Method for promoting enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulose
A lignocellulosic enzyme and lignocellulose technology, which is applied in the field of promoting lignocellulosic enzymatic hydrolysis, can solve the problems of high price and achieve the effect of avoiding desorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
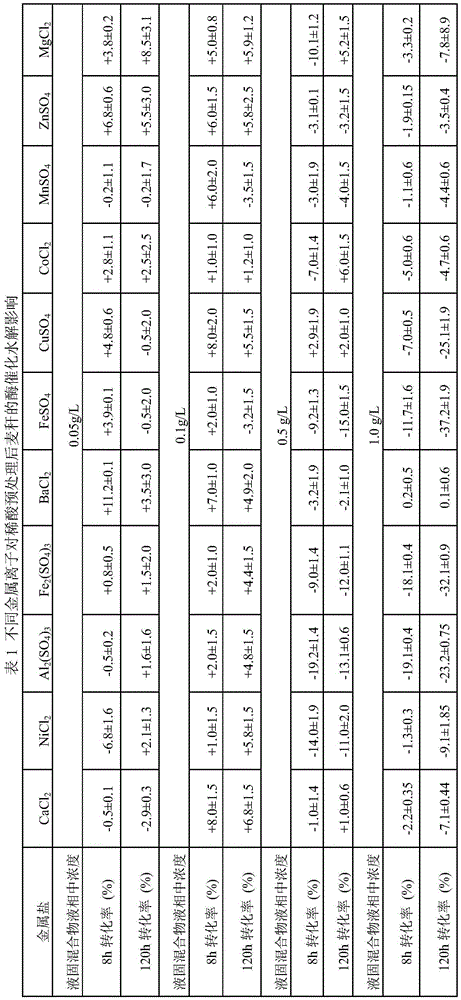
[0038] The wheat straw was pretreated with 0.5% dilute sulfuric acid at 140° C. for 1 hour, and then washed to neutrality, so as to obtain pretreated wheat straw (ie, pretreated lignocellulose). The above pretreated wheat straw was mixed with a sulfuric acid solution of pH 4.8 to obtain a liquid-solid mixture with a solid content of 5%. Add different metal salt solutions to the liquid-solid mixture so that the metal salt concentration in the liquid phase is 0.05-1g / L, and then treat it in a shaker at room temperature with a rotation speed of 150rpm for 1 hour, then filter to remove the liquid, and then use 15FPU / g The amount of cellulase used for solids, the enzymatic hydrolysis is carried out under the conditions of initial pH 4.8, 50° C., and 150 rpm. Among them, the temperature of the enzymatic hydrolysis system is raised from room temperature to 50°C using a gradient temperature rise method, that is, every 5°C increase and then heat preservati...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Effects of various metal ions on enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose with different enzyme dosages
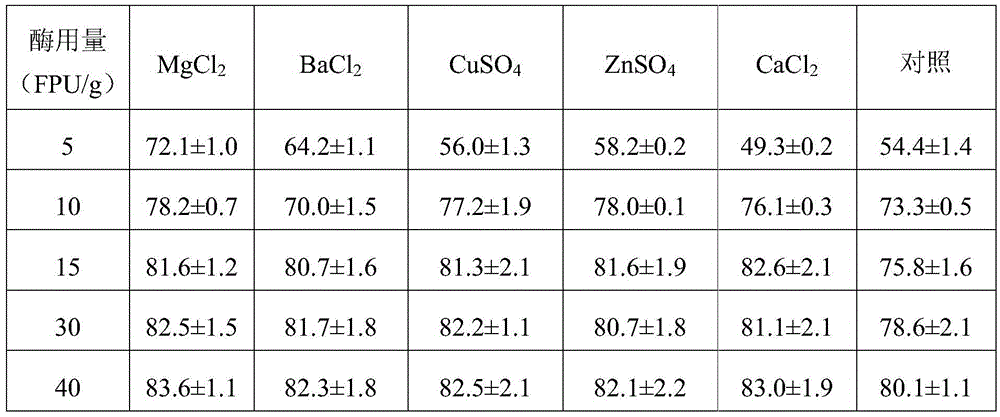
[0042] The used pretreated wheat straw raw material, metal ion treatment and enzymatic hydrolysis process temperature and pH parameters are the same as those in Example 1. Adopt 0.1g / L metal salt concentration, and the cellulase dosage of 5-40FPU / g solid. The control group did not add metal ions, and the enzymatic conversion rate of cellulose after 120 hours is shown in Table 2.
[0043] Table 2 Effects of different metal ions on the conversion rate of cellulose after 120 h at different cellulase dosages
[0044]
[0045] It can be seen from the above table that metal ions have a certain promotion effect on the conversion rate of cellulose under different cellulase dosages, while at lower cellulase dosages, metal ions, especially Mg 2+ showed the most significant promotion effect.
Embodiment 3
[0047] The effect of pH
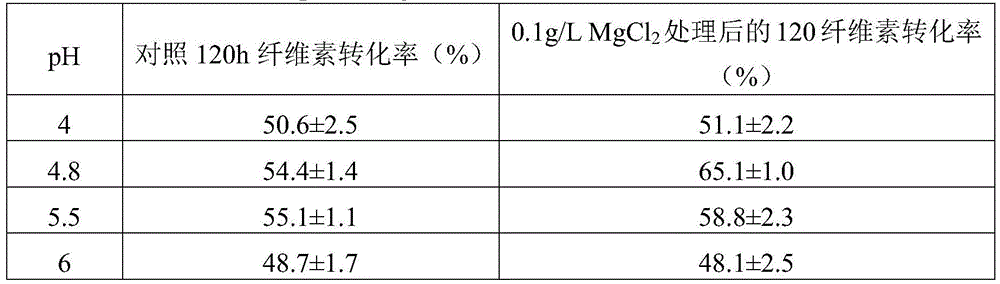
[0048] The pretreated wheat straw raw material and the enzymatic hydrolysis process are the same as in Example 1. Using 0.1g / LMgCl 2 Concentration, changing MgCl 2 The pH value of the system when the solution is used to treat the straw after dilute acid pretreatment, and the treated solid is enzymatically hydrolyzed at the corresponding pH with a cellulase dosage of 5 FPU / g solid. Taking the pretreated wheat straw without adding metal ions as the control, the enzymatic conversion rate of cellulose after 120 h is shown in Table 3.
[0049] Table 3 pH vs. MgCl 2 Effects of Dilute Acid Pretreatment on Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Wheat Straw
[0050]
[0051] It can be seen from the above table that the pH effect on Mg 2+ The promoting effect of metal ions has a significant effect, and the promoting effect of metal ions becomes insignificant when treated at lower or higher pH, and the optimal pH is around 5.0.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com