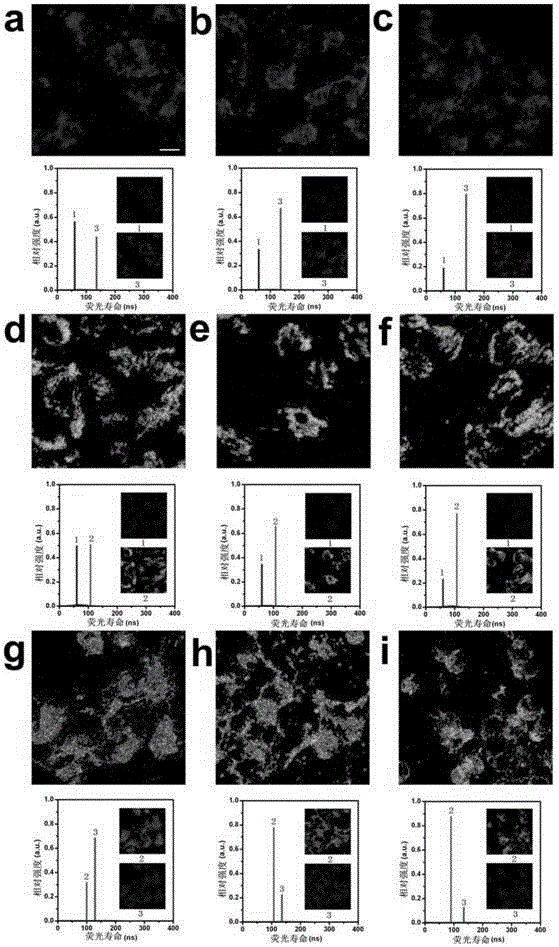
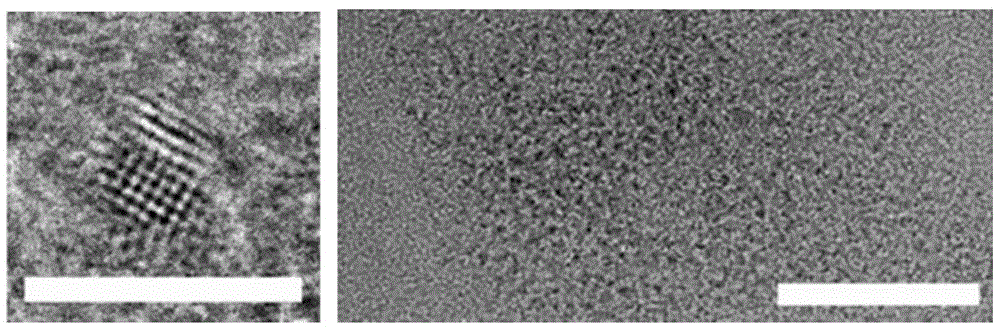
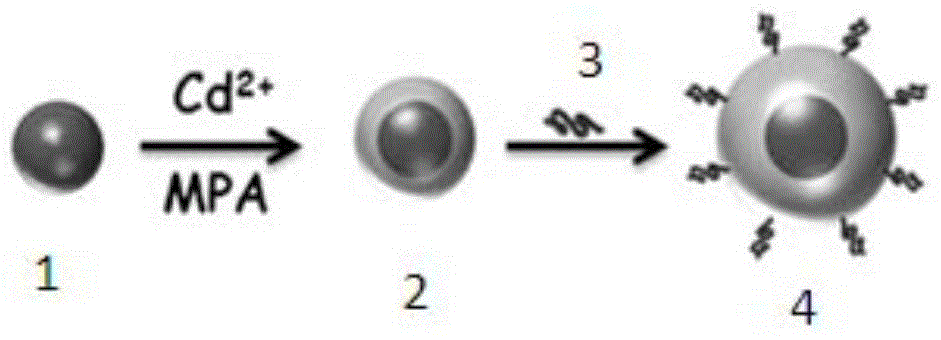Quantum dot for fluorescent lifetime codes and fluorescent lifetime coding method thereof
A technology of fluorescence lifetime and coding method, which is applied in the field of fluorescence lifetime-encoded quantum dots and their fluorescence lifetime encoding, can solve the problems of difficult coding, low quantum yield, and limited application of quantum dots, and achieves improved sensitivity and biocompatibility. Good results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0109] A method for encoding the fluorescence lifetime of quantum dots, comprising the following steps:
[0110] (1) Preparation of the first targeted quantum dots
[0111] (1) Preparation of cadmium telluride powder
[0112] a. Preparation of Cd 2+ CdCl with a concentration of 0.1mol / L 2 Aqueous solution, concentration is the 3-mercaptopropionic acid aqueous solution of 0.2mol / L, standby;
[0113] b. Freshly prepared NaHTe solution: NaBH with a molar ratio of 4.5:1 4 Dissolve Te powder in ultrapure water and react at room temperature for 5 hours to obtain NaHTe solution;
[0114] c. Preparation of CdTe: Take 5mL CdCl 2 Solution, 4.5mL of 3-mercaptopropionic acid solution was adjusted to 30mL to make mixed solution A, transferred to a 50mL three-necked flask, adjusted to pH 10.5 with NaOH solution, passed argon gas into the three-necked flask for deoxygenation for 1 hour, and added freshly prepared NaHTe solution 100 μL, stored at 4°C for 17 hours. Add 60 mL of absolute...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| fluorescence lifetime | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com