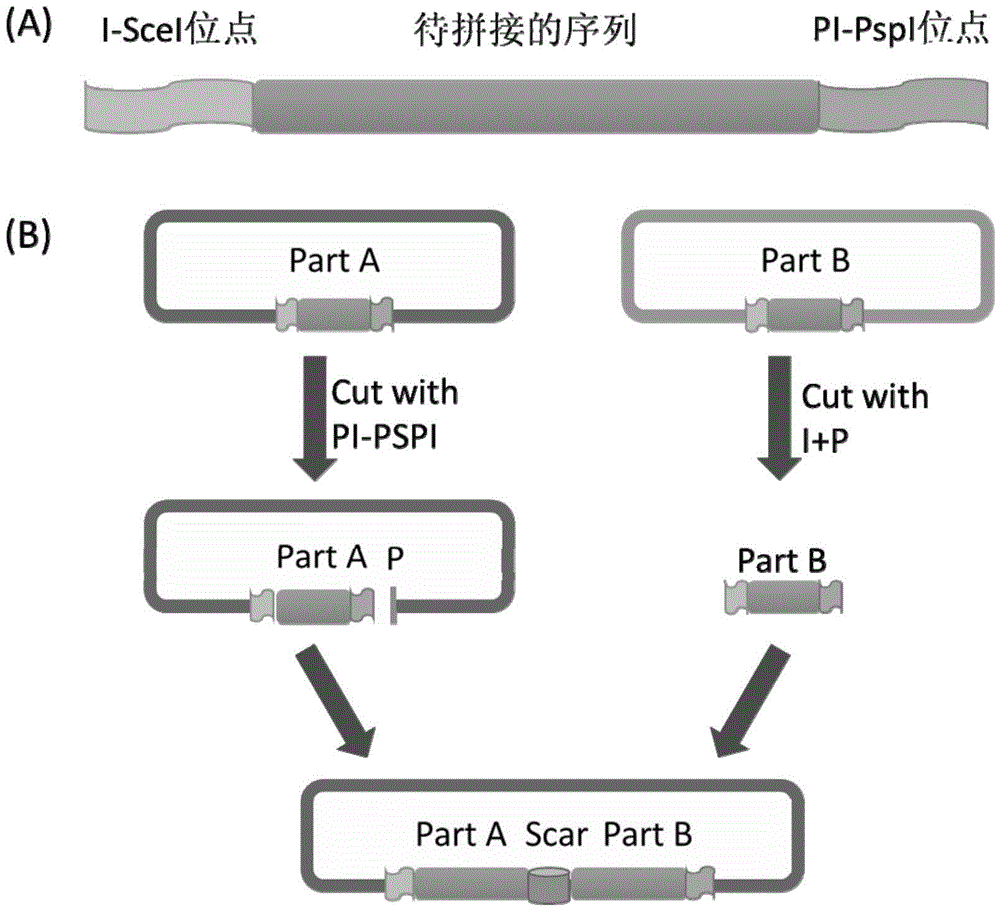
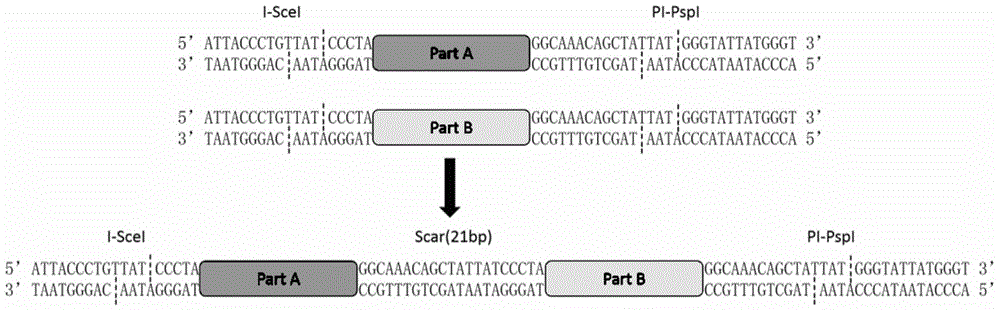
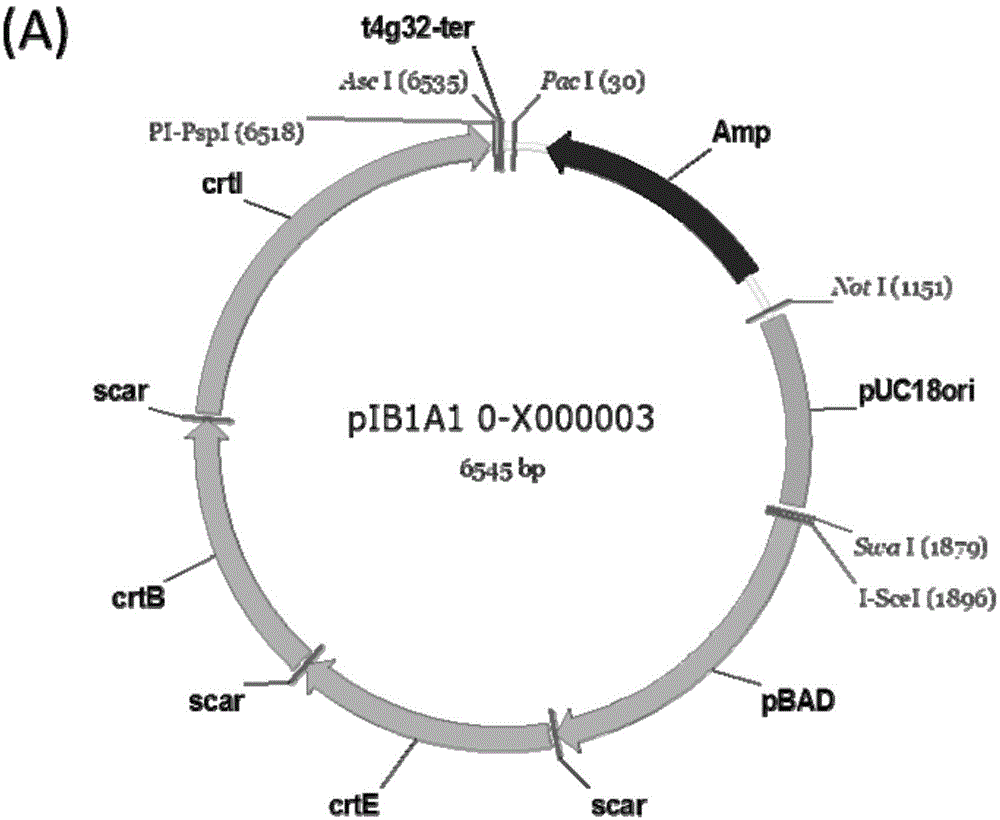
DNA construct and DNA extracorporeal splicing method
A technology of constructs and vectors, applied in the field of genetically modified constructs and DNA in vitro splicing, can solve the problems of limiting the versatility of bio-brick assembly technology, huge workload, and uncertain functions.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0123] Example 1 Heterologous Expression of Lycopene Biosynthesis Gene Cluster
[0124] 1. Using pUC18 as a template, the bla gene and the replicon were amplified by PCR. There were PacI and NotI restriction sites at both ends of the bla gene, and NotI and SwaI-AscI sites at both ends of the replicon. Digest the two fragments with NotI (37°C / 1h), mix and connect the two fragments at an equimolar ratio, add T4PNK (T4PolynucleotideKinase) to the system during connection, connect at 16°C overnight, transform E. coli DH5α, add ampicillin antibiotics in LB Positive clones were screened and verified by sequencing. The correct plasmid was named pJK5.
[0125] 2. Using BBa_274100 as a template to amplify the crtEBI (crtE, crtB, crtI) gene; using pKD46 as a template to amplify the pBAD promoter. Among the above parts, the 5' end of crtE has SwaI and I-SceI sites, and the 3' end has AscI and PI-PspI sites; the 5' end of the other parts only has I-SceI sites, 3 ' ends with only PI-Psp...
Embodiment 2
[0131] Example 2 Heterologous Expression of Actinorhodine Biosynthetic Gene Cluster
[0132] 1. Use pET28a as a template to amplify the kanamycin resistance gene, then use PacI and NotI to double-enzyme digest and remove phosphorus, and recover; at the same time, use these two enzymes to excise the ampicillin resistance gene in pIB1A1_0-C000001, and then ligate Kana resistance gene was inserted, and the resulting plasmid was named pIB1K1_0-C000001. Using the same method, the abramycin resistance gene was amplified using the pSET152 plasmid as a template, and then the ampicillin resistance gene in pIB1A1_0-C000001 was replaced with the abramycin resistance gene to obtain the plasmid pIB1Am1_0-C000001.
[0133] 2. Digest pIB1A1_0-C000001 with SwaI and NotI and dephosphorize it as a carrier, then use these two enzymes to cut the replicon of pCC2FOS (see Example 1 for the preparation of the replicon), and obtain plasmid pIB2A1_0-C000001 after ligation. Digest pIB1K1_0-C000001 wit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com