Method for cultivating Auricularia fuscosuccinea through Lyohyllum waste
A cultivation method, the technique of Laifu mushroom, is applied in the field of cultivating jade fungus with Laifu mushroom waste, which can solve the problems of high cost and inconvenient collection of substrates, and achieve the effects of low cost, convenient collection, good practical application value and promotion value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
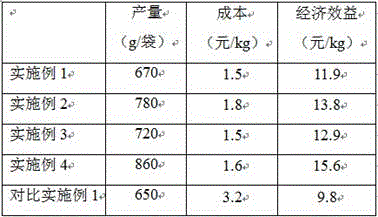
Embodiment 1
[0021] A method for cultivating black fungus with Laifu mushroom waste, the cultivation method is obtained through the following steps with the Laifu mushroom waste as raw material and lime and gypsum as auxiliary materials:
[0022] (1) Waste collection: select Laifu mushroom waste bag, pull out the bag, and collect the waste in a unified way; collect the hard miscellaneous wood leaves falling on the ground, expose them to the sun to remove some miscellaneous bacteria and pests, and weigh the above-mentioned parts by weight ;
[0023] (2) Waste crushing: Dry the Laifu mushroom waste and hard miscellaneous wood leaves from which the bacteria bags have been removed, and then crush them into particles with a diameter of 0.3-0.6cm;
[0024] (3) Adjust the water content: adjust the water content of the waste to 65-70%;
[0025] (4) The first pile fermentation: Mix the waste materials whose water content has been adjusted evenly, and build a pile with a width of 1.5-2m and a pile ...
Embodiment 2
[0030] A method for cultivating Auricularia japonica with Laifu mushroom waste, the cultivation method is raw material of Laifu mushroom waste and decomposed hard miscellaneous wood leaves, wherein the decomposed hard miscellaneous wood leaves are pagoda tree leaves, mulberry leaves, elm leaves, poplar leaves, Chinese toon leaves, camphor leaves and ginkgo leaves are mixed according to the following parts by weight: 3 parts of pagoda leaves, 8 parts of mulberry leaves, 7 parts of elm leaves, 5 parts of poplar leaves, 3 parts of Chinese toon leaves, 8 parts of camphor leaves and 25 parts of ginkgo leaves part, and the weight part of described Lai Fu mushroom waste material is 35 parts; Take lime and gypsum as auxiliary materials, obtain by the following steps:
[0031] (1) Waste collection: select Laifu mushroom waste bag, pull out the bag, and collect the waste in a unified way; collect the hard miscellaneous wood leaves falling on the ground, expose them to the sun to remove s...
Embodiment 3
[0039] A method for cultivating Auricularia japonica with Laifu mushroom waste, the cultivation method is raw material of Laifu mushroom waste and decomposed hard miscellaneous wood leaves, wherein the decomposed hard miscellaneous wood leaves are pagoda tree leaves, mulberry leaves, elm leaves, poplar leaves, Chinese toon leaves, camphor leaves and ginkgo leaves are mixed according to the following parts by weight: 5 parts of pagoda leaves, 10 parts of mulberry leaves, 12 parts of elm leaves, 8 parts of poplar leaves, 5 parts of Chinese toon leaves, 10 parts of camphor leaves and 30 parts of ginkgo leaves part, and the weight part of described Laifu mushroom waste material is 40 parts; Take lime and gypsum as auxiliary materials, obtain through the following steps:
[0040] (1) Waste collection: select Laifu mushroom waste bag, pull out the bag, and collect the waste in a unified way; collect the hard miscellaneous wood leaves falling on the ground, expose them to the sun to r...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com