Method for synthesizing modified sulfamate water reducer by utilizing wastewater generated in tobias acid production process
A sulfamate, production process technology, applied in the field of synthetic modified sulfamate water reducer, can solve problems such as difficult to reuse, complex components, etc., to achieve improved service life, low dosage, strong dispersion ability Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
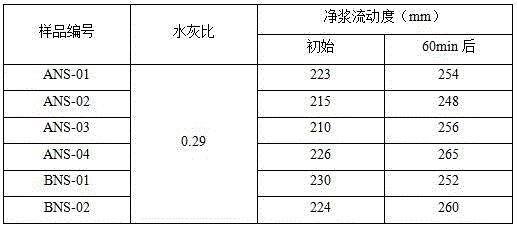
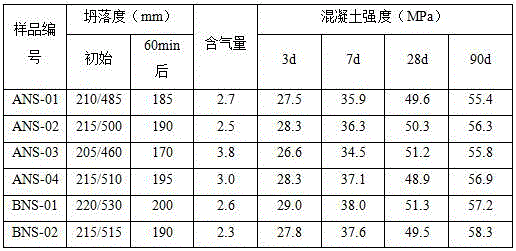
[0028] The organic matter 30g (wherein sodium sulfate content: 13.2%) that extracts in the tunic acid waste water, 18g of sodium sulfanilate and 32g of phenol are dropped in the four-necked reaction flask, add water 185g, heat up while stirring, when temperature rises to At 45°C, use 32% ionic membrane NaOH solution to adjust the pH of the solution to 8.8, continue to heat up to 70°C, and start to drop 26.5g of 37% formaldehyde at this temperature. After the dropwise addition of formaldehyde is completed, the temperature is raised to 98°C, and the reaction is maintained for 8 hours. After the end of the heat preservation reaction, the pH value of the material is adjusted to 11.2 with 32% ionic membrane NaOH solution, and the reaction is carried out at 98°C for 4 hours, and the reaction ends. Cool down to room temperature and unload to obtain the modified sulfamate superplasticizer, numbered ANS-01.
Embodiment 2
[0030] Put 22g of organic matter extracted from tunic acid wastewater (including sodium sulfate content: 9.6%), 15g of sodium sulfanilate and 40g of cresol into a four-necked reaction flask, add 175g of water, and heat up while stirring. When the temperature rises When the temperature reaches 45°C, use 32% ionic membrane NaOH solution to adjust the pH of the solution to 8.3, continue to heat up to 70°C, and start to drop 30.5g of 37% formaldehyde at this temperature. After the dropwise addition of formaldehyde is completed, the temperature is raised to 98°C, and the reaction is maintained for 10 hours. After the end of the heat preservation reaction, the pH value of the material is adjusted to 11.5 with 32% ionic membrane NaOH solution, and the reaction is carried out at 98°C for 3 hours, and the reaction is completed. Cool down to room temperature and unload to obtain the modified sulfamate superplasticizer, numbered ANS-02.
Embodiment 3
[0032] 13g of organic matter extracted from tunic acid wastewater (in which sodium sulfate content: 5.8%), 16g of organic matter extracted in G salt wastewater (in which potassium sulfate content: 8.6%), 17g of sodium p-aminobenzenesulfonate, 40g of bisphenol A and Put 5g of high-activity lignin into a four-necked reaction flask, add 210g of water, and heat up while stirring. When the temperature rises to 45°C, use 32% ionic membrane NaOH solution to adjust the pH value of the solution to 7.7, and continue to heat up to 70°C. And start dropwise addition of 37% formaldehyde 34.6g at this temperature. After the dropwise addition of formaldehyde is completed, the temperature is raised to 100°C, and the reaction is maintained for 9 hours. After the end of the heat preservation reaction, the pH value of the material is adjusted to 11.5 with 32% ionic membrane NaOH solution, and the reaction is carried out at 100°C for 5 hours, and the reaction ends. Cool down to room temperature an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com