Devices for reducing radionuclide emissions during extreme accidents in nuclear power plants
A technology for radionuclides and nuclear power plants, applied in the field of nuclear power, can solve problems such as non-precipitation, and achieve the effect of reducing concentration, solution toxicity and corrosiveness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
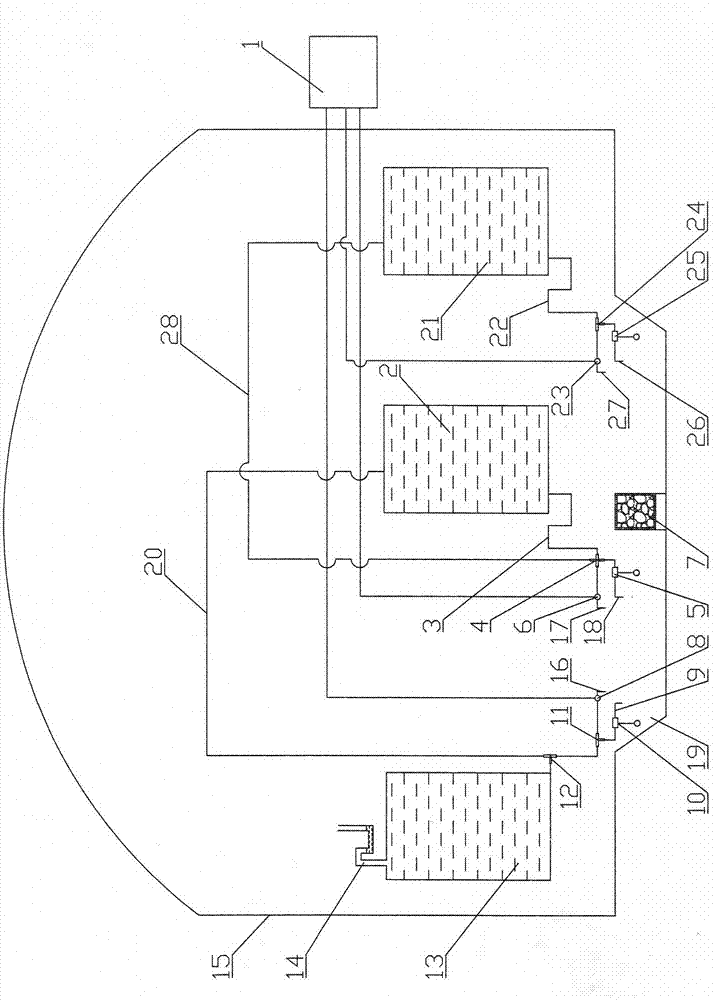
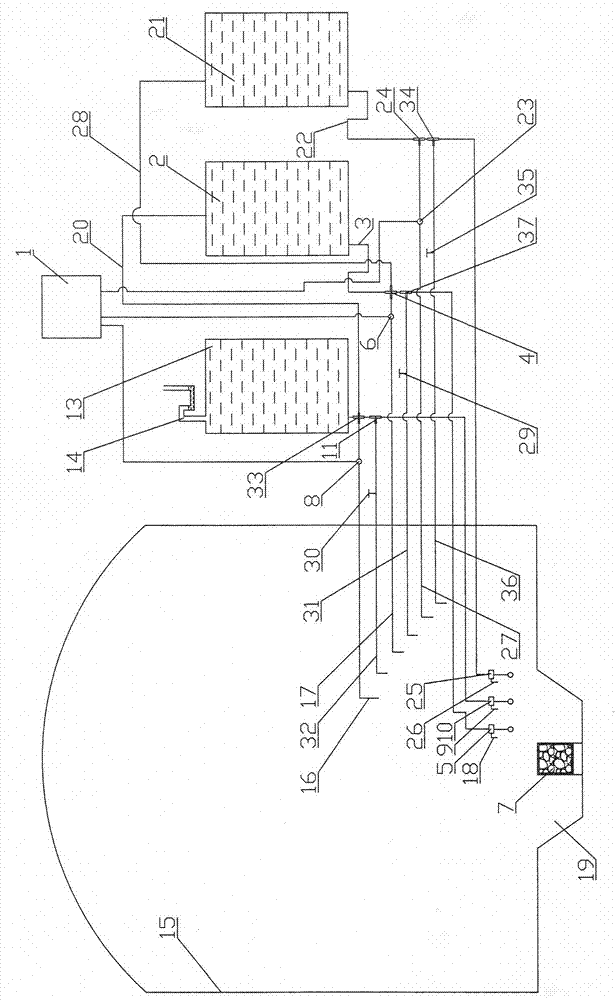
[0041] Embodiment 1. The device for reducing the emission of radionuclides during extreme accidents in nuclear power plants includes an adsorption box 7 that is preset in the pit 19 of the containment 15 and is equipped with high-temperature-resistant inorganic adsorption materials, and is preset in the containment 15 and is equipped with different formulas. The first water tank 13 of the solution, the second water tank 2, the first solenoid valve 8, the second solenoid valve 6, the first float valve 10, the second float valve 5 and the remote controller 1 installed outside the containment 15 of the nuclear power plant.
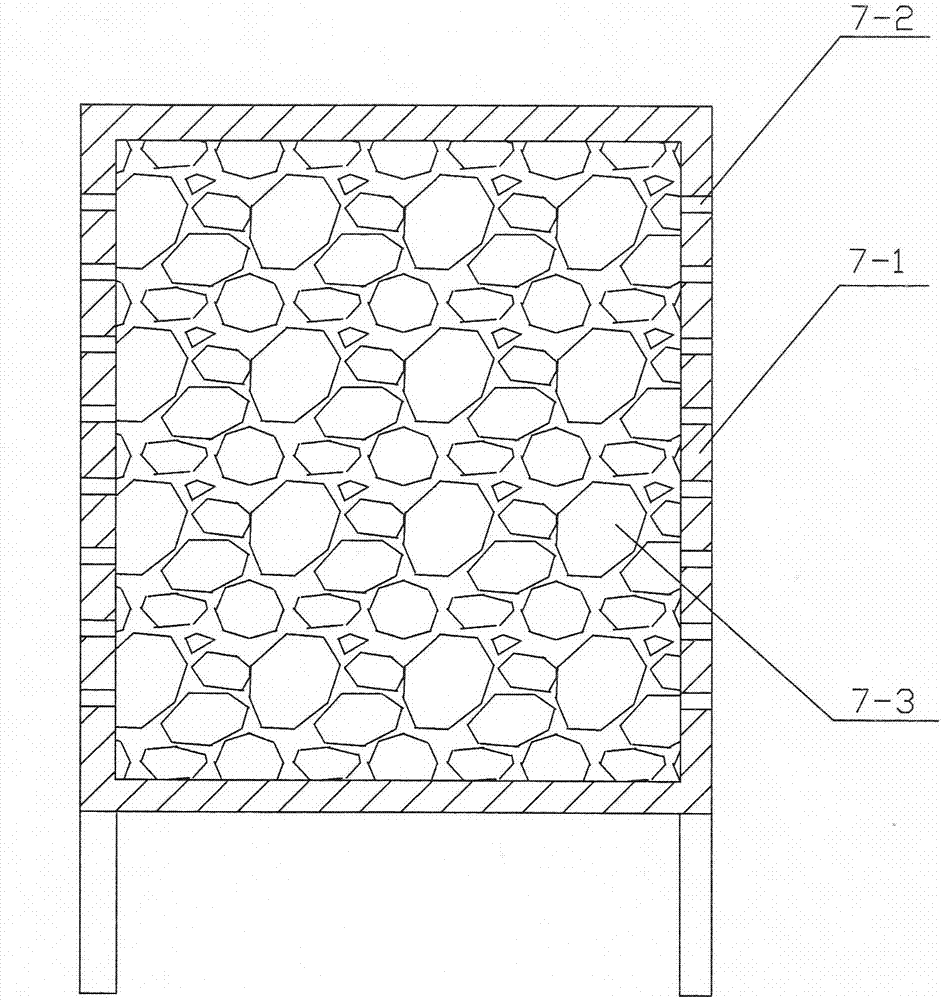
[0042] The adsorption box 7 is composed of a box body 7-1 and a high-temperature resistant inorganic adsorption material contained in the box body 7-1. The box body 7-1 is a square container, and plural walls are arranged on the four walls of the box body 7-1. A through hole 7-2.
[0043] The high temperature resistant inorganic adsorption material is zeolite...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Embodiment 2. The device for reducing radionuclide discharge during extreme accidents in nuclear power plants, referring to Embodiment 1, differs from Embodiment 1 in that:
[0065] The components of the solution in the first water tank 13 are strontium ions, iodide ions, tellurite and boric acid. %-2%, boric acid 1%-4%, and the rest is water.
[0066] When the solution components in the first water tank 13 are strontium ions, iodide ions, tellurite and boric acid, add alkaline solution sodium hydroxide or lithium hydroxide in the first water tank 13 to adjust the pH value of the solution to neutral .
[0067] The solution components in the second water tank 2 are silver ions and boric acid, and the components are expressed in mass %, specifically: 0.1%-4% of silver ions, 1%-4% of boric acid, and the rest is water.
[0068] When the solution components in the second water tank 2 are silver ions and boric acid, an alkaline solution sodium hydroxide or lithium hydroxide...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Embodiment 3: The device for reducing the discharge of radionuclides during extreme accidents in nuclear power plants, including the adsorption box 7 preset in the pit 19 of the containment vessel 15 and equipped with high-temperature-resistant inorganic adsorption materials, and the first float valve preset in the containment vessel 15 10. The second float valve 5 and the first water tank 13, the second water tank 2, the remote controller 1, the first solenoid valve 8, and the second solenoid valve 6 that are preset outside the containment vessel 15 and contain solutions of different formulas.
[0073] The adsorption box 7 is composed of a box body 7-1 and a high-temperature resistant inorganic adsorption material contained in the box body 7-1. The box body 7-1 is a square container, and plural walls are arranged on the four walls of the box body 7-1. A through hole 7-2.
[0074] The high temperature resistant inorganic adsorption material is zeolite, or sodium titanos...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com