Non-homogeneous gradient hard alloy and preparation method thereof
A cemented carbide, non-uniform technology, applied in the field of powder metallurgy, can solve problems such as insufficient wear resistance, increased solubility of fine WC, difficulty in controlling the particle size and proportion of fine WC, etc., to achieve good toughness and strength, superior performance, and excellent cutting edge The effect of mouth strength and impact resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
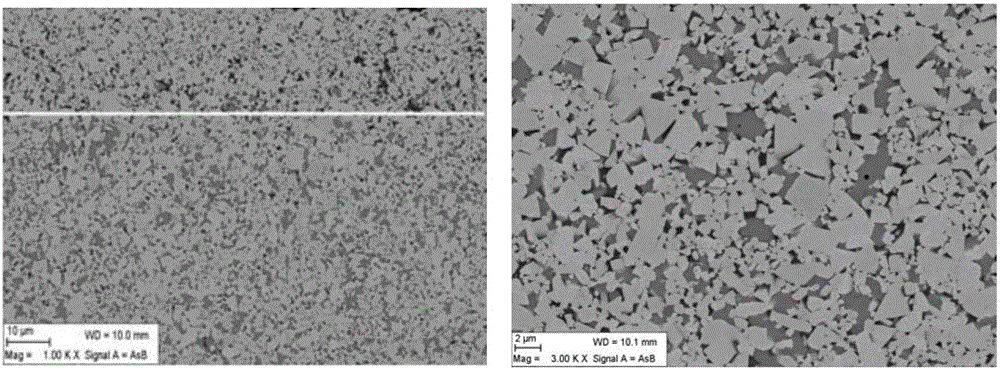
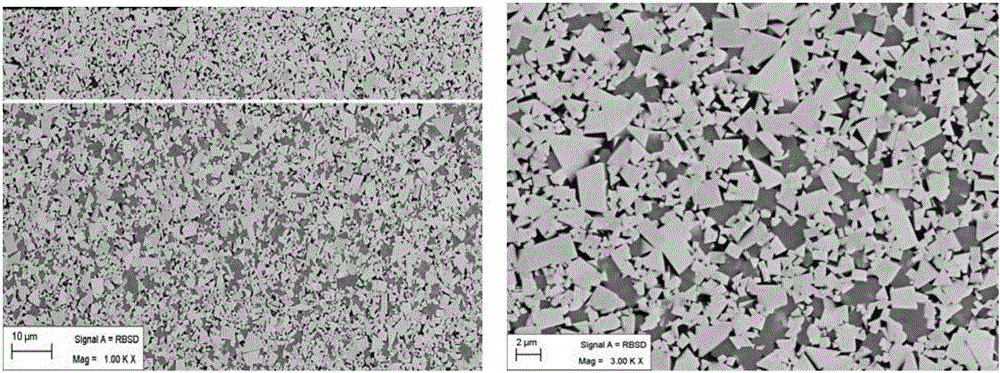
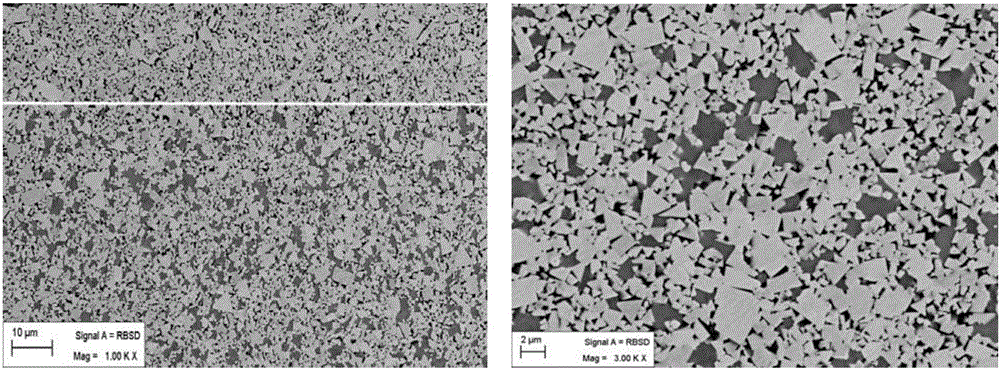
[0045] A kind of non-uniform gradient cemented carbide of the present invention, in this embodiment non-uniform gradient cemented carbide is with 8wt.% Co as binder phase, with 92wt.% tungsten carbide and titanium-containing cubic phase compound as hard phase, wherein the content of the titanium-containing cubic phase compound is 3.4wt.%, and the specific composition of the titanium-containing cubic phase compound is 2.0wt.% (Ti, W) C, wherein the W content is 45.2wt.%, and 0.4wt.% of TiC 0.5 N 0.5 , 1.0 wt.% (Ta, Nb)C, Ta / Nb mass ratio=3. Tungsten carbide (WC) grain distribution has a bimodal structure, one of which is 0.8 μm and the other is 2.8 μm. The original WC powder includes two different particle sizes, coarse and fine. The average particle size of coarse WC powder is 10.0 μm. The average particle size of fine WC powder is 0.5 μm, and the mass ratio of fine WC powder to coarse WC powder is 0.3:1. In this example, the non-uniform gradient cemented carbide has a surfa...
Embodiment 2
[0057] A kind of non-uniform gradient cemented carbide of the present invention, in this embodiment non-uniform gradient cemented carbide is with 8wt.% Co binding phase, with 92wt.% tungsten carbide and titanium-containing cubic phase compound as hard phase, wherein The content of titanium-containing cubic phase compound is 3.4wt.%. 0.5 N 0.5 , 1.0 wt.% (Ta, Nb)C, Ta / Nb mass ratio=3. The grain distribution of tungsten carbide (WC) has a bimodal structure, one of which is 1.0 μm and the other is 2.5 μm. The original WC powder includes two different particle sizes, coarse and fine. The average particle size of coarse WC powder is 8.0 μm. The average particle size of fine WC powder is 1.2 μm; the mass ratio of fine WC powder to coarse WC powder is 0.7:1. In this example, the non-uniform gradient cemented carbide has a surface gradient structure with titanium-containing cubic phase compounds missing, the average binder phase content of the surface gradient structure is 1.5 times...
Embodiment 3
[0069] A kind of non-uniform gradient cemented carbide of the present invention, in this embodiment non-uniform gradient cemented carbide is to use 6wt.% Co binding phase, with 94wt.% tungsten carbide and titanium-containing cubic phase compound as hard phase, wherein The content of titanium-containing cubic phase compound is 3.4wt.%, and its specific composition is 2.0wt.% (Ti, W) C, of which W content is 51.3%, 0.4wt.% TiC 0.5 N 0.5, 1.0 wt.% (Ta, Nb)C, Ta / Nb mass ratio=3. Tungsten carbide (WC) grain distribution has a bimodal structure, one of which is 0.6 μm and the other is 1.9 μm. The original WC powder includes two different particle sizes, coarse and fine. The average particle size of coarse WC powder is 8.0 μm. The average particle size of fine WC powder is 0.8 μm; the mass ratio of fine WC powder and coarse WC powder is 0.8:1. In this example, the non-uniform gradient cemented carbide has a surface gradient structure with titanium-containing cubic phase compound ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com