Degradation reinforcing method for polychlorinated biphenyl in soil or sediment
A polychlorinated biphenyl and sediment technology, applied in the field of soil or sediment remediation, to achieve the effect of improving the degradation rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
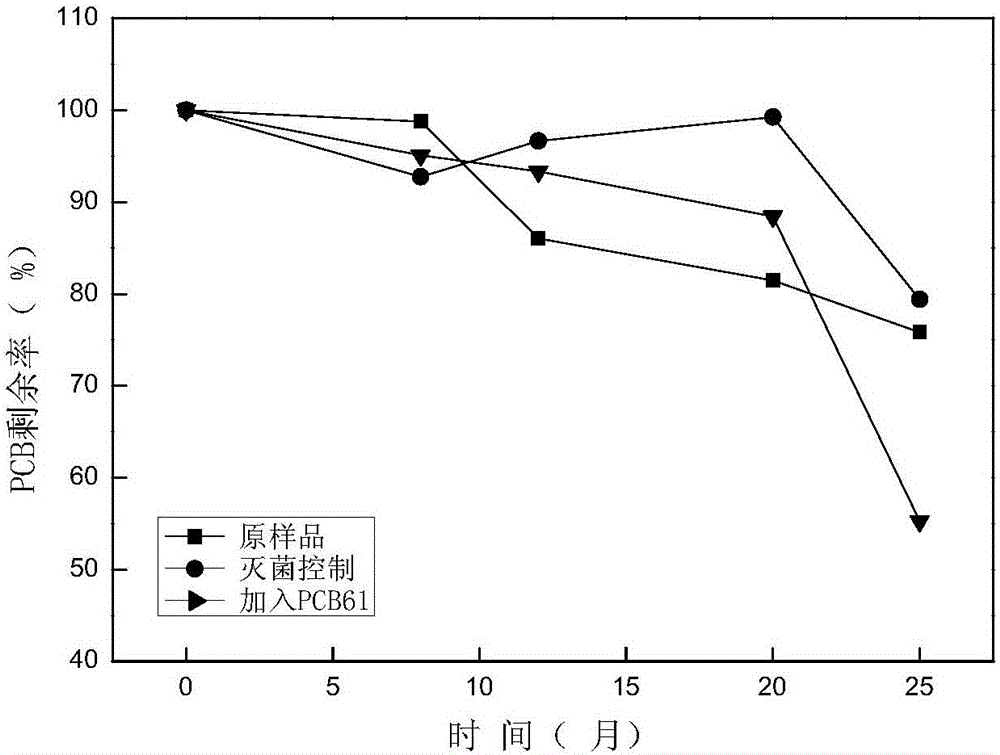
[0028] The method for strengthening the degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls in the soil under the participation of PCB61 of this embodiment is specifically:
[0029] Take an appropriate amount of PCBs-contaminated soil sample and add it to a serum bottle, add nutrient solution and PCB61 to it to form a uniform mud-water mixed culture solution with a mud-water volume ratio of 1:2.5; continuously blow nitrogen for 3 minutes to cause anaerobic state An aluminum foil cover with a vinyl fluoride gasket seals it. Add 10 mL of electron donor per liter of culture medium every month. Complete the intensified process for PCB-contaminated soil / sediment bioremediation.
[0030] The amount of PCB61 added is: 100mg per kilogram of mud-water mixed culture solution.
[0031] In the present embodiment, each liter of the nutrient solution contains: NaHCO 3 , 1.68g; NH 4 Cl, 2.7g; MgCl 2 ·6H 2 O, 0.1g; CaCl 2· 2H 2 O, 0.1g; FeCl 2 4H 2 O, 0.02g; K 2 HPO 4 , 0.27g; KH 2 PO 4 , ...
Embodiment 2
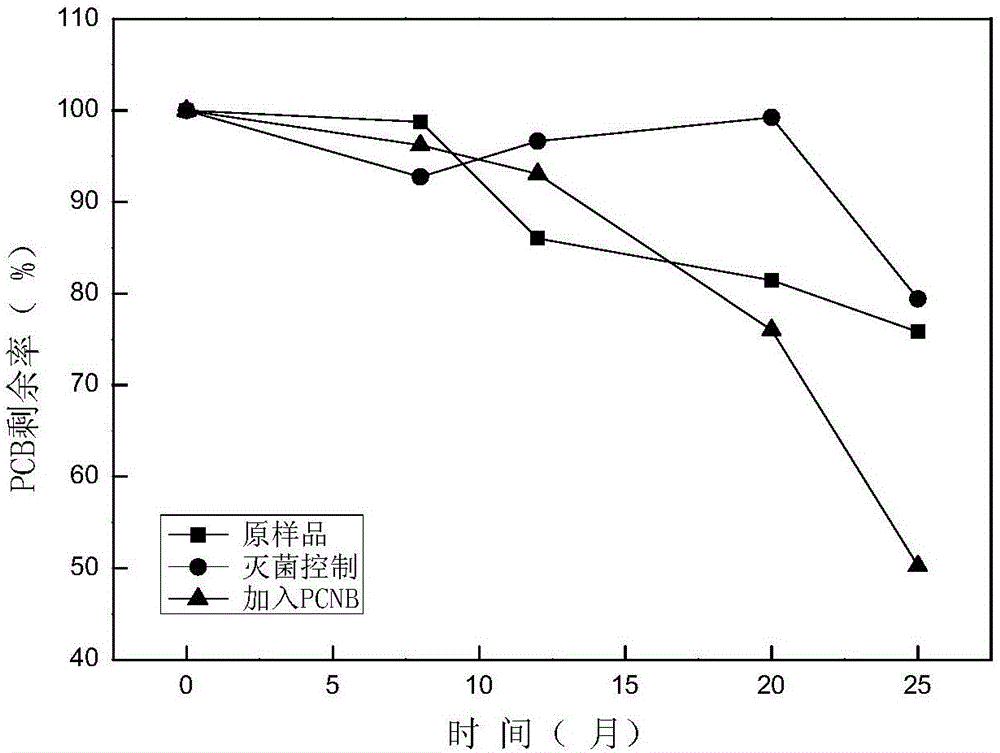
[0040] The method for strengthening the degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls in the soil under the participation of pentachloronitrobenzene of the present embodiment, except that 100 mg of pentachloronitrobenzene is added per kilogram of mud-water mixed culture solution, other features are the same as in Example 1.
[0041] Take regular samples, extract the PCBs in the mud-water mixture, and calculate the degradation rate. The results are as follows: figure 2 shown. Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that within one year of the beginning of the reaction, the changes of several samples were not significant, and after one year, especially after 18 months, the content of PCBs in the samples added with pentachloronitrobenzene began to be more obvious than that in the blank control samples decreased, indicating that the degradation of the PCB was promoted.
Embodiment 3
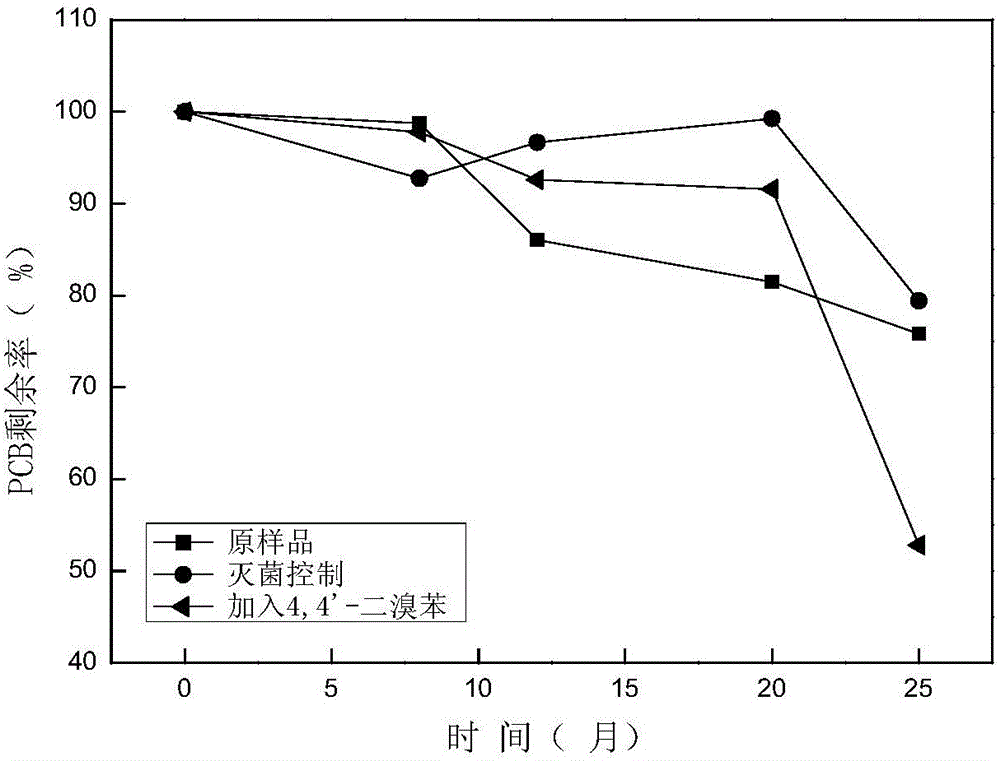
[0043] In the method for strengthening the degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls in soil with the participation of 4,4'-dibromobenzene in this example, except that 100 mg of 4,4'-dibromobenzene is added per kilogram of mud-water mixed culture solution, other characteristics are the same as those in Example 1 same.
[0044] Take regular samples, extract the PCBs in the mud-water mixture, and calculate the degradation rate. The results are as follows: image 3 shown. Depend on image 3 It can be seen that within 20 months of the beginning of the reaction, the changes of several samples were not significant, and the content of PCBs in the sample added with 4,4'-dibromobenzene began to decrease significantly after 2 years compared with the blank control sample, indicating that Promote the degradation of PCB.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com