Graphical microstructure of light emitting diode substrate
A light-emitting diode and graphic technology, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, circuits, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of reducing luminous brightness, reducing the internal quantum efficiency of light-emitting diodes, and high density, so as to achieve the effect of improving light extraction efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] The purpose of the present invention and its structural design and functional advantages will be described based on the preferred embodiments shown in the following figures, so that the examiners can have a more in-depth and specific understanding of the present invention.
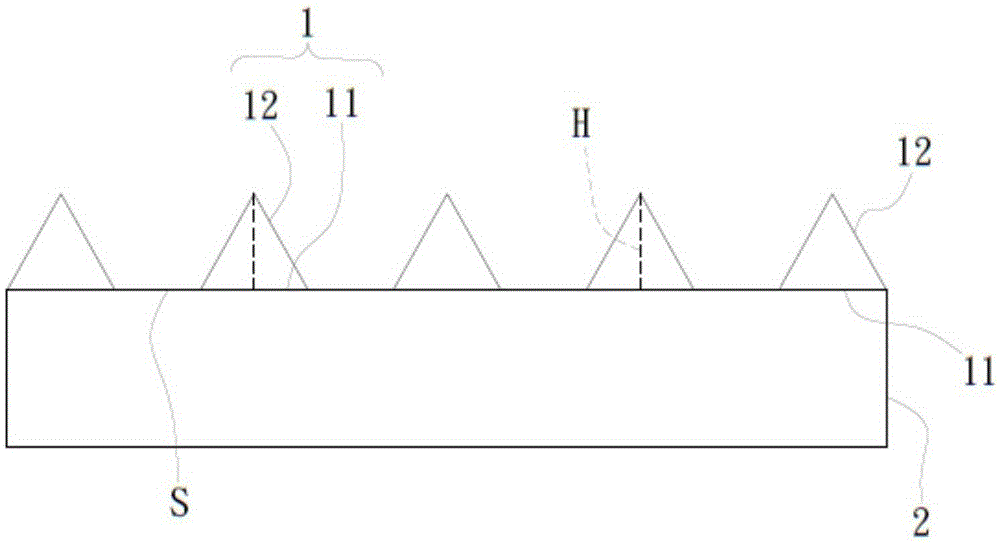
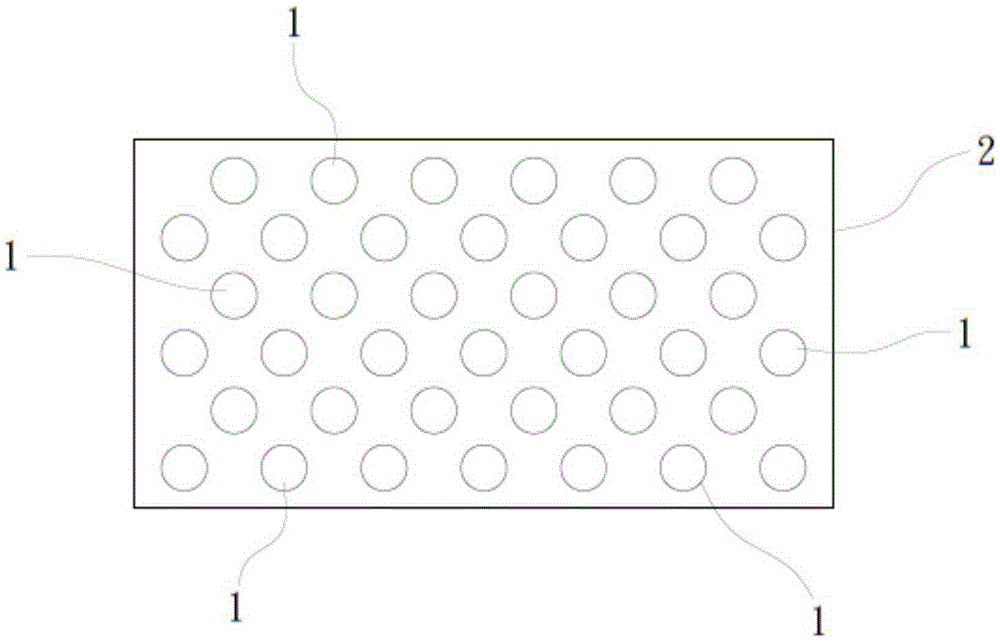
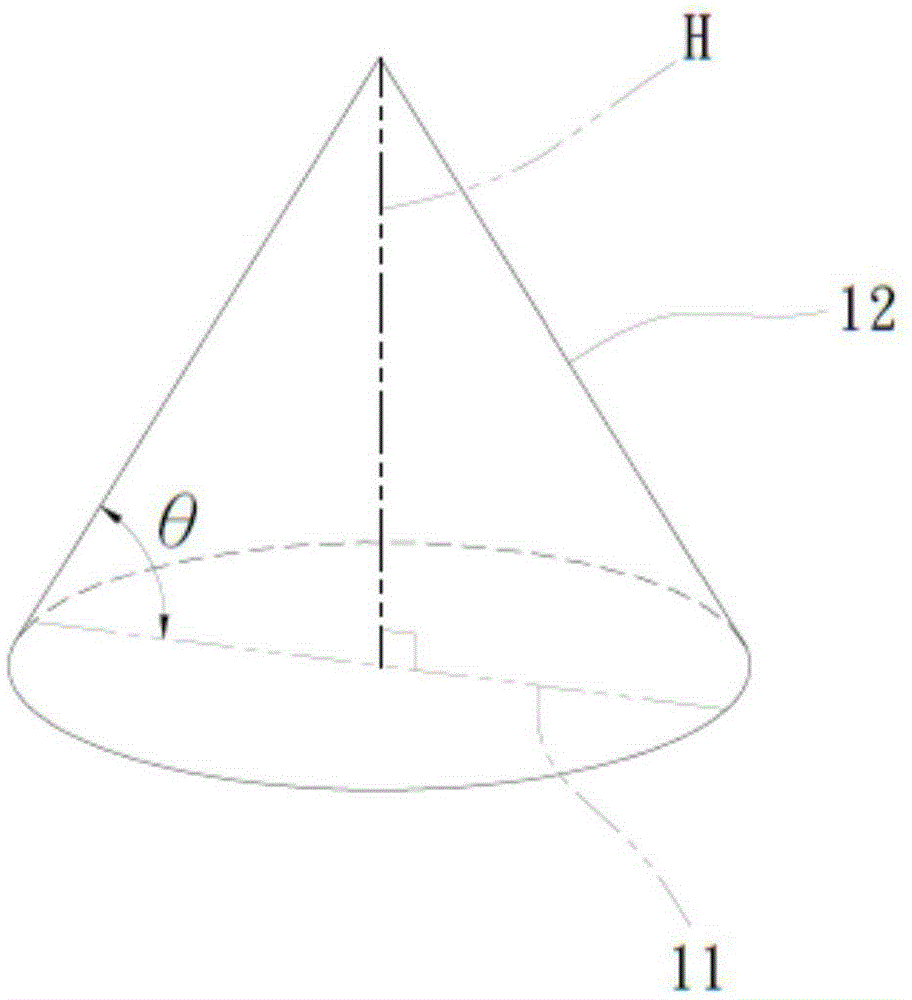
[0030] first, figure 1 It is a schematic cross-sectional view of the patterned microstructure of a preferred embodiment of the patterned microstructure of the light-emitting diode substrate of the present invention; figure 2 It is a top view of the patterned microstructure of a preferred embodiment of the patterned microstructure of the light-emitting diode substrate of the present invention; image 3 It is a schematic diagram of a single patterned microstructure of a preferred embodiment of the patterned microstructure of the light-emitting diode substrate of the present invention; such as Figure 1-3 Shown are a schematic cross-sectional view of the patterned microstructure, a top view of the pa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com