Anticoagulant drug based on cobra venom PIII type metalloprotease and applications thereof
A technology of metalloprotease and cobra venom, applied in peptide/protein components, medical preparations containing active ingredients, enzymes, etc., can solve the problems that cannot be prepared with anticoagulant drugs, achieve no bleeding risk, reduce abnormal coagulation, Effect of lowering fibrinogen levels
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
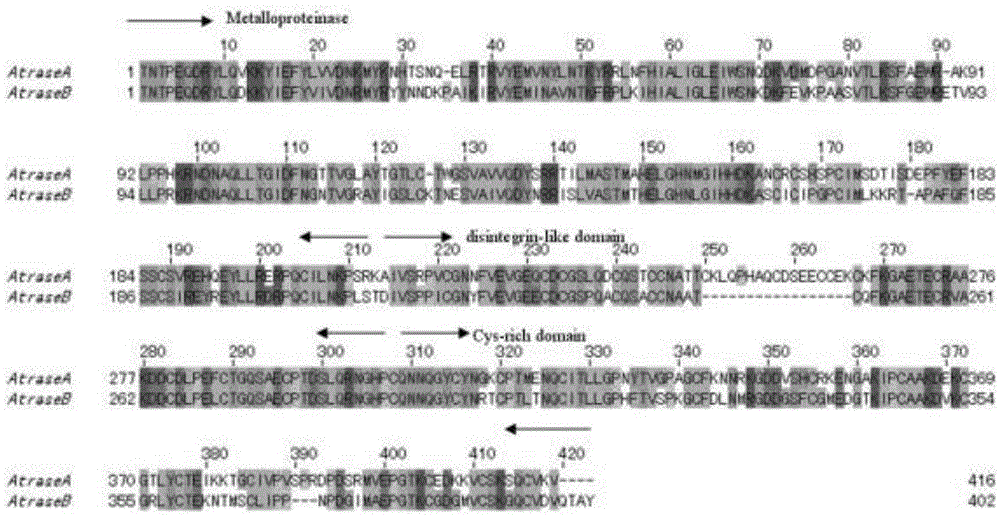
[0047] The target protein is obtained by separating and purifying from the snake venom of Chinese cobra (Zhoushan species cobra) (classification name: Najaatra). The target protein is a single-chain glycoprotein, and its structural analysis shows that it has three structural domains: a metalloprotease domain, a disintegrin-like domain, and a cysteine-rich domain, belonging to the PIII type snake venom metalloprotease ( figure 1 ).
[0048] Table 1 The physical and chemical indicators of the target protein deduced from the primary structure
[0049]
[0050] As shown in Table 1: the target protein has the activity of hydrolyzing the alpha chain of fibrinogen, which can be completely inhibited by metal chelating agents EDTA, EGTA, 1,10-phenanthroline and reducing agent DTT. The actual molecular weights of the target proteins AtraseA and AtraseB are about 51.5 and 49.4kDa respectively, and their sequences are: AtraseA: SEQIDNo.1; AtraseB: SEQIDNo.2; but their apparent molecul...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Anticoagulant effect of cobra venom type PIII metalloprotease (taking AtraseA as an example)
[0067] 1. Anticoagulation in vitro
[0068] 1.1 In vitro experiments on the effects of anticoagulant drugs on the four coagulation indexes
[0069] 1.1.1 Determination method: standard human plasma (purchased from SIEMENS, Germany) was reconstituted in deionized water, shaken gently and allowed to stand at room temperature (25°C) for 15 minutes before use. The samples were diluted to 10 μg / ml, 50 μg / ml, and 100 μg / ml with PBS, respectively. The measurement system of each index is as follows:
[0070] TT: 200μl plasma + 40μl sample;
[0071] APTT: 100μl plasma + 20μl sample;
[0072] PT: 100μl plasma + 20μl sample;
[0073] FIB: 200 μl diluted plasma (standard plasma diluted 10 times) + 40 μl sample;
[0074] The mixture of the above sample and plasma was incubated in a water bath at 37°C for 5 min and 30 min, respectively, and experiments were carried out according to th...
Embodiment 3
[0092] 2. Anticoagulation in Rats
[0093] 2.10.3mg / kg dose anticoagulant anticoagulant effect
[0094] 2.1.1 Animals: SPF grade SD rats, weighing 250-280g. Animals were randomly divided into five groups, namely control group, 2h group, 6h group, 12h group and 24h group, with 10 rats in each group.
[0095] 2.1.2 Method: A sample was injected intravenously into the tail of rats at a dose of 0.3 mg / kg. Rat anesthesia and blood collection: according to the time requirements of different groups, the rats were anesthetized with 1% pentobarbital sodium 20 minutes before the experiment, and each rat was anesthetized with an average injection of 1.4ml pentobarbital sodium. After anesthesia, blood was collected at a ratio of 1:9 with 0.109 mol / L sodium citrate anticoagulant at 30 min, 2 h, 6 h, 12 h, and 24 h.
[0096] 2.1.3 Determination of anti-platelet aggregation
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com