High-mechanical-performance degradable polyurethane material based on isosorbide and polylactic acid and synthesis method of high-mechanical-performance degradable polyurethane material
A polyurethane material and isosorbide technology, applied in the field of polymers, can solve problems such as low mechanical properties, and achieve the effects of improving mechanical properties, solving the problem of small molecular weight and mild reactivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] The synthetic method of the degradable polyurethane material with high mechanical properties based on isosorbide and polylactic acid comprises the following steps:
[0020] (1) Synthesis of polylactic acid-based macromolecular diol: mix isosorbide and DL-lactide at a molar ratio of 1:50, and mix in Sn(Oct) 2 Catalyzed at 140°C and reacted under vacuum for 24 hours, then purified twice with dichloromethane and n-hexane co-precipitation system, and obtained polylactic acid-based macromolecular diol after vacuum drying; the obtained polylactic acid-based macromolecular diol was tested by nuclear magnetic resonance Its weight-average molecular weight measured by method is 7910g / mol;
[0021] (2) Polyurethane material is synthesized: the polylactic acid-based macromolecular diol that step (1) obtains is fully dissolved in anhydrous toluene, press polylactic acid-based macromolecular diol: hexamethylene diisocyanate: isosorbide mol ratio is 1.0: 1.5: 0.5 Add hexamethylene di...
Embodiment 2
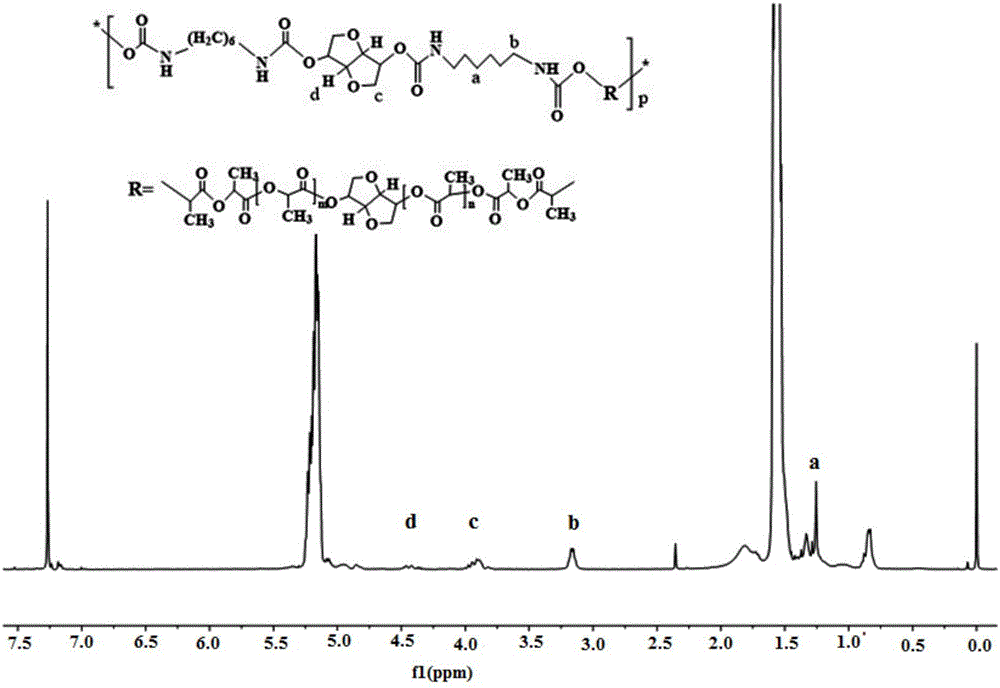
[0025] Based on the synthetic method of the high mechanical property degradable polyurethane material of isosorbide and polylactic acid, step (1) is identical with embodiment 1, and the synthetic method of polyurethane material of step (2) is as follows: the polylactic acid base that step (1) obtains is large The molecular diol is fully dissolved in anhydrous toluene, and the molar ratio of polylactic acid-based macromolecular diol: hexamethylene diisocyanate: isosorbide is 1.0: 1.1: 0.1. After reacting at low temperature for 5 hours, cool down to 30°C, then add isosorbide, react at 30°C for 2 hours, then raise the temperature to 50°C for 10 hours, and purify the product three times with toluene / absolute ethanol system. Gained product proves that this polyurethane material is successfully synthesized through nuclear magnetic resonance characterization (see figure 1 ), its weight-average molecular weight measured by gel permeation chromatography is 6.08×10 4 g / mol, the degree ...
Embodiment 3
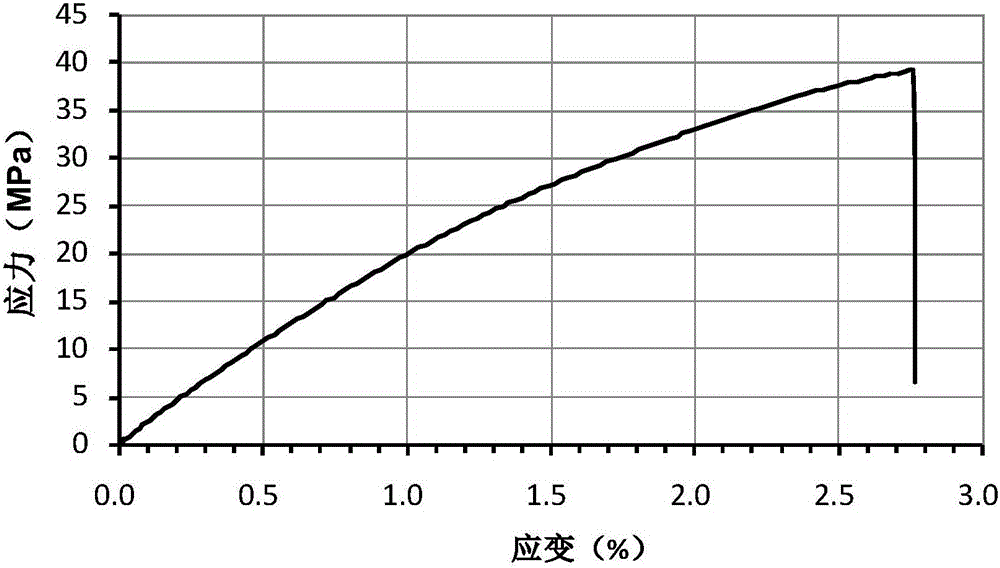
[0027] The synthetic method of the degradable polyurethane material of high mechanical properties based on isosorbide and polylactic acid, step (1) is identical with embodiment 1, and the synthetic method of polyurethane material of step (2) is as follows: the step (1) in the embodiment 1 is obtained The polylactic acid-based macromolecular diol is fully dissolved in anhydrous toluene, and the molar ratio of macromolecular diol: lysine diisocyanate: isosorbide is 1.0: 1.5: 0.5. After reacting for 3 hours, cool down to 50°C, then add isosorbide, react at 50°C for 2 hours, then raise the temperature to 70°C for 10 hours, and purify the product three times with toluene / absolute ethanol system. Gained product proves that this polyurethane material is successfully synthesized through nuclear magnetic resonance characterization (see figure 1 ), its weight-average molecular weight measured by gel permeation chromatography is 13.8×10 4 g / mol, the degree of crosslinking is 0, the tens...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile breaking strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com