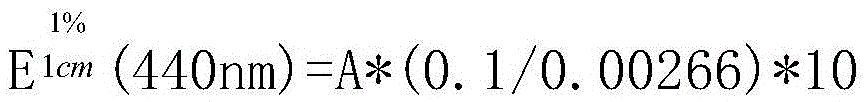Process for extracting coenzyme Q10 from tobacco leaves
A technology for coenzyme and tobacco leaves, which is applied to the technical field of extracting coenzyme Q10, can solve the problems of high cost, high price, and is not suitable for large-scale promotion, and achieves the effects of short time, good effect and improved separation ability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
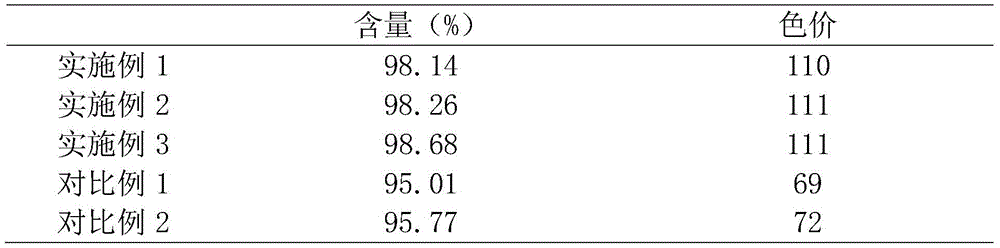
Embodiment 1
[0026] A process for extracting coenzyme Q10 from tobacco leaves, specifically comprising the steps of:
[0027] 1) Pre-treatment: add the same weight of pure water to the tobacco leaf extract obtained by extracting the waste tobacco leaves, put it into a high-pressure tank, and pressurize it to 4kg / cm 2 , make the pressure uniform, and keep it for 5 minutes, then return to normal pressure within 1-3s, and then use the ethanol solution of NaOH and petroleum ether system to dynamically saponify the bound solanesol of the obtained material, crystallize and filter to obtain the solanesol containing the extract;
[0028] 2) Molecular distillation: the extract containing solanesol obtained in step 1) was removed by molecular distillation with a vacuum degree of 0.01Pa, a distillation temperature of 190°C, a scraper speed of 600r / min, and a material flow rate of 1.0mL / min to obtain Light phase solanesol and heavy phase solanesol;
[0029] 3) Column chromatography separation: the h...
Embodiment 2
[0033]A process for extracting coenzyme Q10 from tobacco leaves, specifically comprising the steps of:
[0034] 1) Pre-treatment: add the same weight of pure water to the tobacco leaf extract obtained by extracting the waste tobacco leaves, put it into a high-pressure tank, and pressurize it to 4kg / cm 2 , make the pressure uniform, and keep it for 10min, then return to the normal pressure within 1-3s, and then use the ethanol solution of NaOH and petroleum ether system to dynamically saponify the bound solanesol of the obtained material, crystallize and filter, and obtain the solanesol containing solanesol the extract;
[0035] 2) Molecular distillation: the extract containing solanesol obtained in step 1) was removed by molecular distillation with a vacuum degree of 0.01Pa, a distillation temperature of 190°C, a scraper speed of 600r / min, and a material flow rate of 1.0mL / min to obtain Light phase solanesol and heavy phase solanesol;
[0036] 3) Column chromatography separa...
Embodiment 3
[0040] A process for extracting coenzyme Q10 from tobacco leaves, specifically comprising the steps of:
[0041] 1) Pre-treatment: add the same weight of pure water to the tobacco leaf extract obtained by extracting the waste tobacco leaves, put it into a high-pressure tank, and pressurize it to 4kg / cm 2 , make the pressure uniform, and keep it for 8 minutes, then return to normal pressure within 1-3s, and then use the ethanol solution of NaOH and petroleum ether system to dynamically saponify the combined solanesol, crystallize and filter the obtained material to obtain the solanesol containing the extract;
[0042] 2) Molecular distillation: the extract containing solanesol obtained in step 1) was removed by molecular distillation with a vacuum degree of 0.01Pa, a distillation temperature of 190°C, a scraper speed of 600r / min, and a material flow rate of 1.0mL / min to obtain Light phase solanesol and heavy phase solanesol;
[0043] 3) Column chromatography separation: the h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com