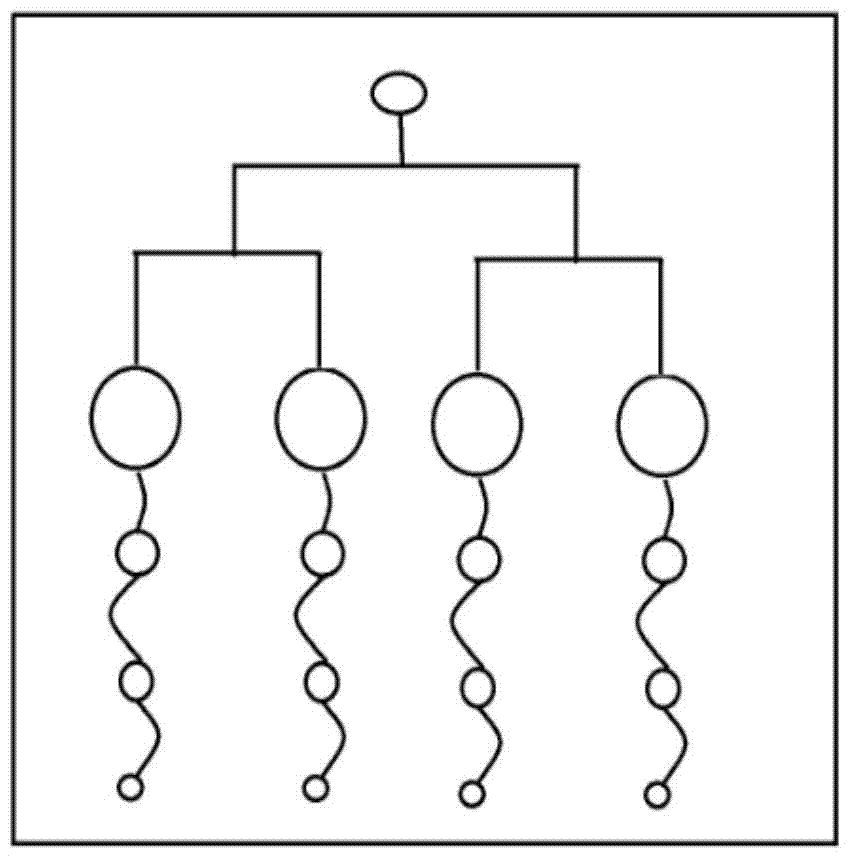
[0026] Such as figure 1 , 2 As shown in , 3, a splitting device used for the detection of four indicators can accurately quantify the amount of samples split into the four reaction chambers. The splitting device is formed by bonding the upper cover sheet 2 and the lower substrate 4 flakes. The upper cover sheet 2 is provided with a sample inlet 1, and the lower substrate 4 is provided with a multi-stage branch branch 5 connected with the sample inlet, and each branch 5 is connected with one end of a corresponding parallel reaction chamber 6, The parallel reaction chambers 6 have the same size, and the other end of the parallel reaction chamber communicates with a plurality of buffer pools 8 through an arc-shaped liquid buffer channel 7. The buffer pools 8 are connected in series, and the size decreases sequentially with the direction of liquid flow. The liquid buffer channels The 7 end communicates with the air ...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2: Preparation method of microfluidic chip
[0036] Step 1: Use computer-aided design software to design the microchannel and microstructure of the shunt device chip, use a high-resolution printer to print the drawn chip structure diagram on the SU-8 glue as a mask, and use standard photolithography to make it Mold, obtain the SU-8 positive mold with the upper cover sheet of the flow splitting device and the microchannel and microstructure of the lower substrate.
[0037]Step 2: Mix the PDMS prepolymer and curing agent according to the mass ratio of 10:1, pump air in a vacuum drying oven, pour it on the surface of the mold obtained in step 1, take it out after baking at 80°C for 1 hour, and slowly remove the PDMS after cooling Peel off the mold, and use a special punching tool to drill out the sample inlet and gas outlet at the corresponding positions.
[0038] Step 3: Put the upper cover sheet and the lower substrate cut into a suitable size into a plasma clea...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Example 3: Microfluidic Chip Workflow
[0040] The sample solution that needs to be split is injected from the sample inlet 1, and the sample solution flows through the split branches 5 at all levels and then flows in from the upper edge of one end of each parallel reaction chamber 6. When the sample is full of the reaction chamber, the sample passes through the other side of the reaction chamber. The arc-shaped liquid buffer channel 7 connected along one end slowly flows into the buffer pool 8 whose size gradually decreases; each segment of the arc-shaped liquid buffer channel 7 connected with the parallel reaction chamber 6 and the buffer pool 8 all flows from the reaction chamber 6 and the buffer pool 8 The upper edge of the upper edge is connected and connected, so that the sample in the reaction chamber 6 will not flow out if it is not full. During the sample flow process, the parallel reaction chamber 6 with larger volume flows into the buffer pool 8 with smaller ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com