Mono-alkyl-substituted H bond bioxindol-containing monomer, preparation of its copolymer and application thereof
A mono-alkyl, copolymer technology, applied in the field of organic semiconductor materials, can solve the problems of obvious phase separation, unfavorable formation of H bonds, low PCE, etc., and achieve the effect of simple and effective synthesis method, good UV absorption, and narrow molecular weight distribution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
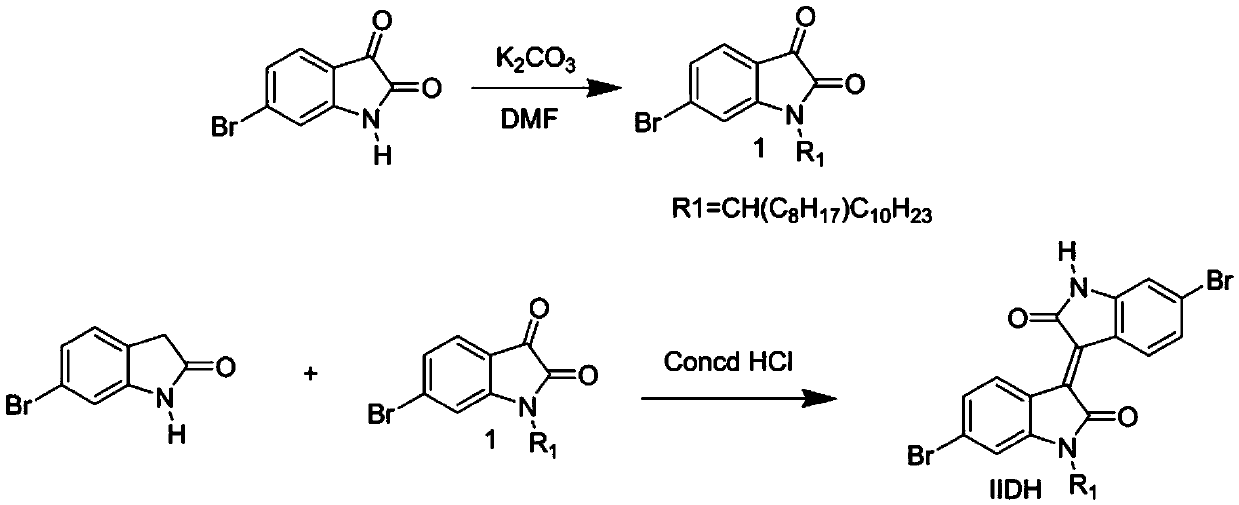
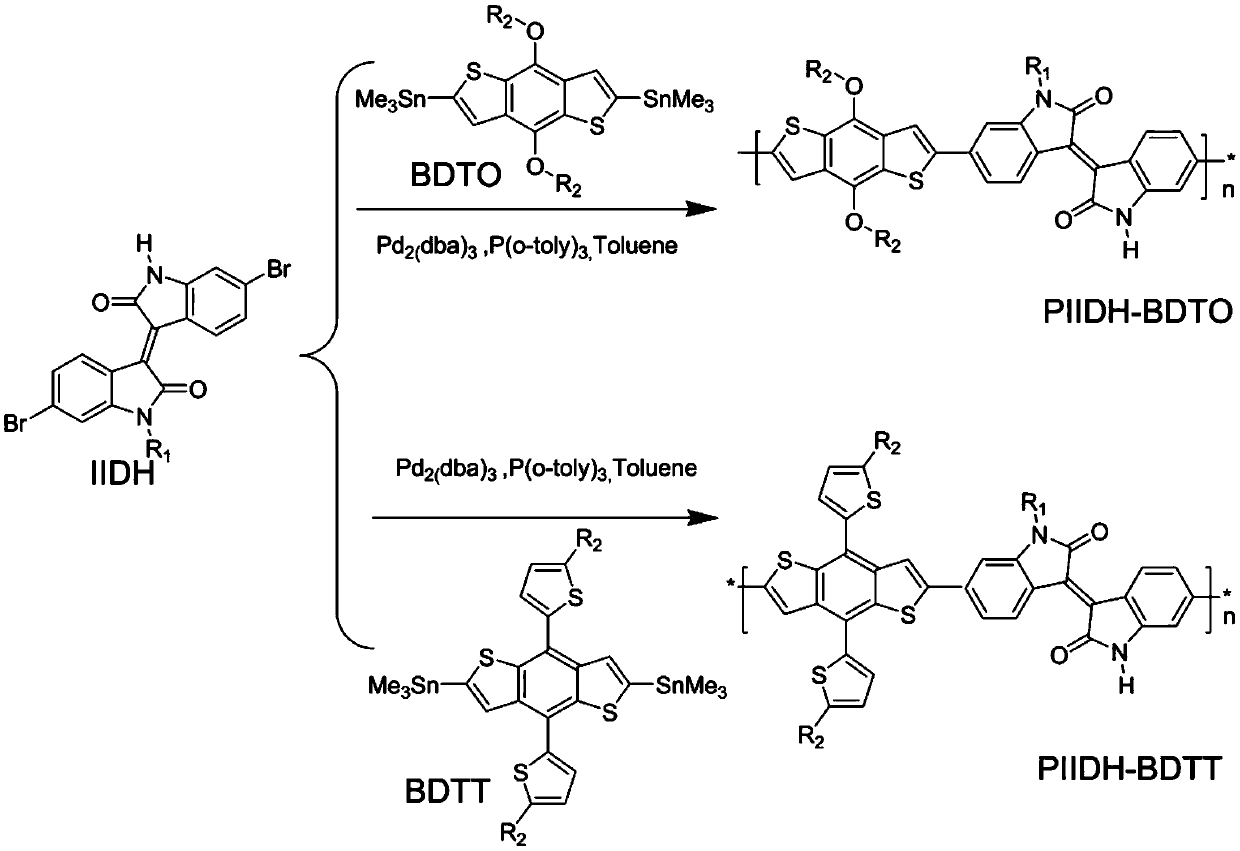
[0039] This embodiment provides a monoalkyl-substituted H bond-containing isoindigo monomer IIDH and its benzodithiophene bistin copolymer (PIIDH-BDTO and PIIDH-BDTT), the structural formula of which is shown in Table 1 (wherein, 100>n>1), the synthetic route of its monomer IIDH can be found in figure 1 , the synthesis of polymers PIIDH-BDTO and PIIDH-BDTT see figure 2 shown.
[0040] Table 1
[0041]
[0042]
[0043] This embodiment also relates to the preparation method of polymer PIIDH-BDTO and PIIDH-BDTT, comprising the following steps:
[0044] (a) Synthesis of intermediate compound benzodithiophene bistin derivatives
[0045] The synthetic structural formula of intermediate compound benzodithiophene bistin derivative is
[0046] For its detailed preparation method, see the literature "Hwang, Y.J; Kim, F.S; Xin, H; Jenekhe, S.A; New Thienothiadiazole-Based Conjugated Copolymers for Electronics and Optoelectronics. ;FullereneDerivative-DopedZincOxideNanofilma...
Embodiment 2
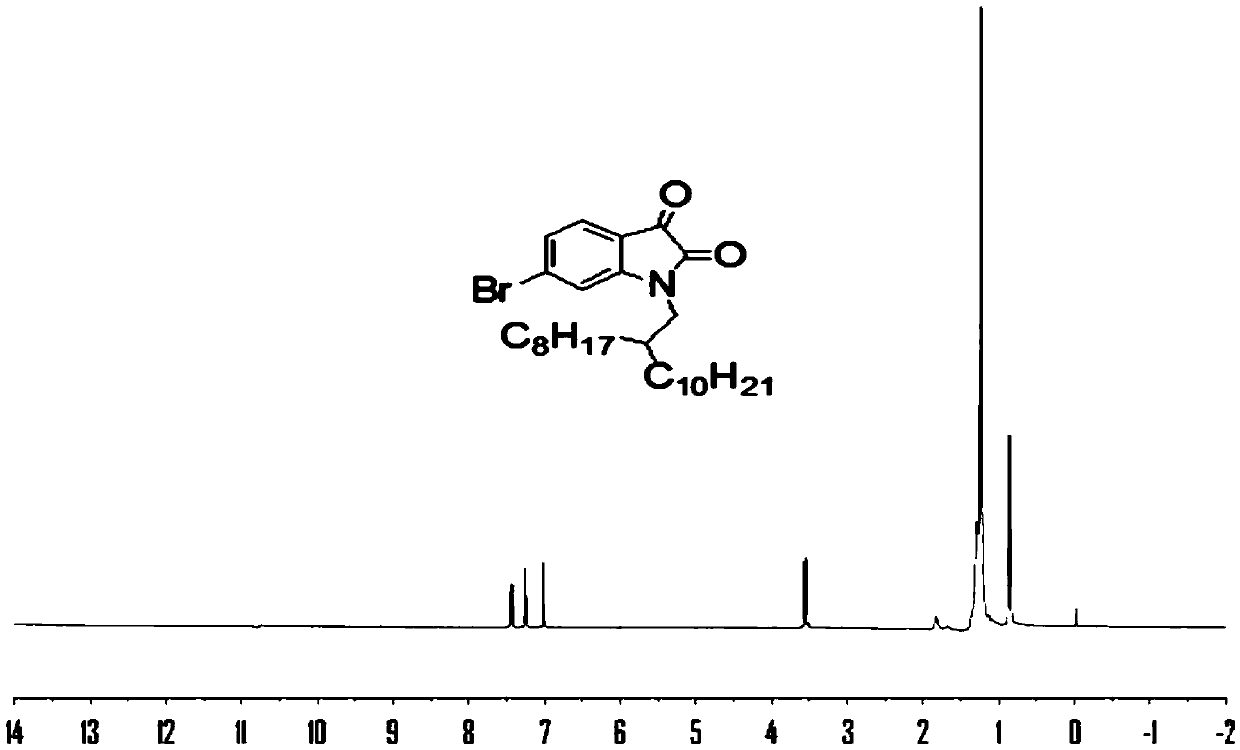
[0065] This example relates to the H NMR spectrum and C NMR spectrum of the monoalkyl-substituted H-bond-containing isoindigo monomer in Example 1, as well as the UV absorption spectrum and electrochemical properties of the polymers PIIDH-BDTO and PIIDH-BDTT. image 3 with Figure 4 The H NMR and C NMR spectra of compound 1 are given respectively, Figure 5 with Image 6 The H NMR and C NMR spectra of monomeric IIDH are given. Figure 7 The UV spectra of the polymers in chloroform solution are given. The maximum absorption peaks of these two polymers in chloroform solution are very close, at 630 and 625 nm, respectively. PIIDH-BDTO has a little red shift, but not obvious. Figure 8 The ultraviolet absorption spectrum of the polymer solid film is given. The UV-Vis absorption of the solid film is obviously red-shifted, and the maximum absorption peaks are 669 and 634nm, respectively, which are 39 and 9nm red-shifted compared with the chloroform solution. The onset absorption ...
Embodiment 3
[0067] This example relates to the use of the polymers PIIDH-BDTO and PIIDH-BDTT of Example 1 as active layer materials in thin-film solar cells. Using polymers PIIDH-BDTO and PIIDH-BDTT as donor materials (D), fullerene (PC7 1 BM) As the acceptor material (A), the photovoltaic performance of the material was tested using the bulk heterojunction structure. The test conversion efficiency data of polymer solar cell devices is shown in Table 2, and the I-V curve is shown in Figure 10 . The highest conversion efficiency of PIIDH-BDTT in the preliminary test is 1.73%.
[0068] Table 2
[0069] polymer
[0070] In summary, the monoalkyl substituted H-bond-containing isoindigo and benzodithiophene copolymer of the present invention has a rigid planar Π conjugated system, good ultraviolet absorption, and the material can be processed by solution, and has a good performance in photovoltaic devices. application prospects.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com