Gas sensor
A gas sensor and sensor electrode technology, which can be used in instruments, scientific instruments, measuring devices, etc., to solve problems such as large-scale gas sensors and achieve high precision.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
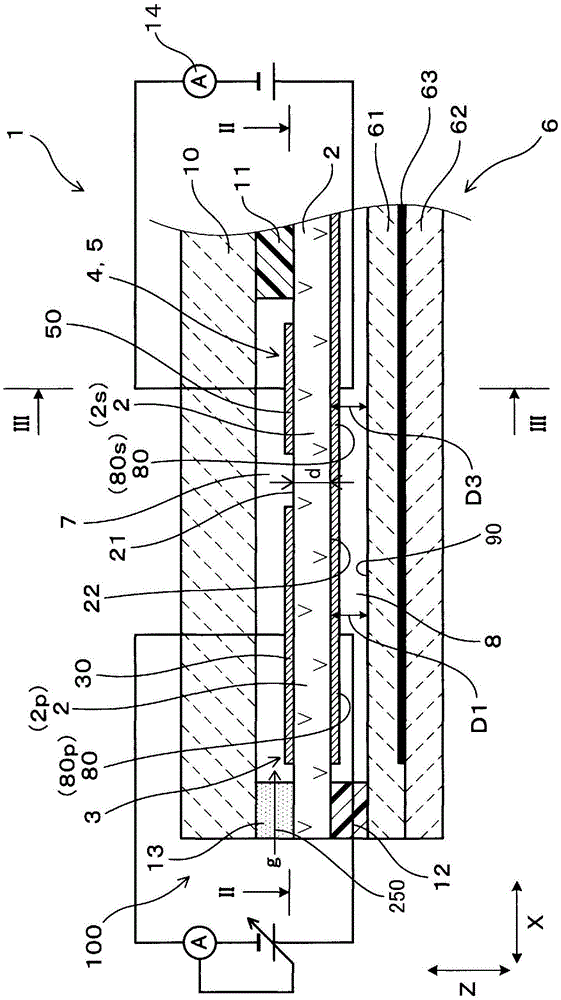
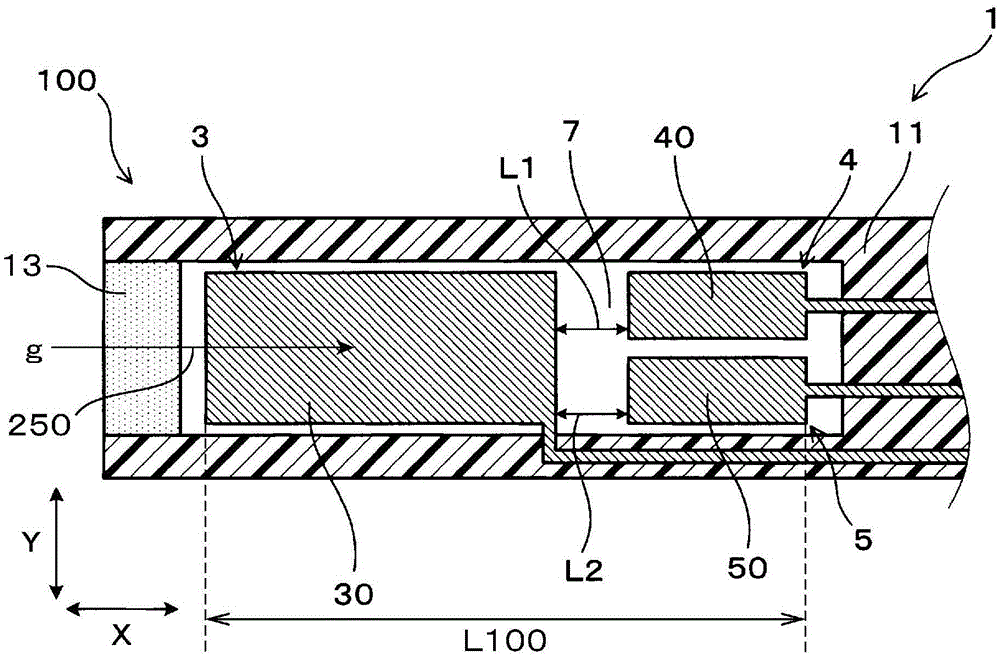
[0037] use Figure 1 ~ Figure 4 The gas sensor 1 of the first embodiment will be described. The gas sensor 1 is used to measure the concentration of a predetermined gas component contained in the oxygen-containing gas g. like figure 1 As shown, the gas sensor 1 includes: a gas chamber 7, a reference gas chamber 8, a plate-shaped solid electrolyte body 2 (2p, 2m, 2s), a pump electrode 30, a monitoring electrode 40, a sensor electrode 50, a reference electrode 80, and a A plate-shaped heater 6 having a predetermined thickness. A gas g containing oxygen is introduced into the gas chamber 7 , and a reference gas is introduced into the reference gas chamber 8 .
[0038] Solid electrolyte body 2 is provided between gas chamber 7 and reference gas chamber 8 . The solid electrolyte body 2 is a plate-shaped body made of a material having oxygen ion conductivity, such as zirconia and ceria.
[0039] like figure 1 As shown, the solid electrolyte body 2 has a predetermined thickness...
Embodiment 2
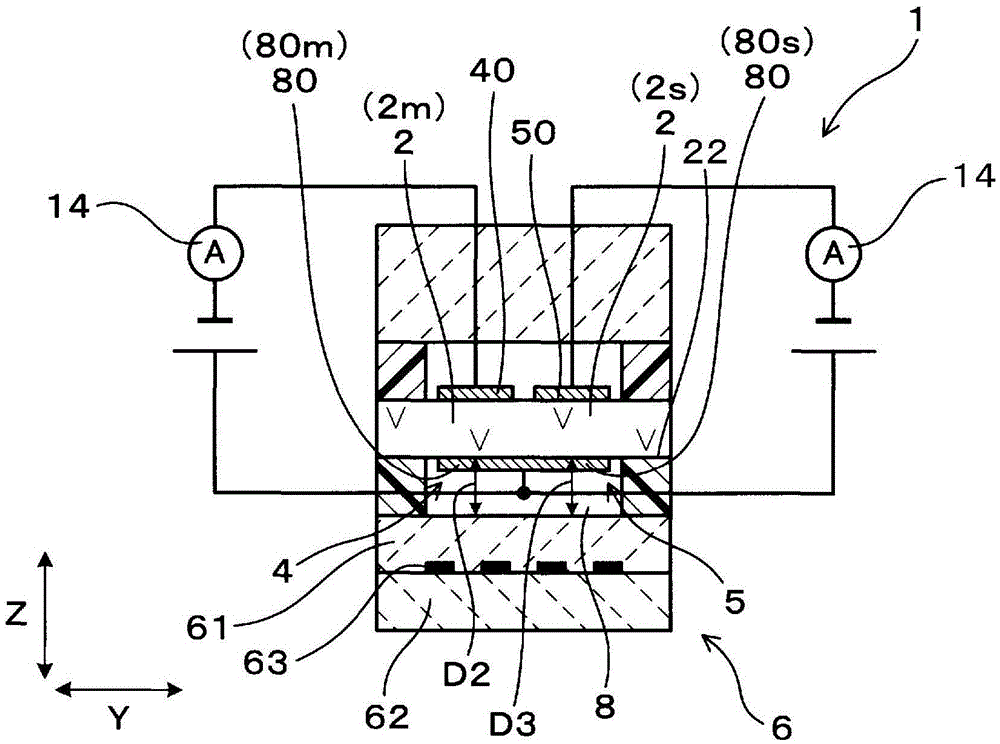
[0085] Figure 5 The gas sensor 1 according to Example 2 is shown. The gas sensor 1 has a plurality of solid electrolyte bodies 2 . Specifically, the gas sensor 1 includes two solid electrolyte bodies 2 (2a, 2b). In addition, the pump unit 3 is configured using one solid electrolyte body 2a, and the monitoring unit 4 and the sensor unit 5 are configured using the other solid electrolyte body 2b. In the Z direction, the distance Da between one solid electrolyte body 2 a and the heater 6 is equal to the distance Db between the other solid electrolyte body 2 b and the heater 6 . To be precise, the distance Da is the shortest distance between the main surface 22a of the solid electrolyte body 2a and the main surface 90 of the insulating layer 61 opposite to the main surface 22a, and the distance Db is the distance between the main surface 22b of the solid electrolyte body 2b and the insulating layer 61. The shortest distance between the main faces 90 of the layers 61.
[0086]...
Embodiment 3
[0090] Image 6 The gas sensor 1 according to Example 3 is shown. The gas sensor 1 is different from the first embodiment in the position of the heater 6 . That is, a gas chamber 7 is provided between the heater 6 and the solid electrolyte body 2 . Further, heater 6 faces solid electrolyte body 2 across gas chamber 7 .
[0091] Other configurations are the same as in Embodiment 1. In addition, in Image 6 Among the symbols used in , the same parts as those used in Example 1 represent the same components as in Example 1, unless otherwise indicated.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com