Ceramic shaver cutter
A technology for razors and knives, which is applied in the field of ceramic razor knives, can solve the problems of reducing production costs and ceramic knives are fragile, and achieve high density, facilitate industrial production, and enhance practicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
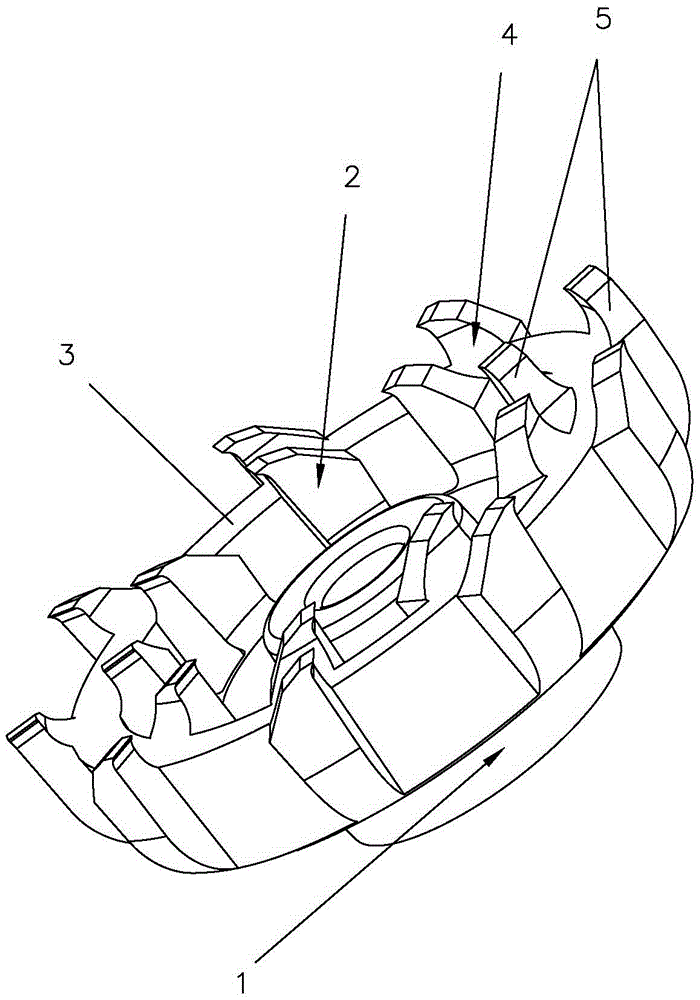
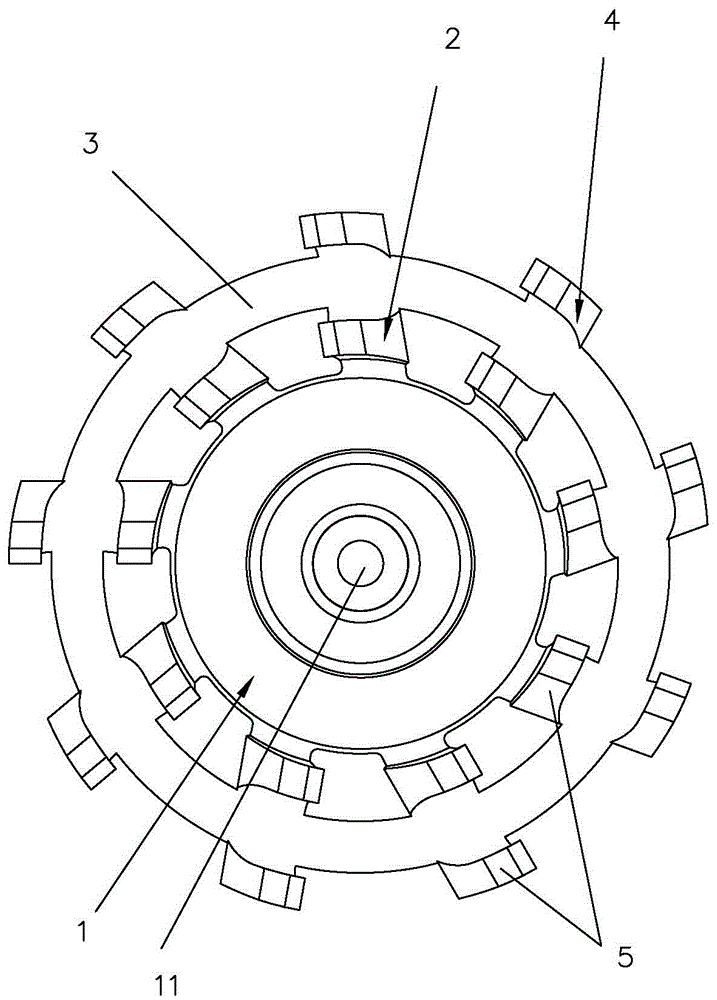
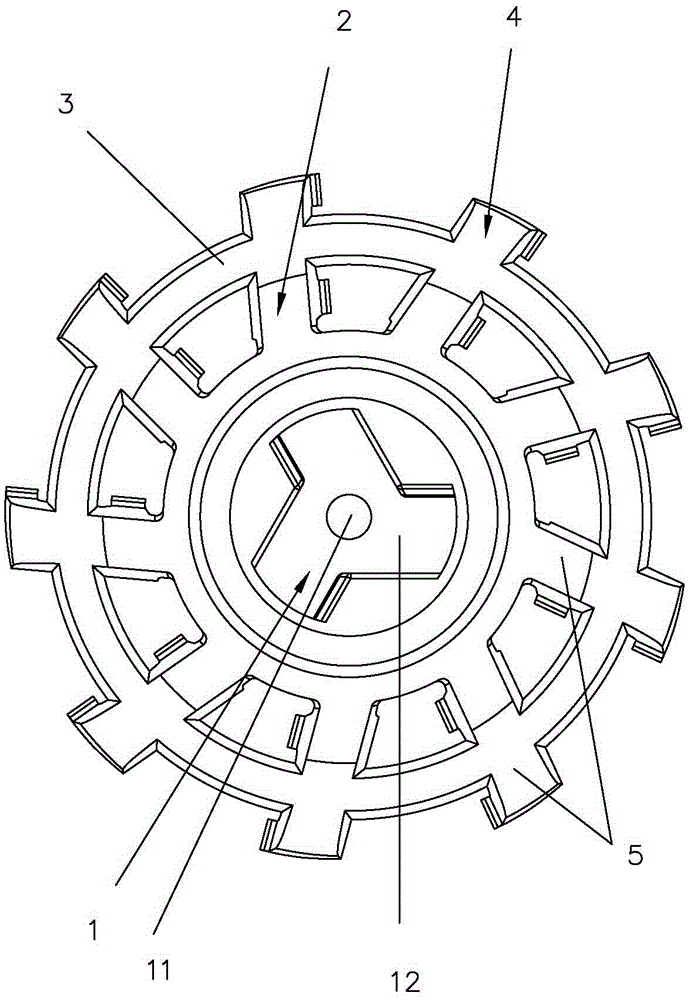
[0028] Such as Figure 1-3 As shown, a ceramic razor tool of this embodiment includes a circular ring piece 3, an inner ring blade group 2, an outer ring blade group 4, a blade base 1, the inner ring blade group 2, the outer ring blade group 4 Each is composed of at least one blade 5, the bottom inner side of the blade 5 of the outer ring blade set 4 is connected with the outer ring wall of the ring piece 3, and the bottom outer side of the blade 5 of the inner ring blade set 2 is connected to the ring piece The inner ring wall of the inner ring 3 is connected, the bottom inner side of the blade 5 of the inner ring blade set 2 is connected with the blade base 1, the top of the blade 5 is provided with a blade, and the blade 5 is composed of ceramic material.
[0029] This embodiment realizes the reliable connection between the blade 5 and the blade base 1 through the reinforcement structure of the inner ring blade group 2-ring blade 3 outer ring blade group 4, which greatly enhanc...
Embodiment 2
[0040] The structure of a ceramic razor blade of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1, and it will not be redundant here.
[0041] The difference of this embodiment is:
[0042] The ceramic material of this embodiment is a zirconia ceramic material, including the following mass fractions of raw materials: 80 parts nano-zirconia, 14 parts alumina, 9 parts aluminum borate whiskers, 6 parts yttrium oxide, 3 parts kaolin, 15 parts Titanium carbide.
[0043] It can be prepared by the following steps: (1) Ball milling: mixing nano-zirconia, alumina, yttrium oxide, kaolin, and titanium carbide by ball milling; (2) mixing: adding 550 parts by weight of water, 1.8 parts by weight of coupling agent, and 1.5 parts by weight Parts of binder, 4 parts of dispersant and aluminum borate whiskers, stirred and mixed for 28 minutes, spray dried to obtain particles; (3) Hot pressing: extrude the particles into a calciner for two sintering and one sintering It is calcined in a nitrogen a...
Embodiment 3
[0045] The structure of a ceramic razor blade of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1, and it will not be redundant here.
[0046] The difference of this embodiment is:
[0047] The ceramic material of this embodiment is a zirconia ceramic material, including the following mass fractions of raw materials: 86 parts of nano zirconia, 16 parts of alumina, 10 parts of aluminum borate whiskers, 8 parts of yttrium oxide, 4 parts of kaolin, 20 parts Titanium carbide.
[0048] It can be prepared by the following steps: (1) Ball milling: mixing nano-zirconia, alumina, yttrium oxide, kaolin, and titanium carbide by ball milling; (2) mixing: adding 500 parts by weight of water, 0.1 parts by weight of coupling agent, and 0.2 parts by weight Parts of binder, 3 parts of dispersant and aluminum borate whiskers, stirred and mixed for 20 minutes, spray-dried to obtain particles; (3) Hot pressing: extruding the particles into a calciner for two sintering and one sintering It is calcin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com