Composite emulsifier with double stimulus-response performance
A dual-stimuli-response, compound emulsifier technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, chemical/physical processes, dissolution, etc., to achieve high efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
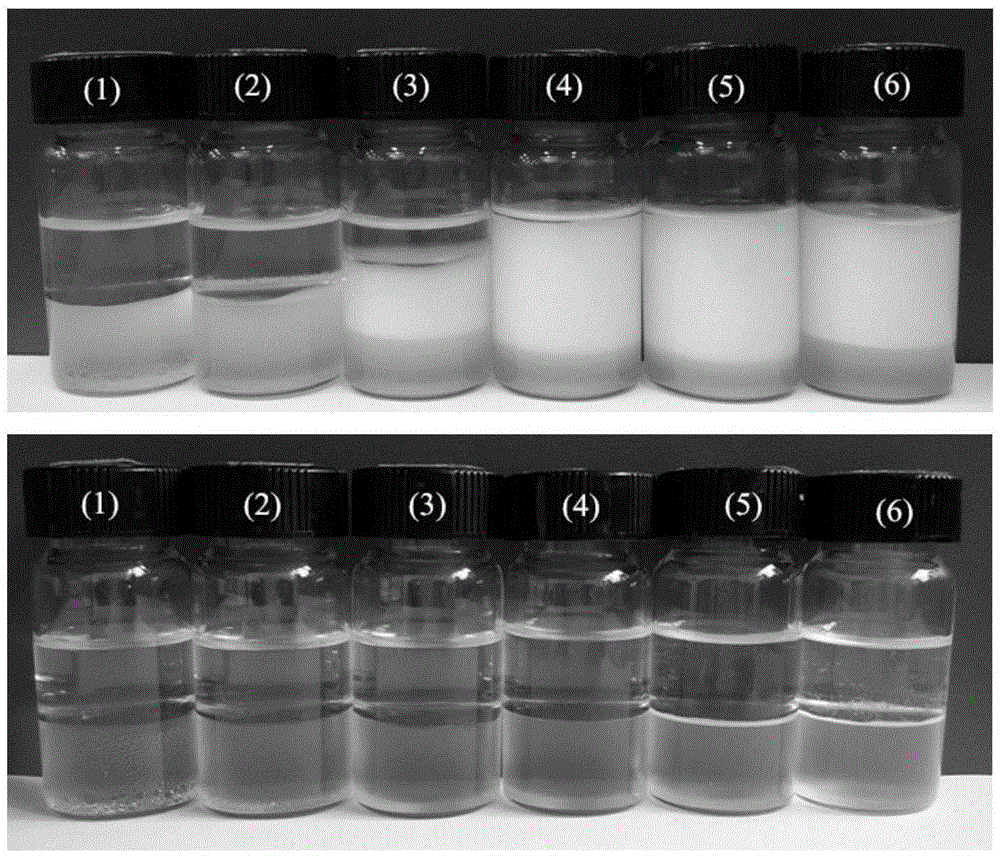
[0018] Example 1: CO 2 / N 2 - Performance test of light dual stimulus-responsive surfactant stable emulsion. Disperse the surfactant intermediate in ultrapure water (resistance = 18.2Ω), pass CO 2 Gas, when the solution is clear, dilute to a series of concentrations. In a 25mL cylindrical vial, add 7mL of aqueous surfactant solution (concentration99%), and emulsify with a high-shear emulsifier (IKA, rotor diameter 1cm) at 11,000rpm 2min (the same below), a stable emulsion cannot be obtained, as shown in the figure. It shows that the surfactant cannot stabilize the emulsion when the concentration is less than the CMC.
Embodiment 2
[0019] Example 2: CO 2 / N 2 -Surface activation of nano-silica particles by light dual stimulus-responsive surfactants. Take 7mL of surfactant aqueous solutions with a series of concentrations and put them into 25mL columnar vials, add 0.035g of commercial nano-silica particles (HL-220, the primary particle size is about 20nm, and the BET specific surface area is 200m 2 / g, produced by Wuxi Jinding Longhua Chemical Co., Ltd.), disperse the particles (50W, 1min) with an ultrasonic disperser (JYD-650, Shanghai), add 7mL of n-decane, emulsify with a high-shear emulsifier for 2min, and obtain stable O / W type Pickering emulsion, the appearance photos and micrographs of the emulsion were taken after standing for one week. image 3 The micrographs show that, with separate CO 2 / N 2 -Compared with photoactive dual-stimuli-responsive surfactants, nanoparticles and very low concentrations of surfactants can stabilize emulsions, and the diameter of emulsion beads is 100-500 μm, which...
Embodiment 3
[0020] Example 3: CO of Pickering Emulsions 2 / N 2Responsive validation. Ultrasonically disperse 0.035g of nano-silica particles in 7mL of surfactant aqueous solution (concentration: 0.01mM), add 7mL of n-decane, and homogeneously emulsify with a high-shear emulsifier for 2min to obtain a stable O / W Pickering emulsion liquid. Place the emulsion in a water bath at 70 °C and bubble N into it 2 After one hour, the emulsion breaks and the oil and water separate. The relevant mechanism is: heating and bubbling N 2 The surfactant in the bicarbonate state decomposes and becomes a surface-free intermediate state, which desorbs from the surface of the silica particles, so the particles become too hydrophilic, lose surface activity, and desorb from the oil / water interface back to the surface. to the water phase, the emulsion breaks. When the solution was bubbled with CO at room temperature 2 , the surfactant intermediate is reprotonated, and then adsorbed to the surface of the si...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com