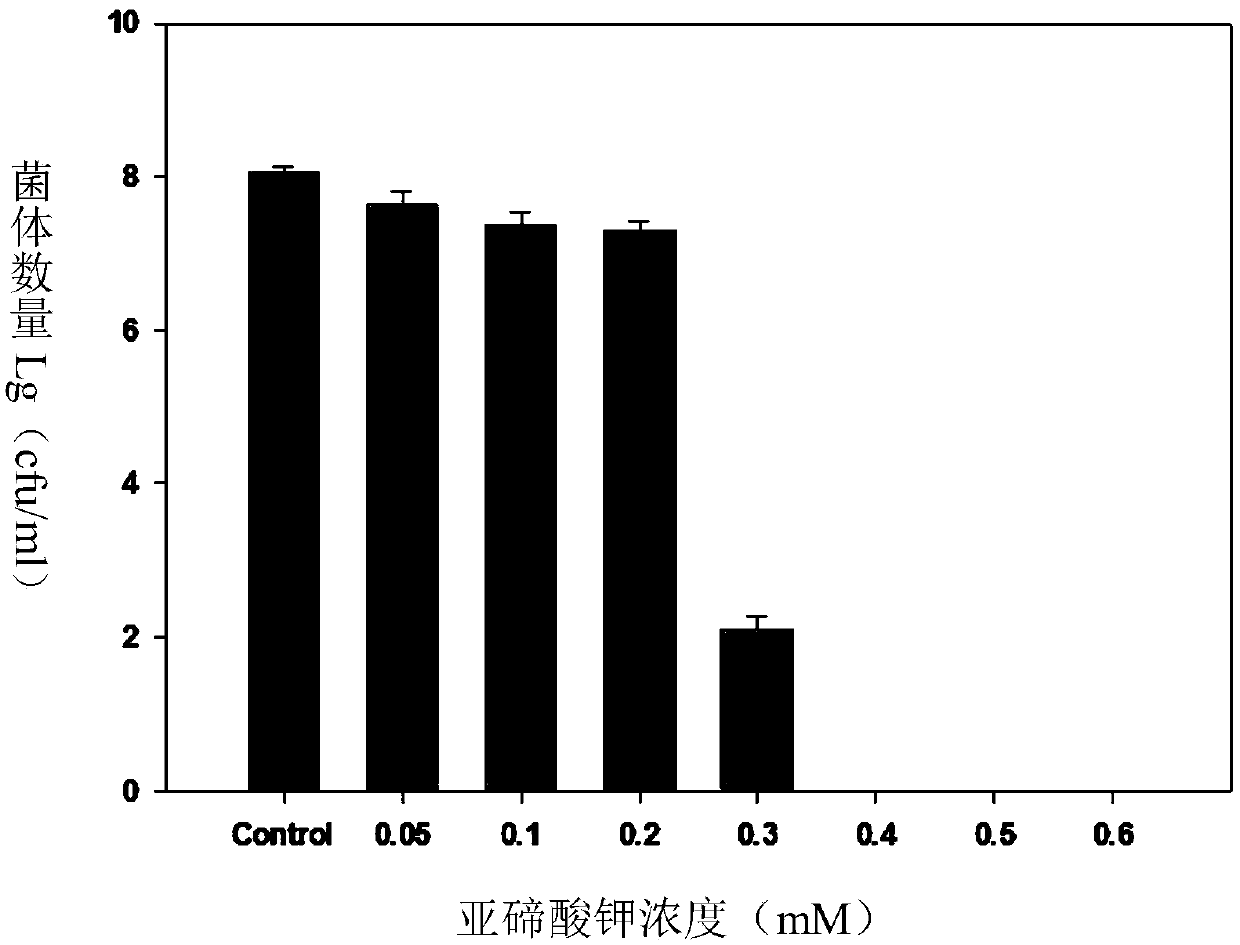
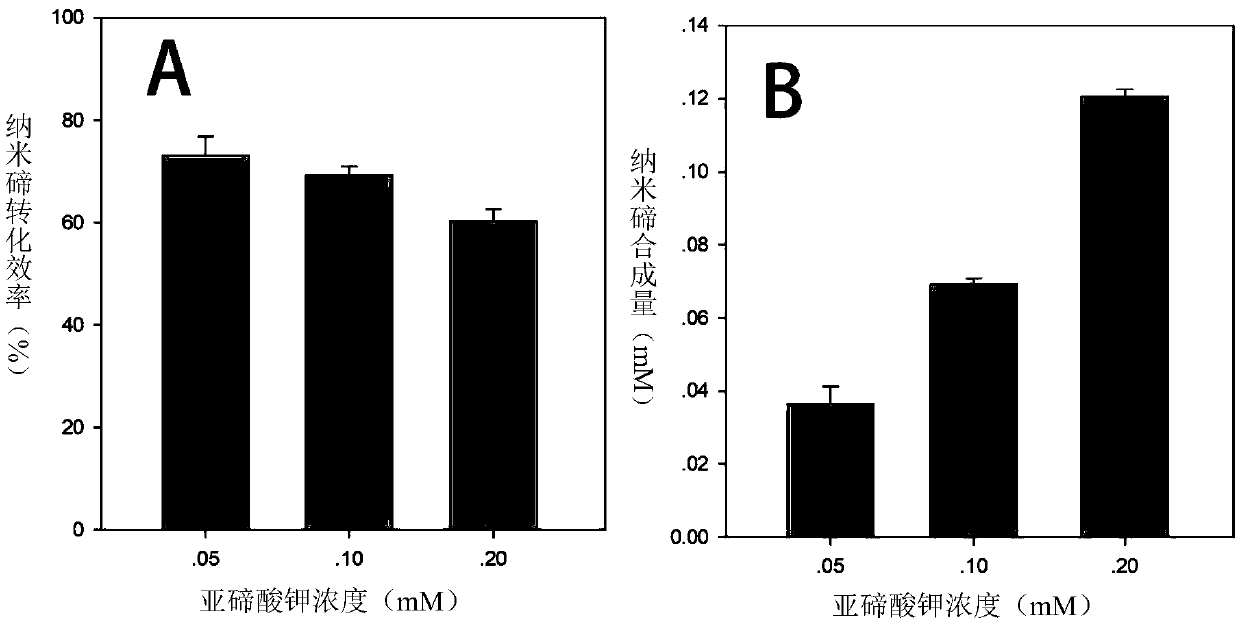
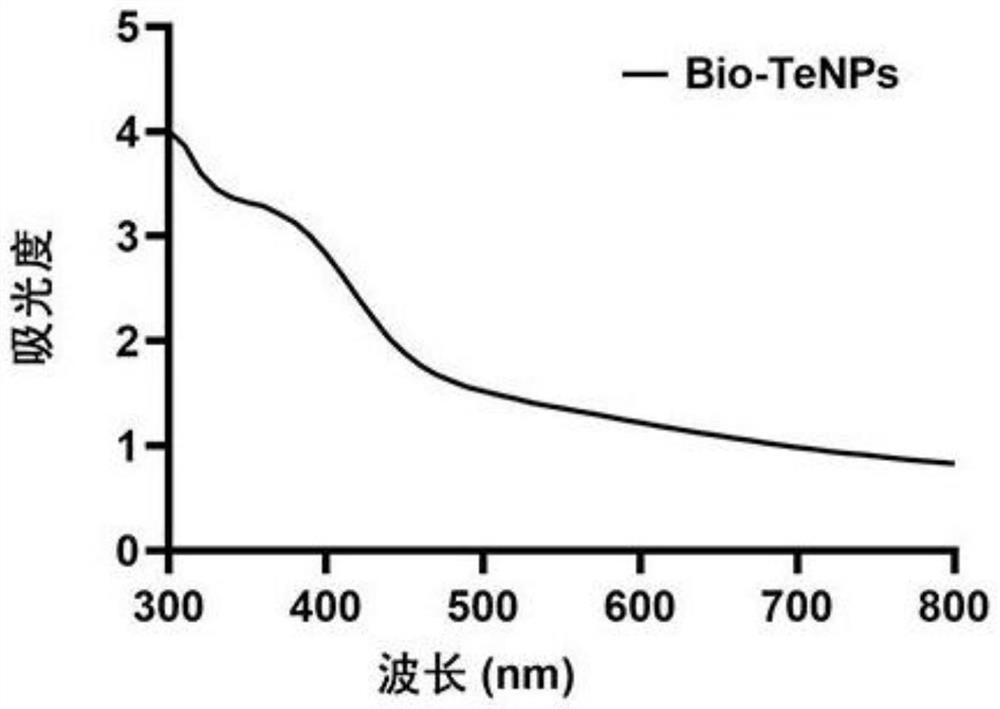
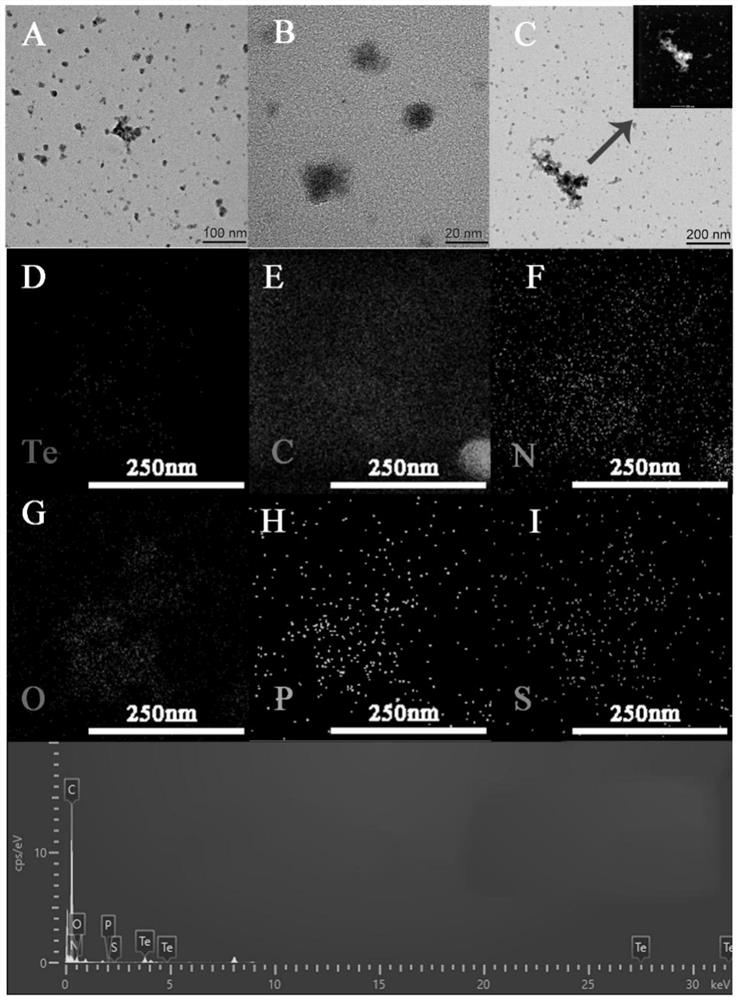
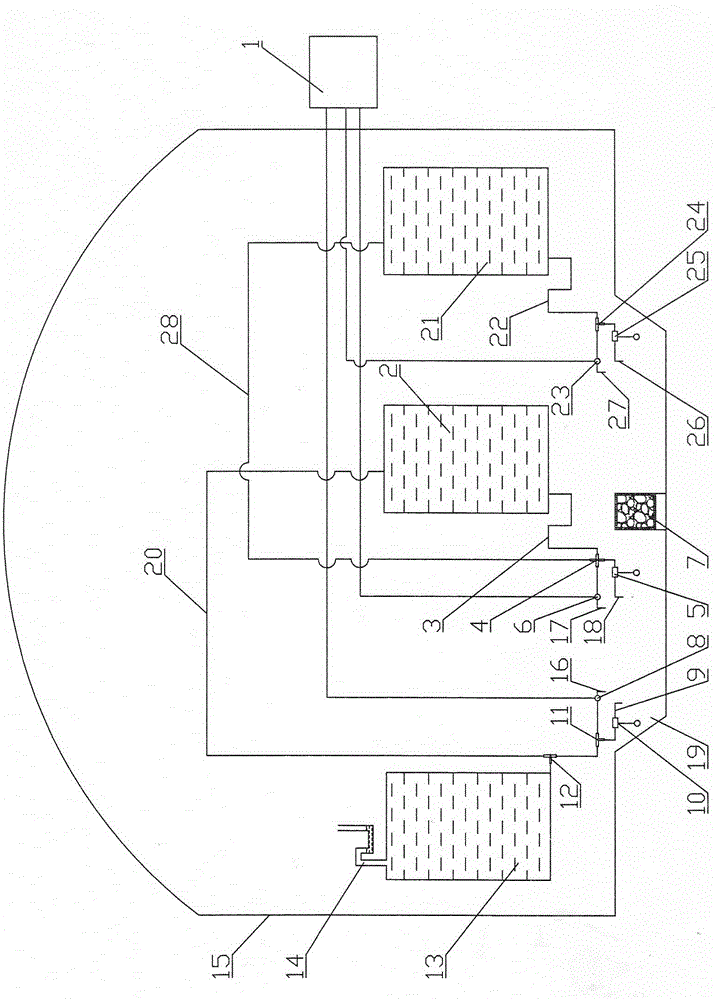
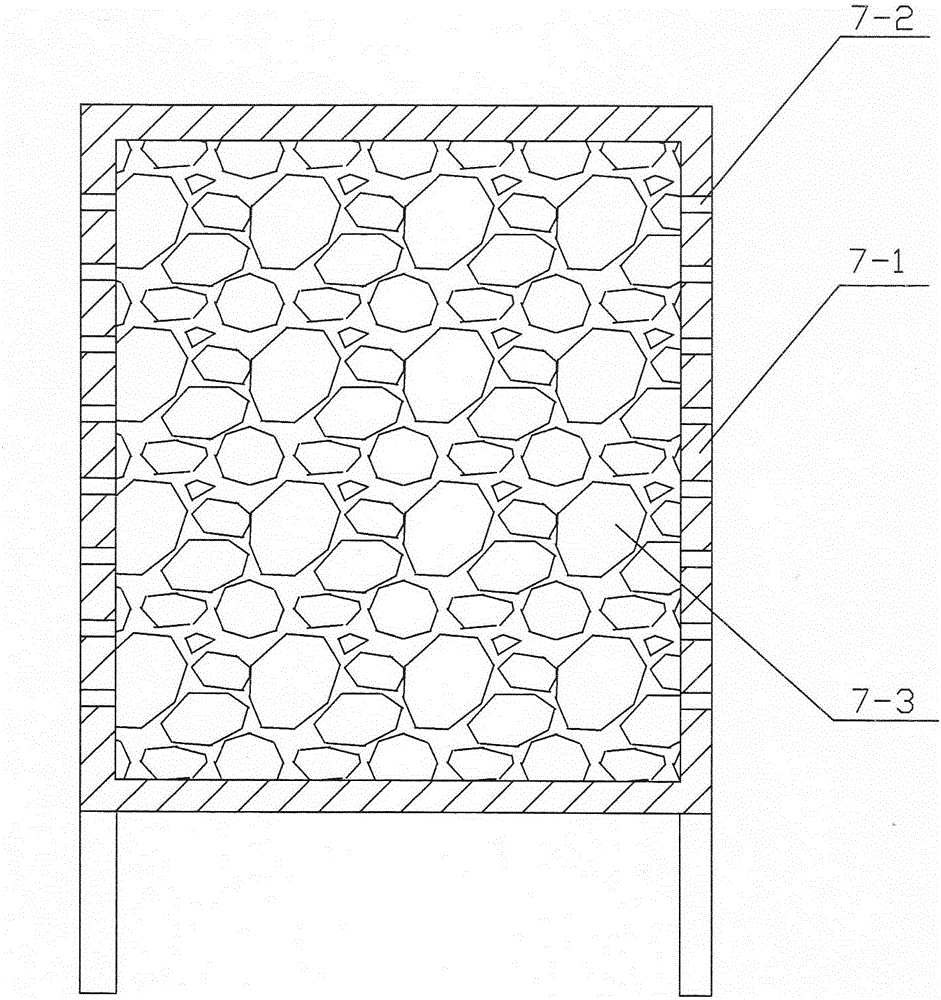
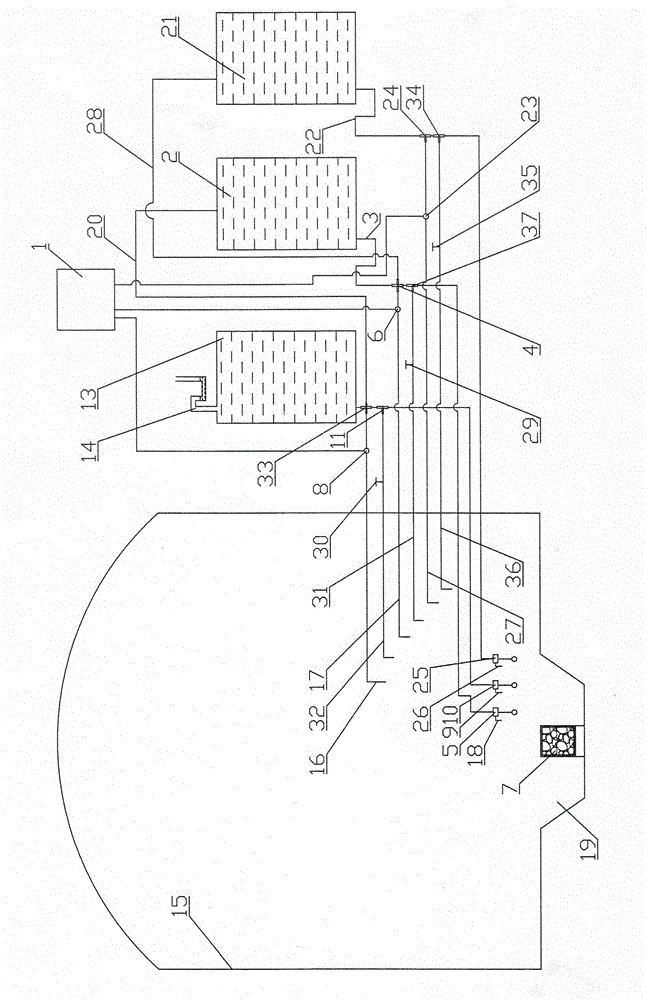
Patents
Literature
37 results about "Tellurous acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tellurous acid is an inorganic compound with the formula H₂TeO₃. It is the oxoacid of tellurium(IV). The compound is not well characterized. An alternative way of writing its formula is (HO)₂TeO. In principle, tellurous acid would form by treatment of tellurium dioxide with water, that is by hydrolysis. The related conjugate base is well known in the form of several salts such as potassium hydrogen tellurite, KHTeO₃.
Culture medium capable of simultaneously enriching five kinds of food-borne pathogenic bacteria and preparation method for culture medium
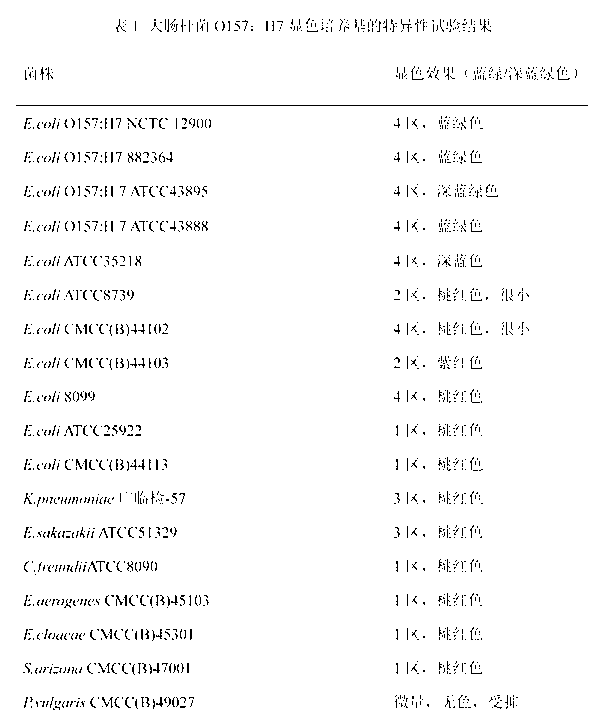
ActiveCN102660474AImprove detection efficiencyLow costBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliFood borne
The invention relates to a culture medium for simultaneous composite enrichment of five kinds of food-borne pathogenic bacteria, namely Salmonella, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes and Shigella, and a preparation method for the culture medium. Food-borne pathogenic bacteria are a significant reason to cause food positioning, so the rapid and accurate detection of the food-borne pathogenic bacteria has an important practical significance for preventing and controlling food safety incidents. The culture medium is characterized by comprising the following components: 10.0 g of peptone, 10.0 g of sodium chloride, 9.0 g of disodium hydrogen phosphate, 1.5 g of monopotassium phosphate, 0.1 g of cholate, 0.1 mg of potassium tellurite, 1.0 g of lithium chloride, 3.0 g of glucose, 2.0 g of mannitol, 2.5 g of sodium pyruvate, 1.0 g of aesculin and 1,000 mL of distilled water, wherein the pH value is 7.1 to 7.5. The culture medium can simultaneously enrich five kinds of target pathogenic bacteria, can be used for separation and identification of target bacteria, can also be used for the molecular detection of multiple pathogenic bacteria on the same detection platform, provides technical support for a method for rapidly detecting five kinds of pathogenic bacteria in food, and meets the requirement of simultaneous detection of five kinds of food-borne pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES +1
Culture medium for composite enrichment of salmonella, Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio cholerae, and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101412977AShorten enrichment timeBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesSulfite salt
The invention relates to a complex enrichment medium used for salmonella, vibrio parahaemolyticus and comma bacillus and a method for preparing the same. The formulation components of the complex enrichment medium in weight portion are as follows: 0.5 to 1.5 portions of buffer peptone water, 1000 portions of distilled water, 1.0 to 5.0 portions of glucose, 1.0 to 5.0 portions of mannitol, 0.03 to 0.06 portion sodium pyruvate, 0.5 to 2.5 portions of anhydrous sodium sulfite, 1.0 to 10.0 portions of sodium citrate, 5.0 to 25.0 portions of sodium chloride, 1 to 5 portions of cholate, and 0.0005 to 0.0025 portion of potassium tellurite. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, adding the buffer peptone water and the like into the distilled water, and sterilizing the mixture after heating and melting; and secondly, cooling the mixture to 50 DEG C, and then adding the potassium tellurite into the mixture to be mixed evenly. The complex enrichment medium can integrate two steps of primary enrichment and selective enrichment of bacterial detection to shorten the enrichment time to 24 hours, can perform enrichment on three target pathogens at the same time, and can inhibit the growth of other microorganisms.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
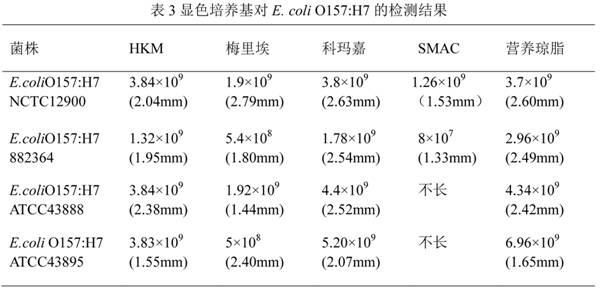
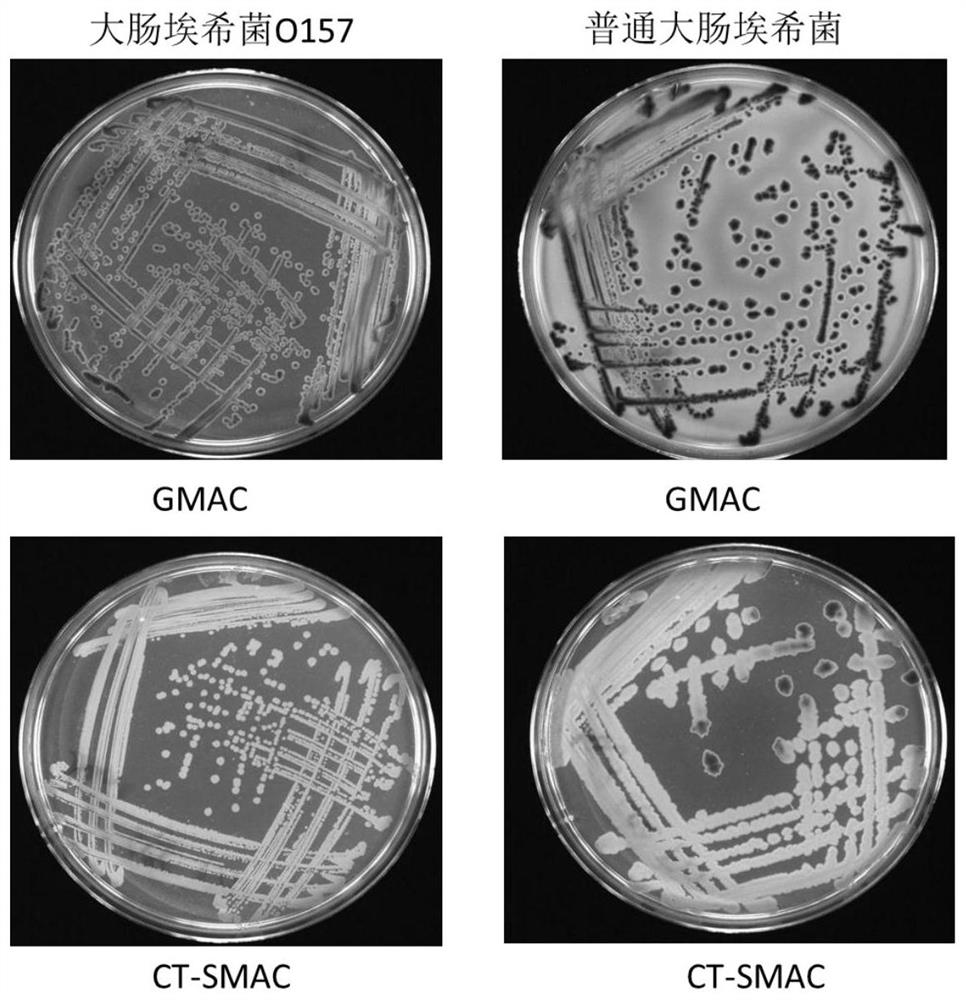
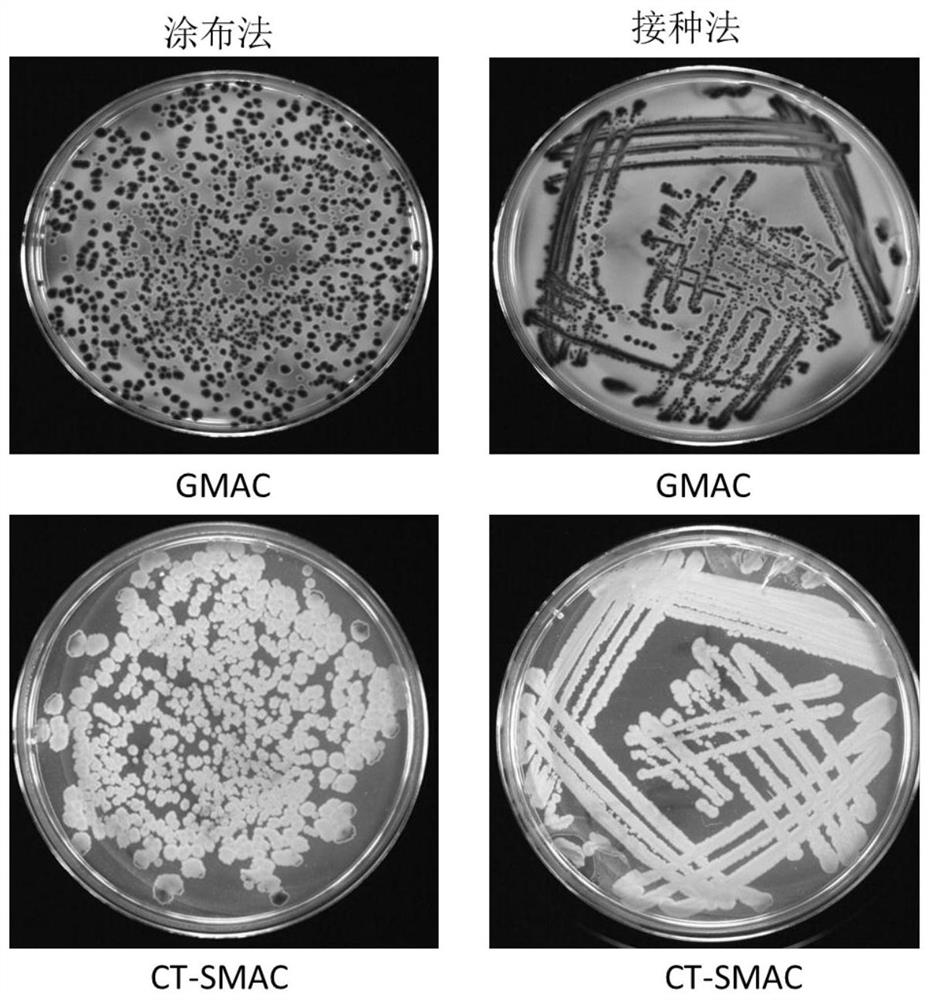
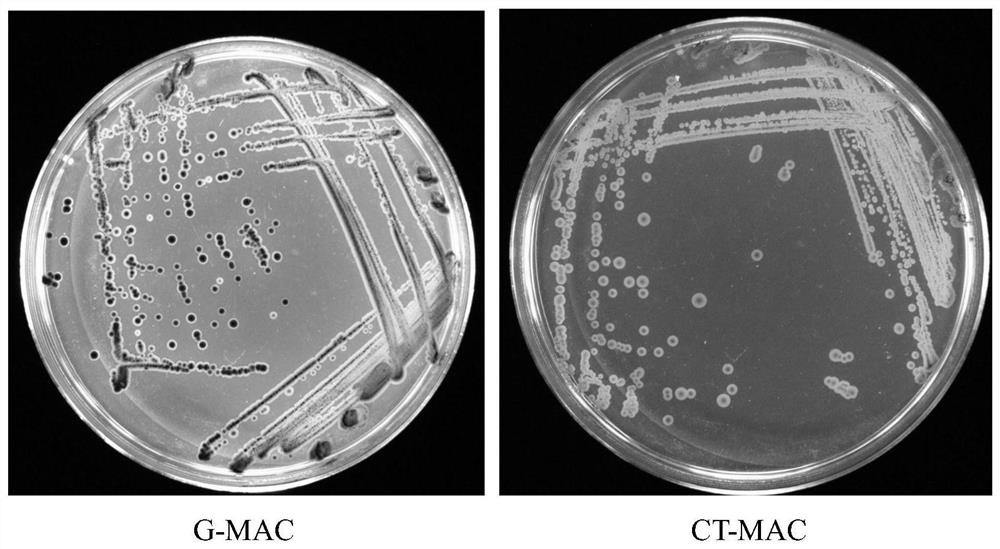
Chromogenic medium used for detecting esherichia coli O157:H7
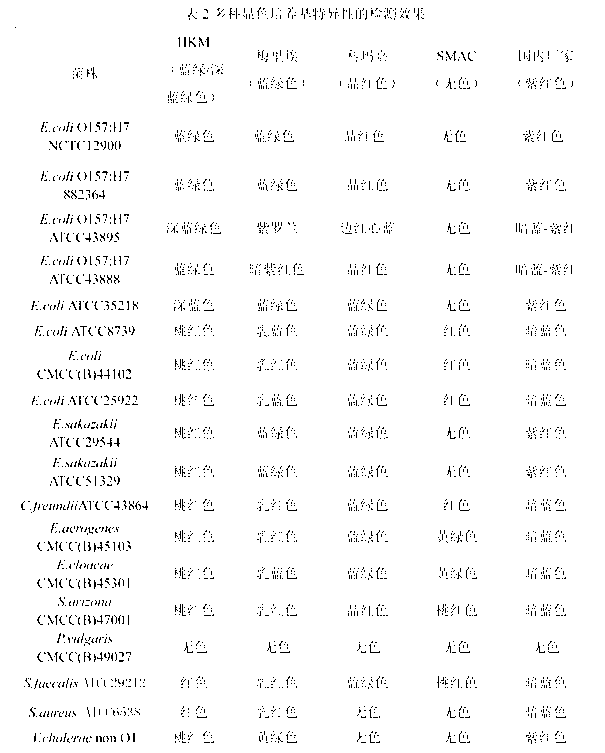
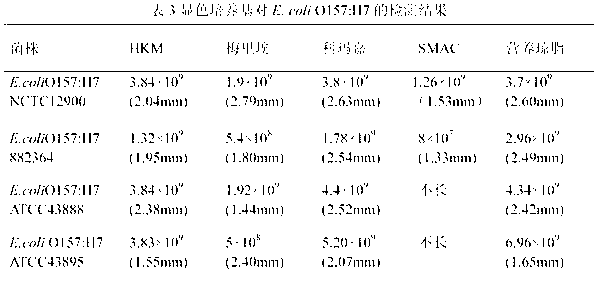
ActiveCN102424832AHigh detection sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyThio-
The invention discloses a chromogenic medium used for detecting esherichia coli O157:H7. The medium comprises agar, peptone, beef extract powder, sodium chloride, sorbitol, inositol, neutral red, beta-galactosidase chromogenic substrate, beta-glucuronidase chromogenic substrate, isopropyl-beta-D- thiogalactopyranoside, natrium taurocholicum, potassium tellurite and cefixime. The chromogenic medium used for detecting esherichia coli O157:H7 of the present invention has the advantages of high sensitivity, good specificity, direct bacterial strain discrimination according to colony color, short detection period and strong operationality, is suitable for treating high-reflux samples, is capable of comprehensively, systematically and accurately detecting and preliminarily identifying the esherichia coli O157:H7 in food production and environment, and provides a novel approach for rapidly detecting the microbes.
Owner:GUANGDONG HUANKAI MICROBIAL SCI & TECH
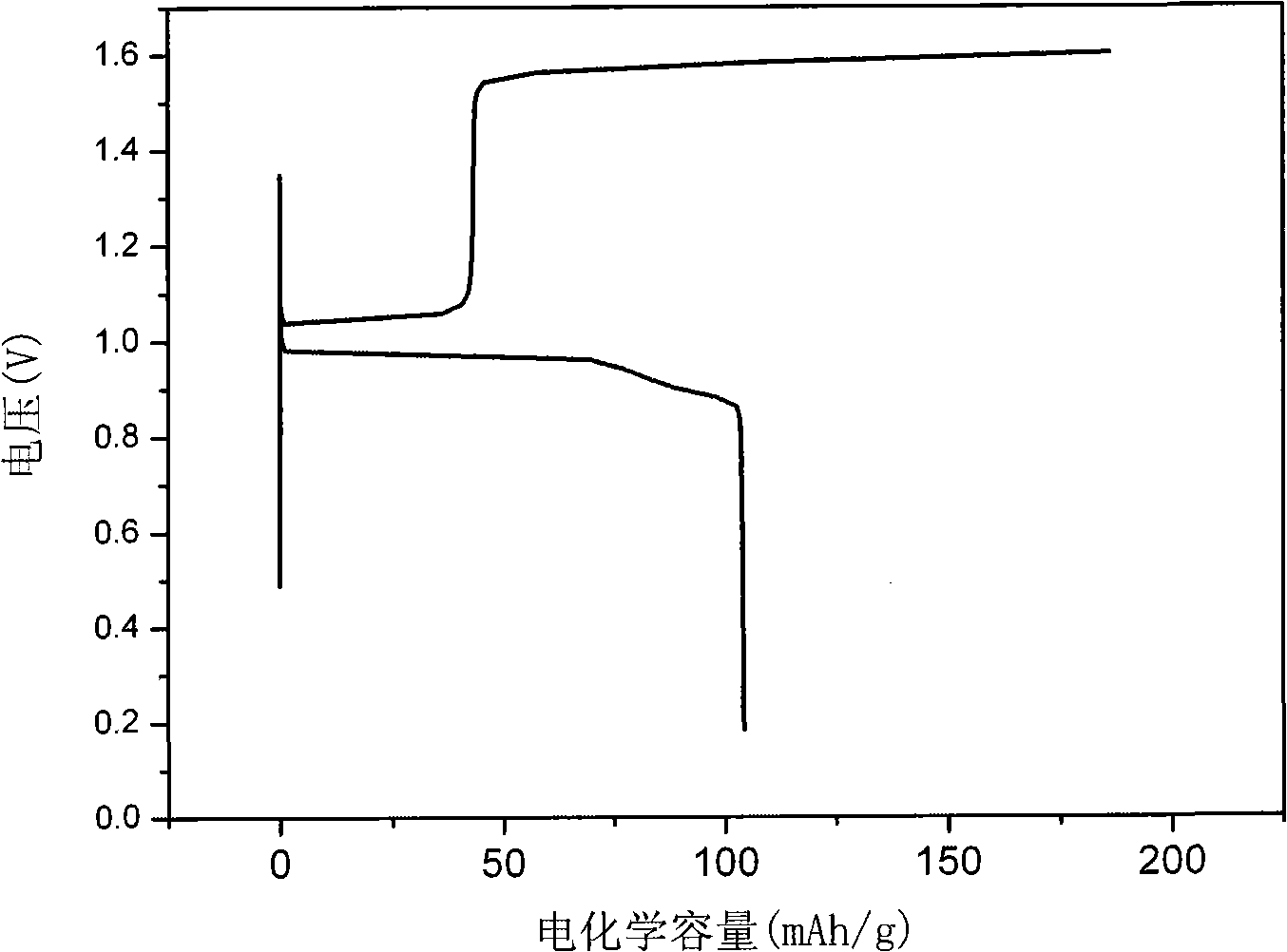
Bismuth base hydrogen storage material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101513994AUniform sizeSingle formCell electrodesBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsTe elementSolvent
The invention relates to a bismuth base (bismuth selenide, bismuth telluride) hydrogen storage material and a preparation method thereof, relating to low temperature liquid phase synthesis of bismuth base material and the application thereof on hydrogen storage, lithium storage and electrode material. The invention is characterized in that water is taken as solvent, bismuth salts such as bismuth nitrate, bismuth chloride and the like as a bismuth source, and water-soluble tellurium (selenium) acid salts (such as sodium tellurite, selenium substituted sodium sulfate, sodium selenite) or tellurium (selenium) acids (such as orthotelluric acid, tellurous acid and selenous acid) as a tellurium source (selenium) source; proper coordination agents (such as nitrilotriacetic acid, hexamethylene diamine tetraacethyl and the like) and reducing agents (such as vitamin C, sodium borohydride and the like) are added for liquid phase reaction synthesis at the low temperature of 60-80 DEG C. The bismuth selenide crystal grains prepared by the invention take on flower shapes with the sphere diameter of 1-6mum, and the bismuth telluride crystal grains take on sheet shapes with nanometer diameter; the hydrogen storage performance reaches over 100mAh.g. The method has the advantages of cheap raw material, simple technique, convenient operation, easy mass production, etc.
Owner:中国科学院上海硅酸盐研究所苏州研究院
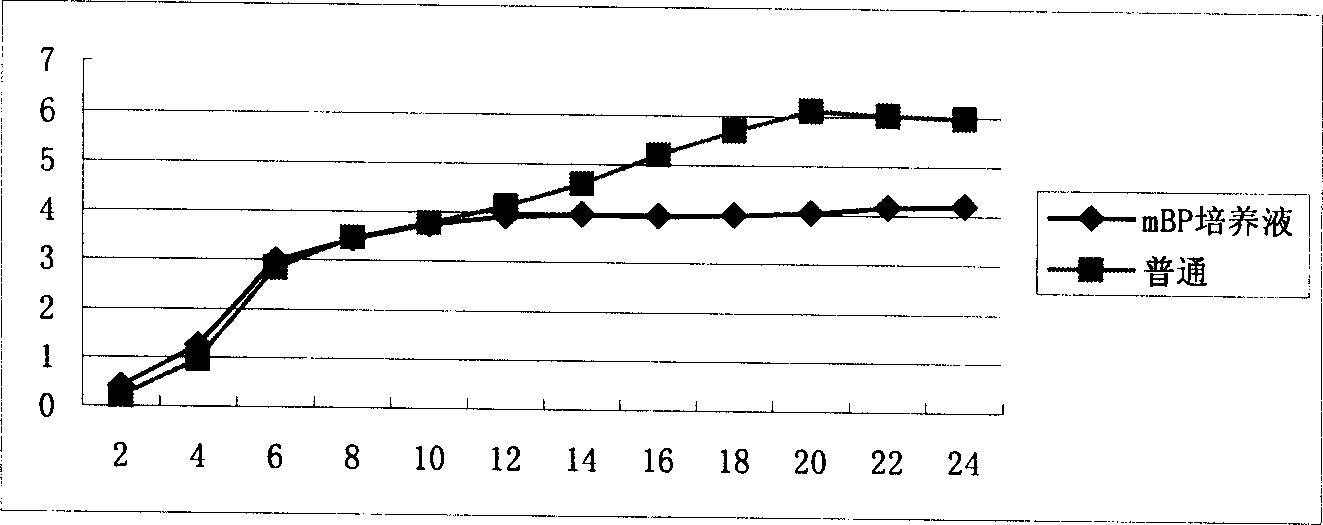
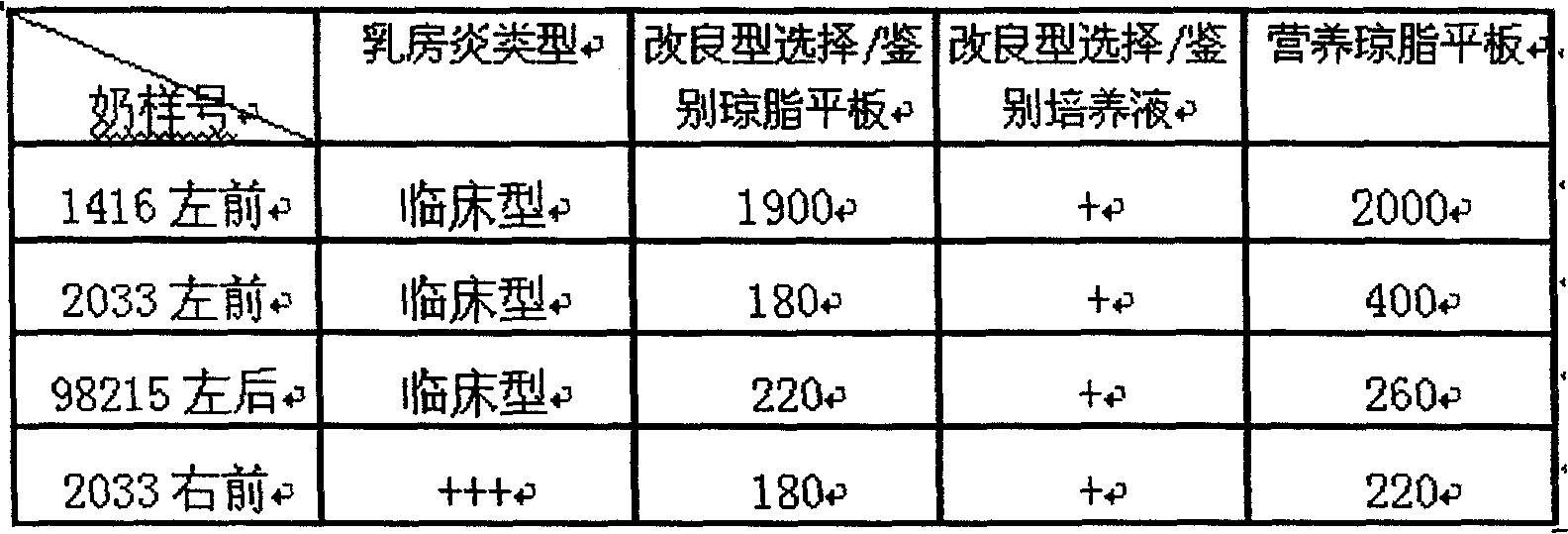
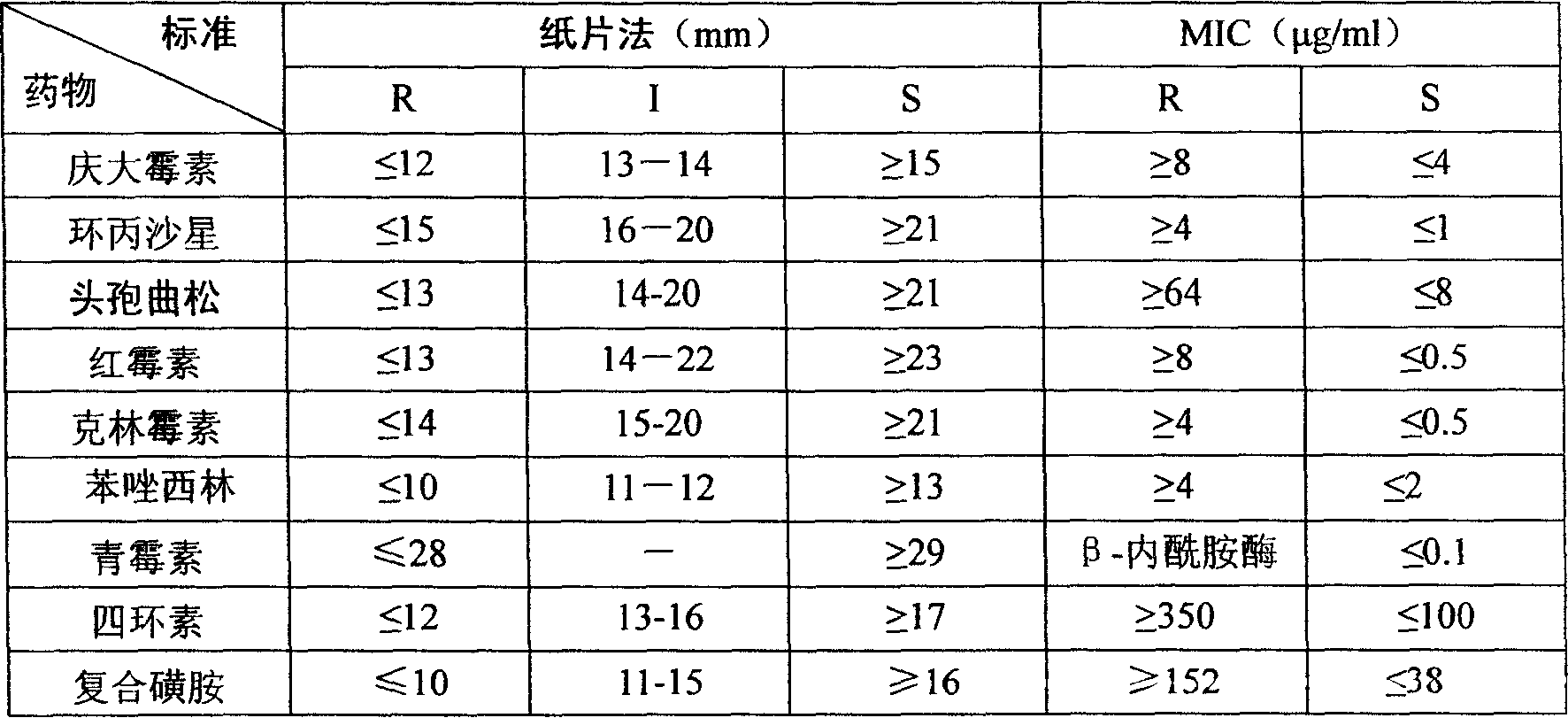
Preparing method for cow mammitis staphylococcus culture fluid and its use
InactiveCN1858234AQuick selection/identificationRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibiotic sensitivityYeast
The preparation process of cow mammitis staphylococcus culture fluid and its use belongs to the field of animal epidemic disease diagnosing, preventing and treating technology. The preparation process includes dissolving peptone 10 g, yeast powder 5 g, sodium pyruvate 10 g, glycin 12 g and lithium chloride 5 g in water of 980 ml; regulating pH to 7.3 with sodium hydroxide; sterilizing at 121 deg.c; cooling to 50+ / -10 deg.c; adding bacteria-free 1% concentration potassium tellurite water solution in 10 ml and Tween-80 in 7 ml, and preservation at 4 deg. c. The culture fluid may be used in the fast identification of cow mammitis staphylococcus and antibiotic sensitivity test.
Owner:兆丰华生物科技(南京)有限公司
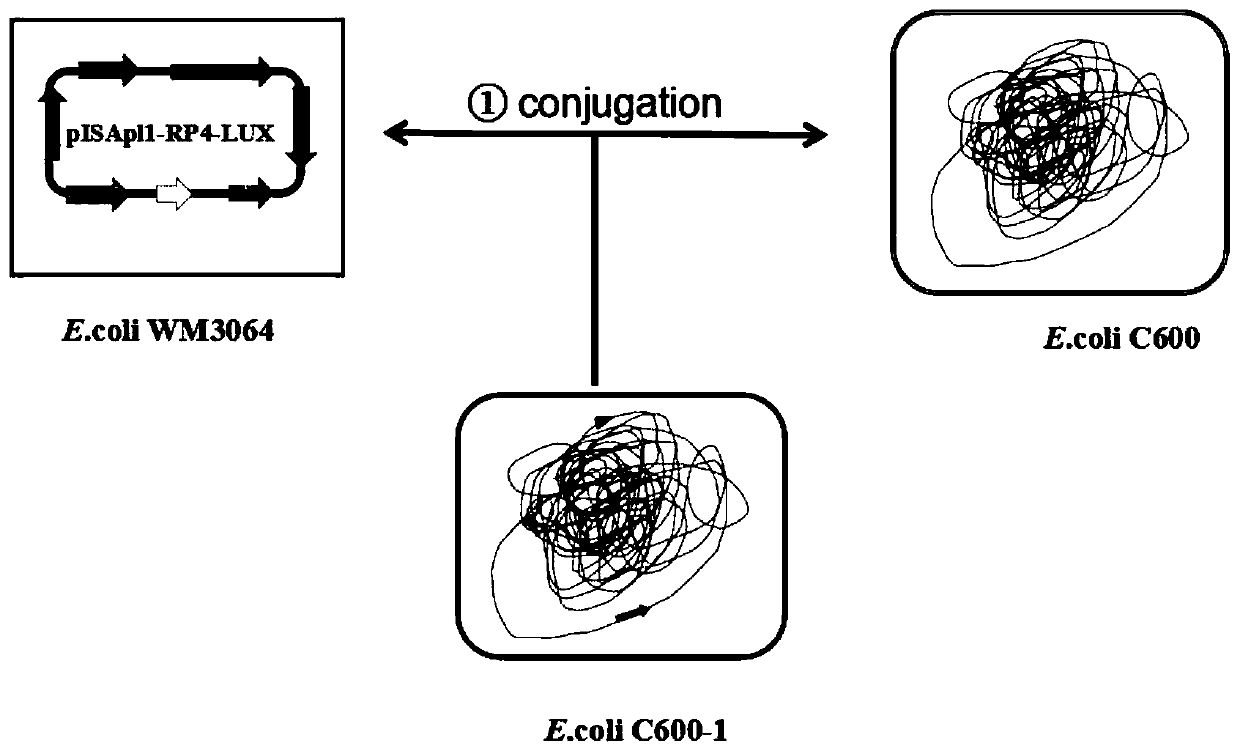
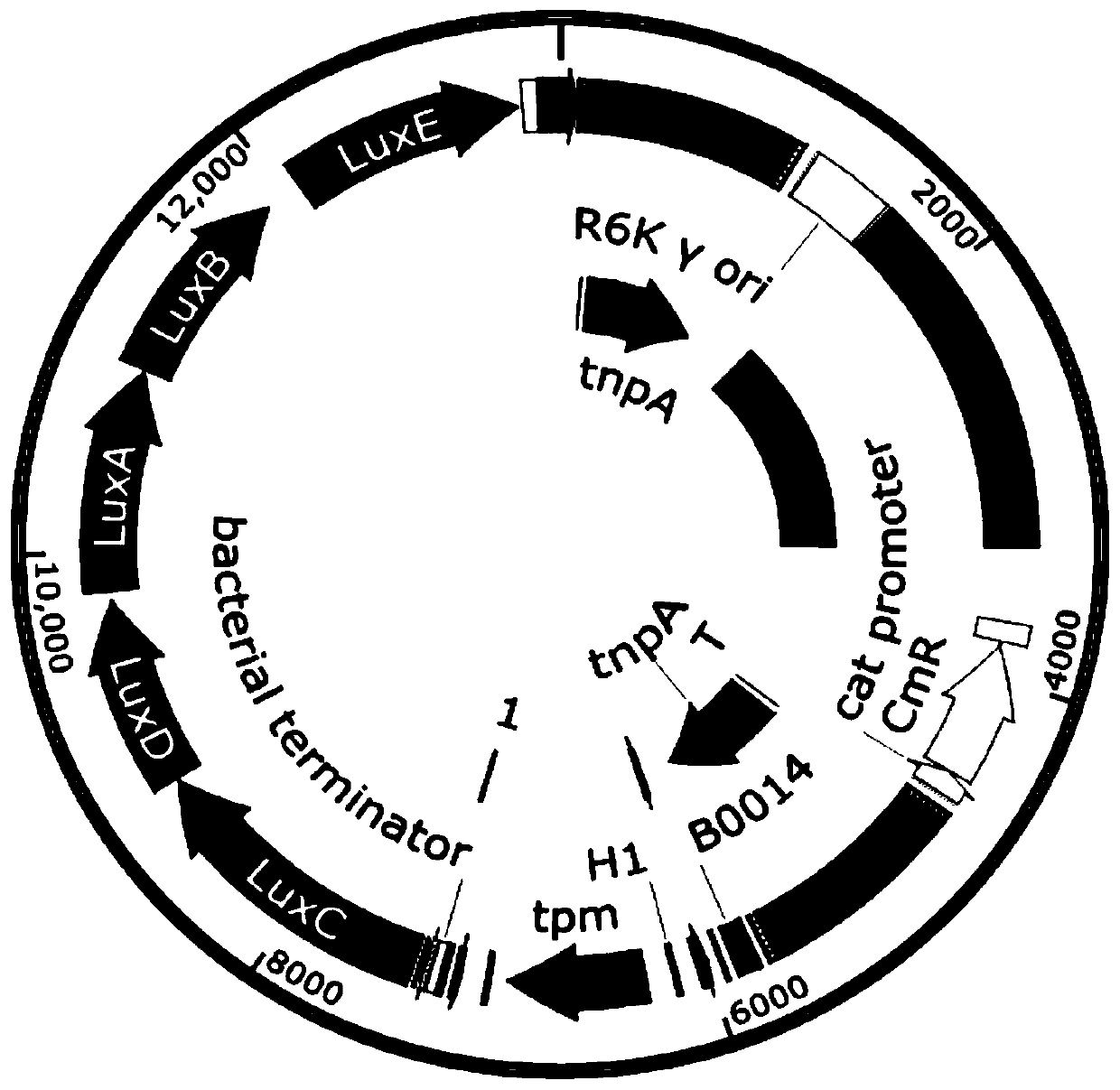
Fluorescent strain E. coli C600 and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN110066820AImprove stabilityGenetic stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesTransfer geneMixed culture
The invention provides a fluorescent strain E. coli C600 and a construction method and application thereof. By constructing a recombinant plasmid containing an R6k replicon, a transposition unit and an RP4 conjugative transfer gene, the recombinant plasmid is transferred to a host bacterium in which the recombinant plasmid can replicate to obtain a recombinant strain, the recombinant strain and E.coli C600 are subjected to mixed culture, and then the fluorescent strain E. coli C600 can be obtained through screening, wherein the transposition unit is formed by using two ISApl1 for sandwichinga Lux gene cluster and a tellurite drug-resistance gene in the middle. The exogenous gene acquiring capability of the fluorescent strain E. coli C600 is not influenced, the stability is high, stable inheritance can be ensured, the fluorescent property cannot lose along with bacterium passage, and thus the fluorescent strain E. coli C600 can serve as a recipient bacterium for conjugation experiments. By adopting the fluorescent strain E. coli C600, recipient bacteria and zygotes can be identified more efficiently and more intuitively in the fields related to plasmid conjugational transfer, andtherefore the fluorescent strain E. coli C600 has good application prospects.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Plants with Increased Yield
A method for producing a plant with increased yield as compared to a corresponding wild type plant whereby the method comprises at least the following step: increasing or generating in a plant or a part thereof one or more activities of a polypeptide selected from the group consisting of 26S proteasome-subunit, 50S ribosomal protein L36, Autophagy-related protein, B0050-protein, Branched-chain amino acid permease, Calmodulin, carbon storage regulator, FK506-binding protein, gamma-glutamyl-gamma-aminobutyrate hydrolase, GM02LC38418-protein, Heat stress transcription factor, Mannan polymerase II complex subunit, mitochondrial precursor of Lon protease homolog, MutS protein homolog, phosphate transporter subunit, Protein EFR3, pyruvate kinase, tellurite resistance protein, Xanthine permease, and YAR047C-protein.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
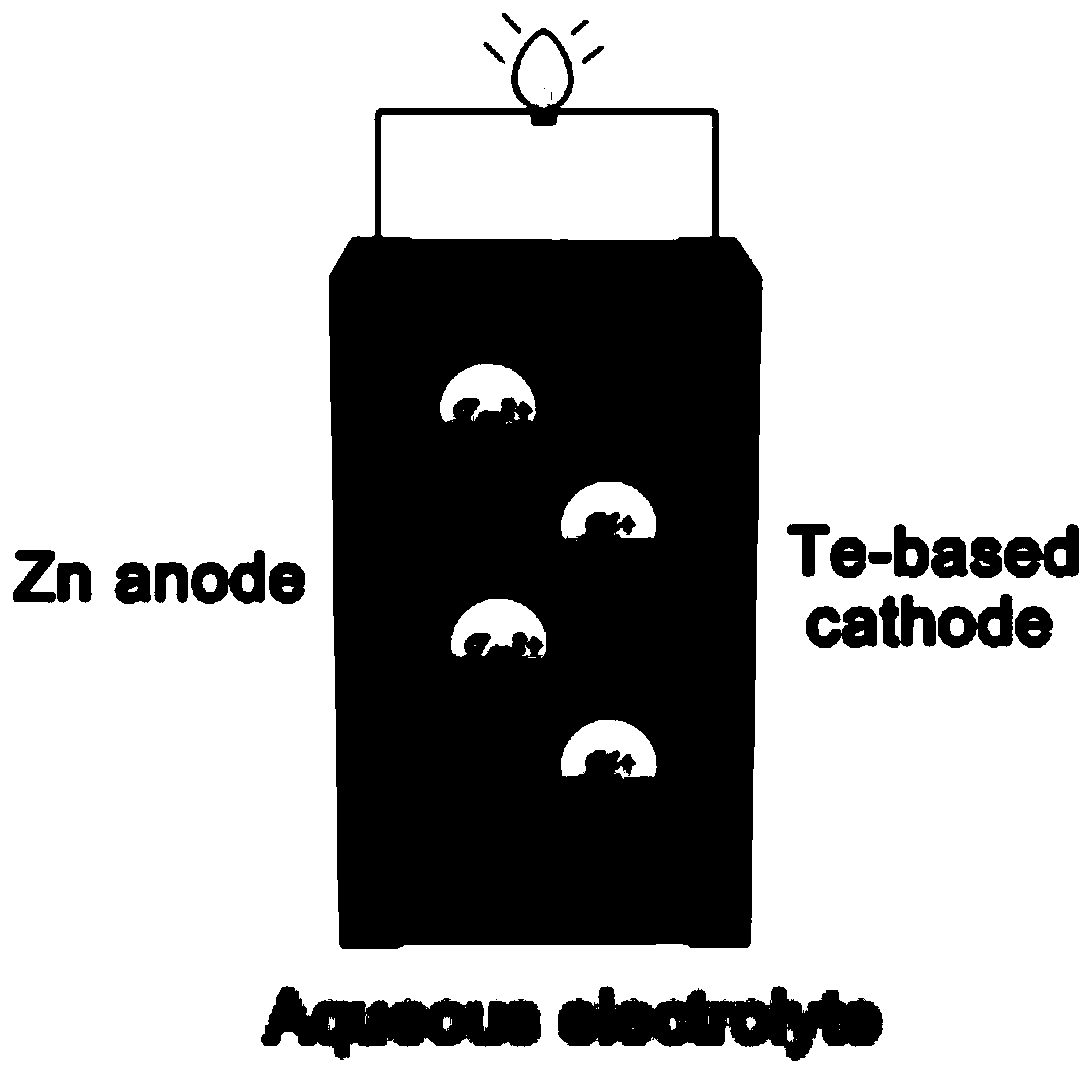
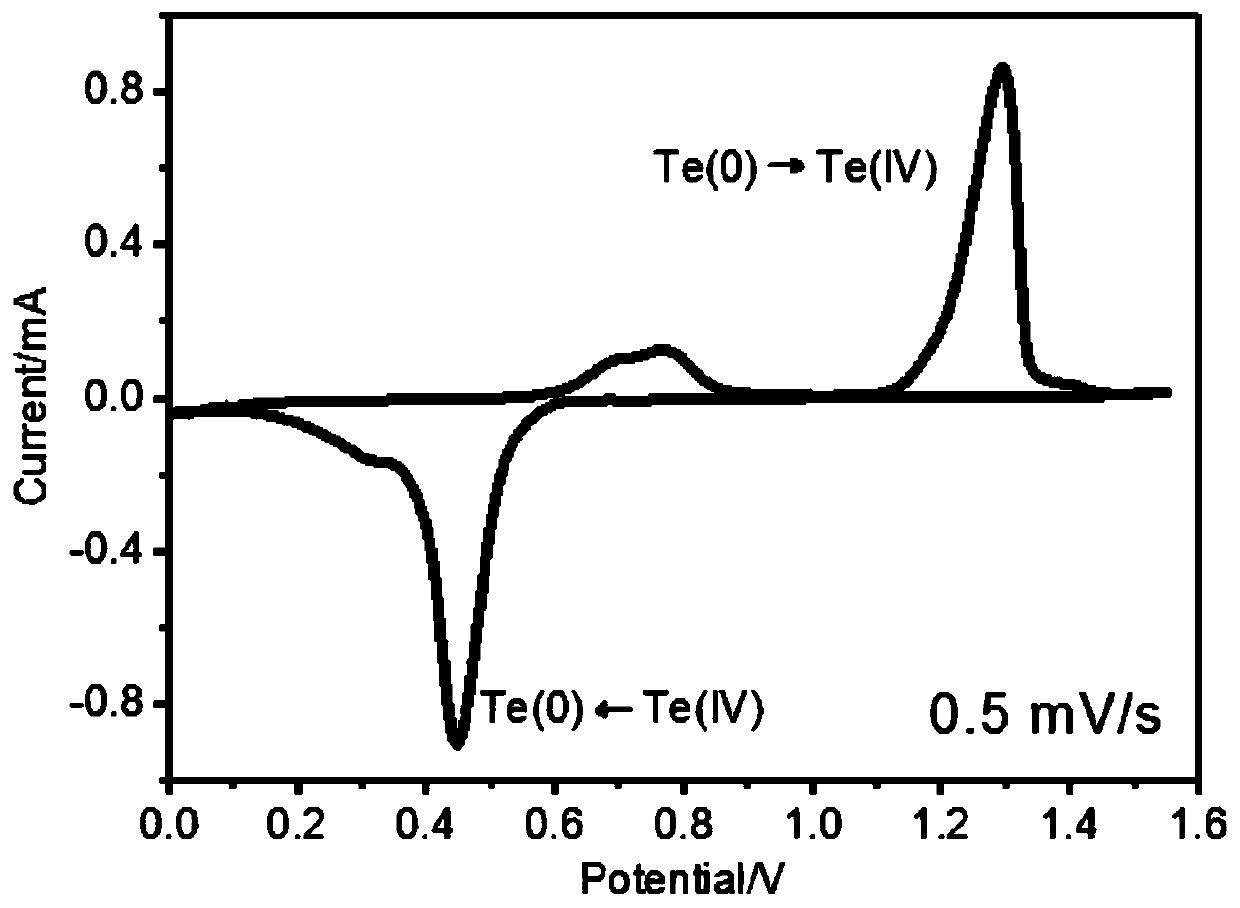
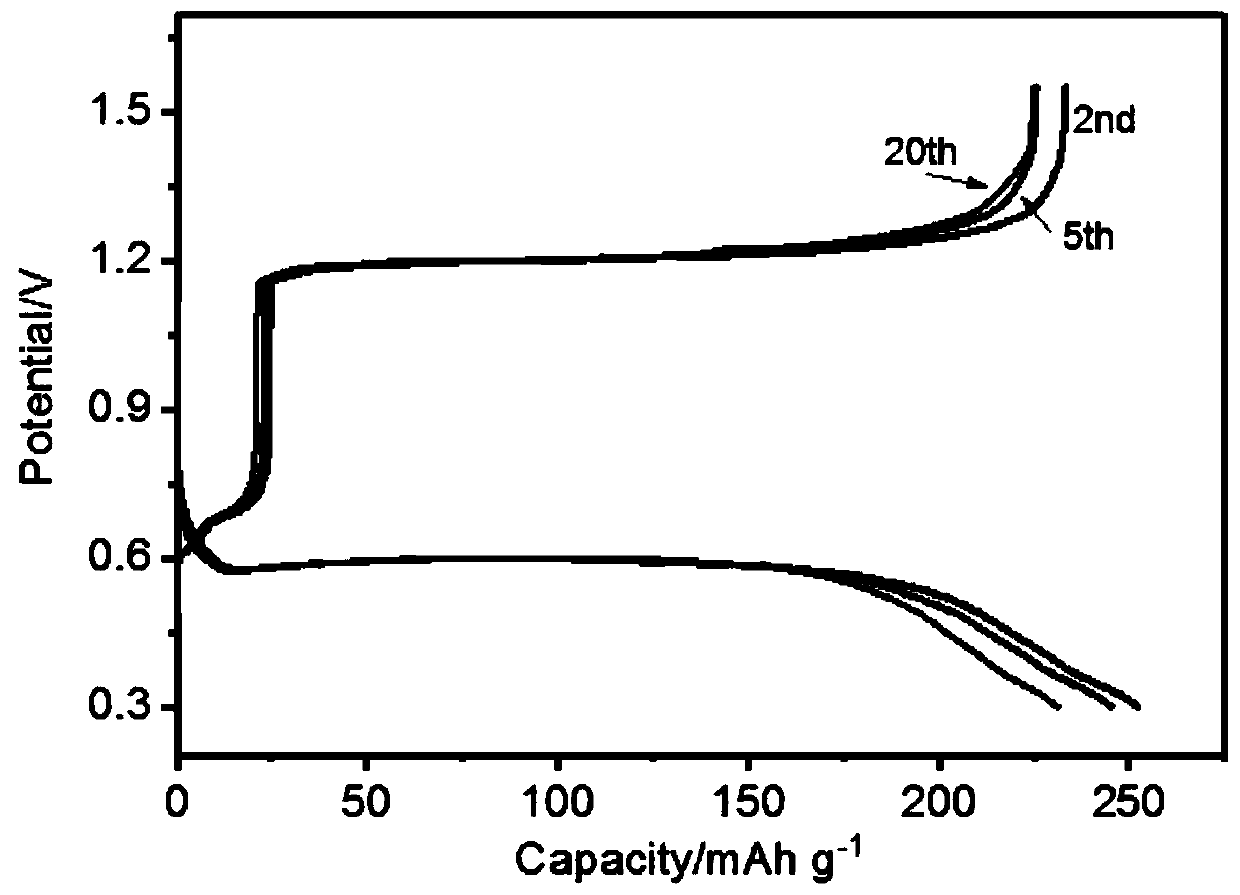
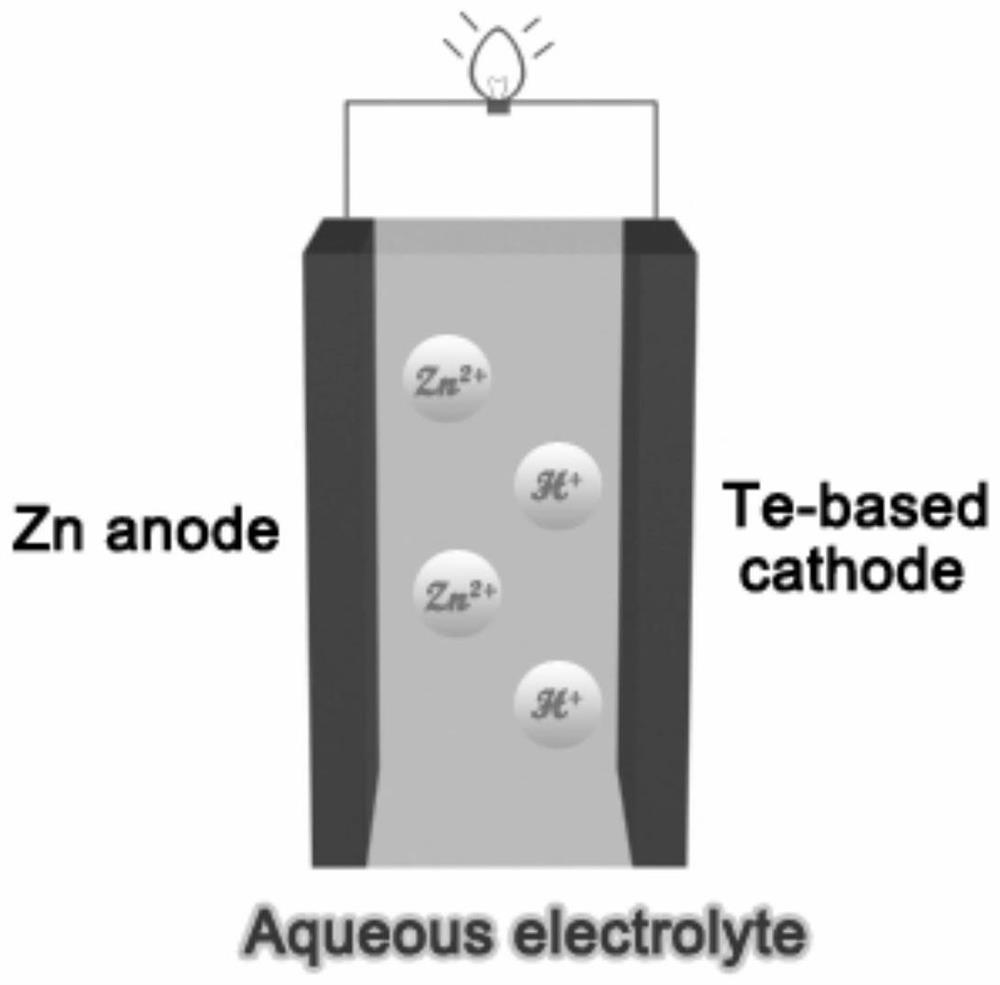
Aqueous zinc-tellurium secondary battery
ActiveCN110034342AIncrease capacityImprove cycle performanceCell electrodesFinal product manufactureElectrical batteryAqueous electrolyte
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Culture medium for enriching salmonella, shigella and staphylococcus aureus in composite way and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102827795AShorten enrichment timeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyLithium chloride
The invention discloses a culture medium for enriching salmonella, shigella and staphylococcus aureus in a composite way and a preparation method thereof. The culture medium comprises 13-16 parts of tryptone, 4-7 parts of soy peptone, 2-3 parts of monosodium orthophosphate, 2-3 parts of glucose, 1,000 parts of distilled water, 0.07-0.13 part of bile salt, 25-40 parts of sodium chloride, 0.4-1 part of lithium chloride, 1.5-3.5 parts of mannite and 0.0002-0.0004 part of potassium tellurite, and the pH of the culture medium is 7.1-7.3. The culture medium can be used for restraining the growth of other pathogenic microorganisms while enriching three target pathogenic bacteria simultaneously, can be directly applied to separate culturing of target bacteria and biological assay experiments, and can be directly applied to a detection technology for a plurality of pathogenic bacteria based on one detection platform such as multiple PCRs (Polymerase Chain Reactions) and the like for making a diagnosis report.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
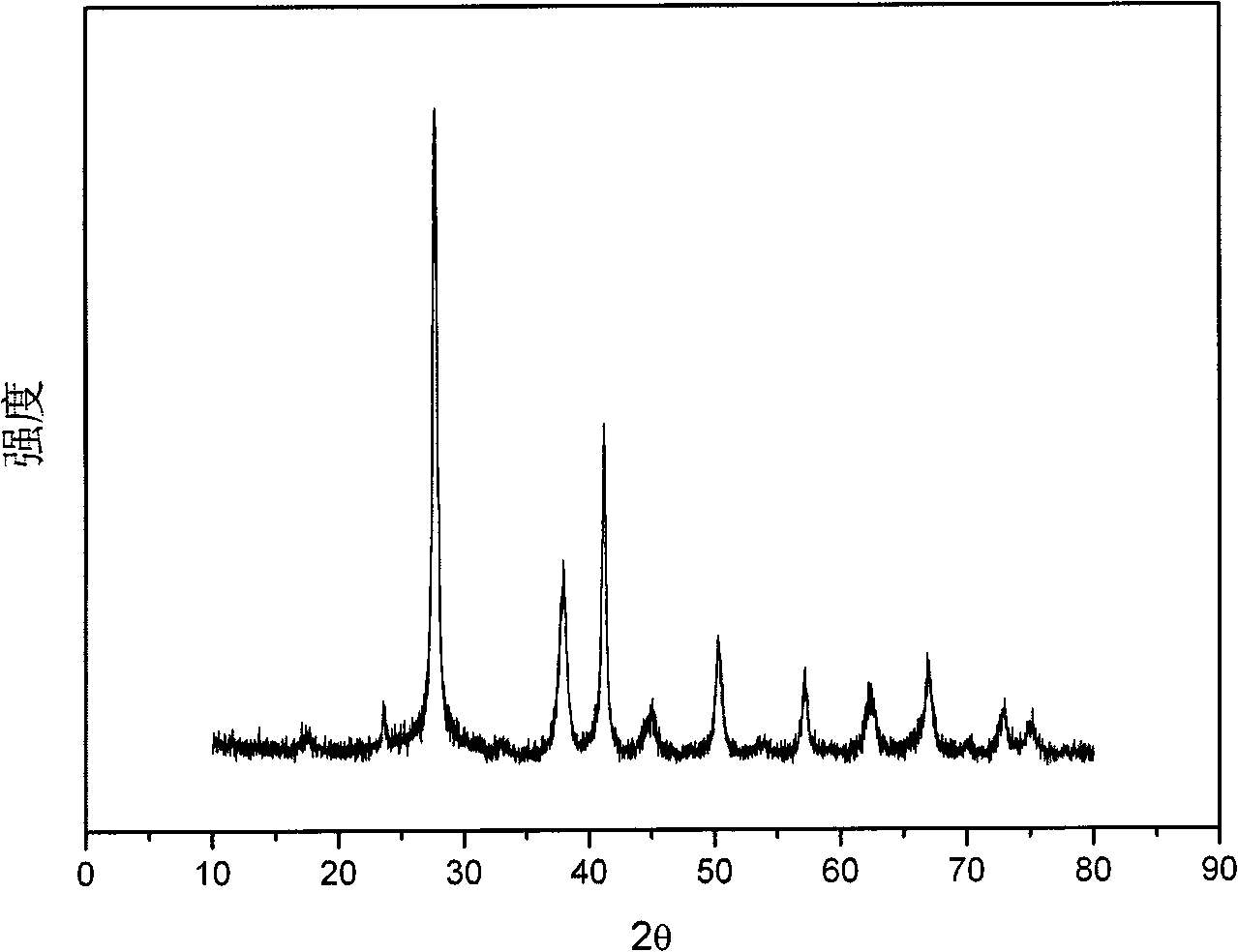
Nonlinear optical crystal vanadium cadmium tellurite
InactiveCN101294301ANonlinear Optical Performance ImprovementImprove thermal stabilityPolycrystalline material growthSingle crystal growth detailsNonlinear optical crystalSpace group
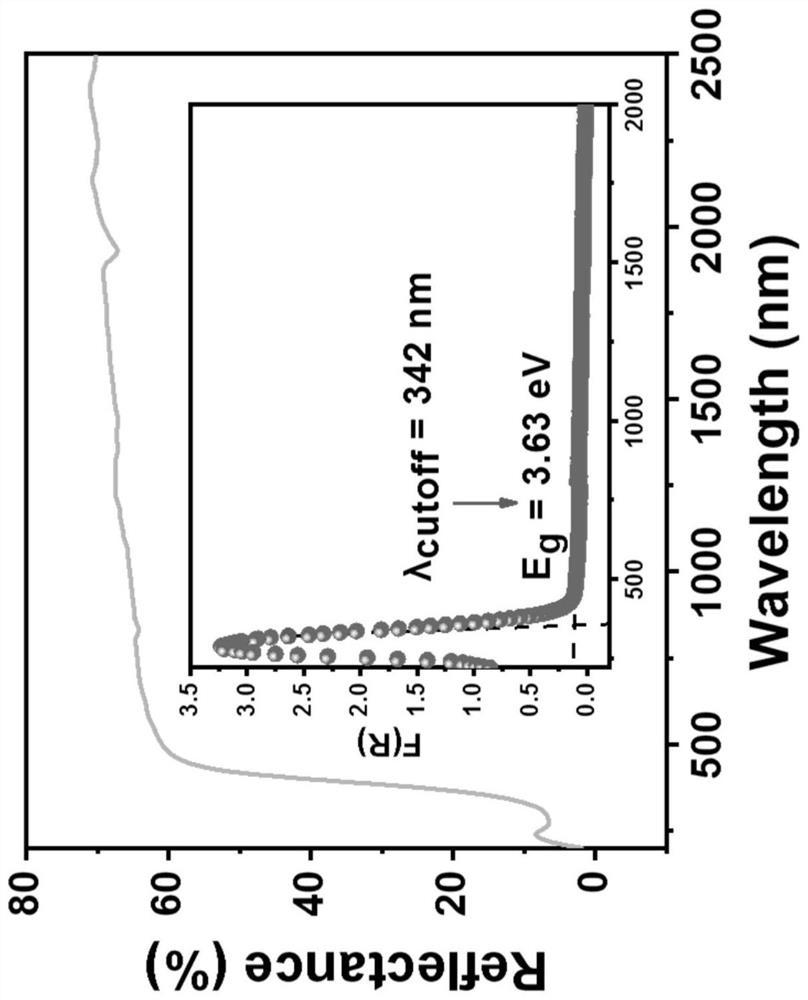
The invention relates to non-linear optical crystal, in particular to tellurous acid vanadium cadmium, which belongs to the non-linear optical material and the synthesis thereof. The chemical formula of the crystal is Cd4V2Te3O15; the molecular weight is 1174.28; the crystal belongs to the orthohombic system; the space group is P212121; the unit cell parameters are: a is equal to 1174.28, b is equal to 16.0478(11), c is equal to 16.2349(11), alpha is equal to 90 DEG, beta is equal to 90 DEG, gamma is equal to 90 DEG, V is equal to 1406.70(17)3, and Z is equal to 4. The crystal is prepared by adopting a high temperature solid-state method. The tellurous acid vanadium cadmium (Cd4V2Te3O15) has excellent non-linear optical property, and the powder SHG coefficient is equivalent to KDP coefficient.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of biosynthesizing nanometer tellurium by utilizing bacillus licheniformis and application of method
ActiveCN108676817AReduce the impactAvoid secondary pollutionMaterial nanotechnologyMicroorganism based processesBacillus licheniformisTumor cells
The invention discloses a method of biosynthesizing nanometer tellurium by utilizing bacillus licheniformis and application of the method. The invention provides bacillus licheniformis S13 (with the preservation number being CGMCC No.11742) as a new strain capable of reducing tellurite, and the bacillus licheniformis S13 can convert tellurium in an ion state to nanometer tellurium so as to removethe tellurium from the environment; and meanwhile, by utilizing the inhibition ability of the nanometer tellurium to tumor cells, the application in anti-tumor aspect is provided, and a foundation isprovided to further study and application of biological nanometer tellurium in the aspect of medicines in future.
Owner:王昊
Moringa oleifera straw mediated synthesized biological tellurium nanoparticles and antibacterial and antiviral application thereof
ActiveCN114569558ACheap sourceEasy way to getAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryBiotechnologyMoringa
The invention provides a Moringa oleifera straw mediated synthesized biological tellurium nanoparticle. The Moringa oleifera straw mediated synthesized biological tellurium nanoparticle is prepared by a method comprising the following steps: taking Moringa oleifera straw and water to prepare a solid-liquid mixture; filtering and collecting filtrate; mixing and stirring the filtrate and potassium tellurite to react; centrifuging and taking precipitate; and after washing, re-suspending in deionized water to obtain the product. The invention also provides antibacterial and antiviral application of the biological tellurium nano material. The technical blank of synthesizing the biological tellurium nanoparticles with antibacterial and antiviral functions by using moringa oleifera in the prior art is filled, and the preparation method is low in production cost, simple in synthesis process, safe, efficient, high in product stability, rich in biological function, wide in application range, remarkable in antibacterial effect, good in antiviral effect and environmentally friendly. The method has a wide market prospect.
Owner:HUBEI NORMAL UNIV
Culture medium for composite enrichment of salmonella, Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus, and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101412978BShorten enrichment timeBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyLithium chloride
The invention discloses a complex enrichment medium used for salmonella, listeria monocytogenes and staphylococcus aureus and a method for preparing the same. The complex enrichment medium comprises the following components in weight portion: 15 to 19 portions of tryptone, 2 to 4 portions of peptone, 2 to 3 portions of sodium dihydrogen phosphate, 2 to 3 portions of glucose, 0.5 to 1.5 portions of aesculin, 1, 000 portions of distilled water, 1 to 2.5 portions of sodium pyruvate, 3 to 10.0 portions of mannitol, 1.0 to 25.0 portions of sodium chloride, 1 to 2.5 portions of lithium chloride, 0.0001 to 0.0002 portion of potassium tellurite, and 0.005-0.015 portion of nalidixic acid, wherein the pH value is between 7.1 and 7.5. The complex enrichment medium can inhibit the growth of other pathogenic microorganisms while performing enrichment on three target pathogens, thus the complex enrichment medium can be directly applied to the isolation culture and the biological assay test of target bacteria, and can also be directly applied to a detection technology of a plurality of pathogens based on one detection platform for multiple PCR and the like to make a diagnostic report.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Thorny magnetic nickel telluride nano wires with functionalized gold nanoparticles as well as preparation, application
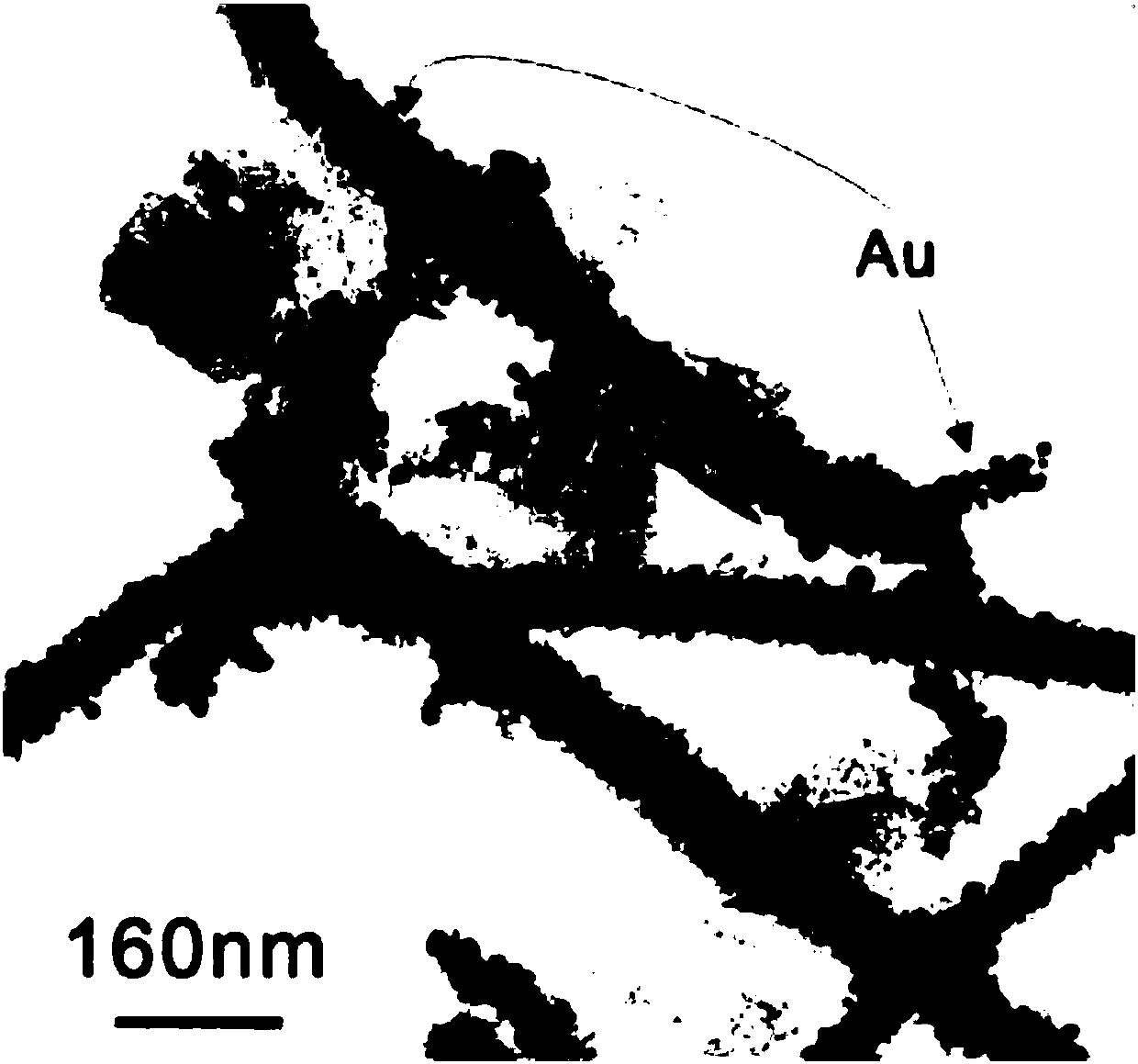
InactiveCN107720711ASimple post-processingEvenly distributedMaterial nanotechnologyBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsNickel saltNanoparticle
The invention discloses a preparation method of a thorny magnetic nickel telluride nano wires. The method comprises the following steps: tellurous acid or tellurite is added into an aqueous solution of nickel salt, and stirring is carried out in order to obtain a turbid solution; a hydrazine hydrate solution is added dropwisely into the turbid solution, stirring is carried out till the solution isbrown, and a mixed solution is obtained; a hydrothermal reaction is carried out for the mixed solution, the hydrothermal reaction temperature is 120-160 DEG C, hydrothermal reaction time is 4-10 hours, washing is carried out, and drying is carried out in order to obtain the thorny magnetic nickel telluride nano wires. The invention also discloses the thorny magnetic nickel telluride nano wires. The invention also discloses the thorny magnetic nickel telluride nano wires with functionalized gold nanoparticles. The invention also discloses the preparation method of the thorny magnetic nickel telluride nano wires with functionalized gold nanoparticles. The invention also discloses an application of the thorny magnetic nickel telluride nano wires with functionalized gold nanoparticles.
Owner:HEFEI NORMAL UNIV
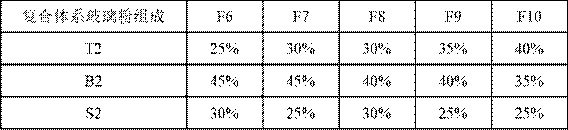
Composite system glass powder for secondary gate electrode silver paste of crystalline silicon solar cell
PendingCN114213026AGood application effectIncrease effective contactNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialCable/conductor manufactureSilver pasteSilicon solar cell
The invention discloses composite system glass powder which is formed by combining tellurite, borate and silicate and is used for silver paste of an auxiliary gate electrode of a crystalline silicon solar cell. In the temperature rising process of sintering of the auxiliary gate electrode silver paste, the tellurite is firstly melted and spread on the silicon surface, so that the sintering reaction between silicon and silver is blocked; then, borate is melted and penetrates through the antireflection layer on the silicon surface in an etching mode, and a silver-silicon conductive contact window is opened; and finally, melting the silicate to inhibit the erosion of the glass melt to the silicon surface and generate a passivation effect. In the cooling process after sintering, silver dissolved by tellurite and brought to the interface is separated out, and a large number of silver colloid particles are formed. Therefore, the composite system glass powder provided by the invention has the effects and characteristics of increasing effective contact of silver and silicon, reducing contact resistance, passivating a silicon surface and the like, and the application performance of the auxiliary gate electrode silver paste can be remarkably improved.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method of electrocatalysing nitrogen reduction catalyst
ActiveCN111298813APromote catalytic effectGood ammonia productionPhysical/chemical process catalystsElectrolysis componentsPtru catalystAmmonia production
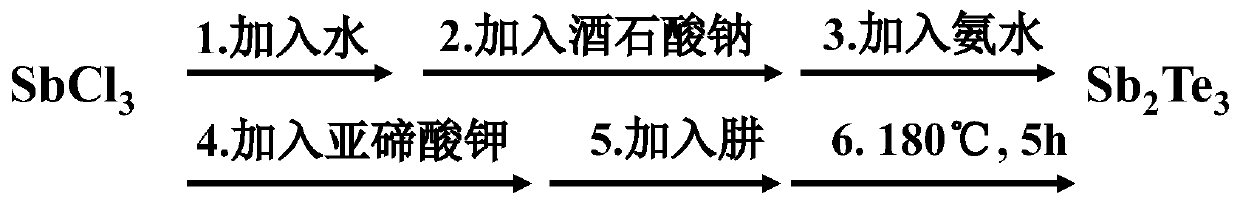
The invention belongs to the technical field of electro-catalytic ammonia production, and discloses a method of electrocatalysing nitrogen reduction catalyst. The method comprises the following steps:firstly, introducing telluride into electro-catalytic nitrogen reduction by utilizing the hydrogen storage capacity of the telluride, selecting elements with favorable adsorption action on nitrogen,and realizing higher ammonia yield at 0V by virtue of the hydrogen storage property of the telluride, wherein the telluride is prepared from Sb2Te3, Bi3Te4, CoTe and CdTe2; taking Sb2Te3 as an example, the synthesis method of the Sb2Te3 comprises the following steps: SbCl3 is dissolved in water, then 25mg of sodium tartrate, 25mL of ammonia water, 22mg of potassium tellurite and 10mL of hydrazineare sequentially added and stirred for 5min, and the mixture is put into a reaction kettle to react at 180 DEG C for 5h; the nitrogen reduction properties of Sb2Te3, Bi3Te4, CoTe and CdTe are compared, and it is found that telluride has a great prospect in nitrogen reduction under low voltage.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for quantitatively detecting staphylococcus aureus in food
PendingCN111961704AThe result is accurateImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisBiotechnologyPetri dish
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively detecting staphylococcus aureus in food. The method comprises four steps of preparation, sample preparation, culture and counting. After a sample isprepared, each dilution sample sucks 1mL of sample homogenate into a culture dish, then adding 15-20mL of a Baird-Parker culture medium solution added with potassium tellurite egg yolk enrichment broth into each culture dish, performing uniform mixing, then performing culturing, counting suspicious colonies after culturing, and carrying out confirmation and identification on the suspicious colonies by virtue of a plasma coagulase test. Different from existing coating methods, the method provided by the invention can be used for rapidly, simply, conveniently and accurately determining staphylococcus aureus in food.
Owner:郑州中检科测试技术有限公司
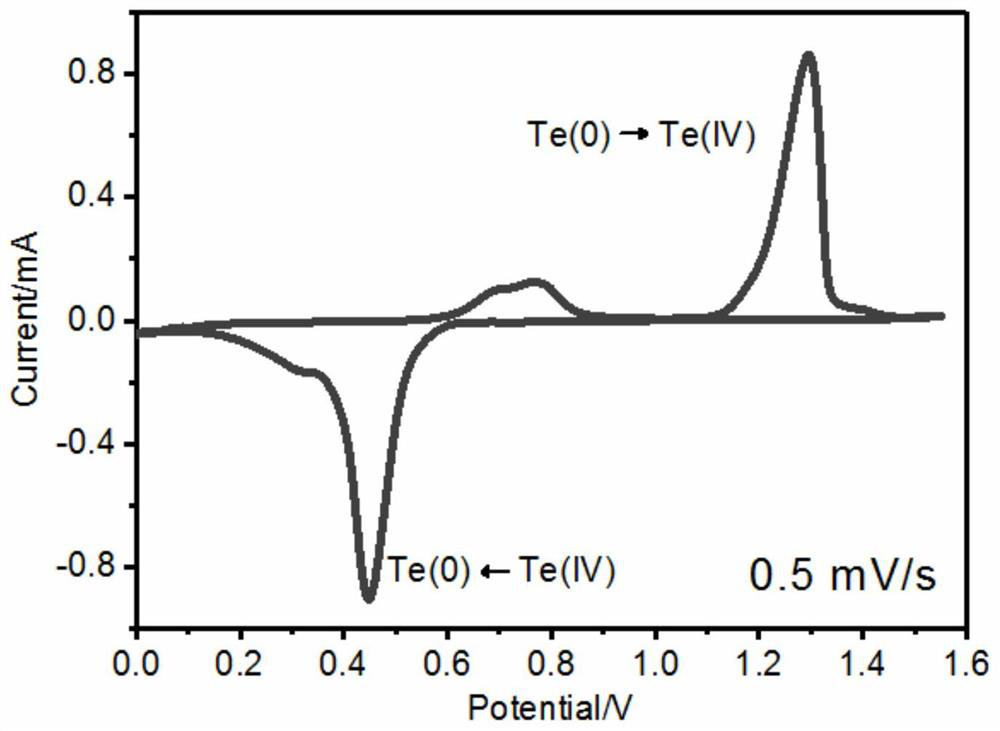
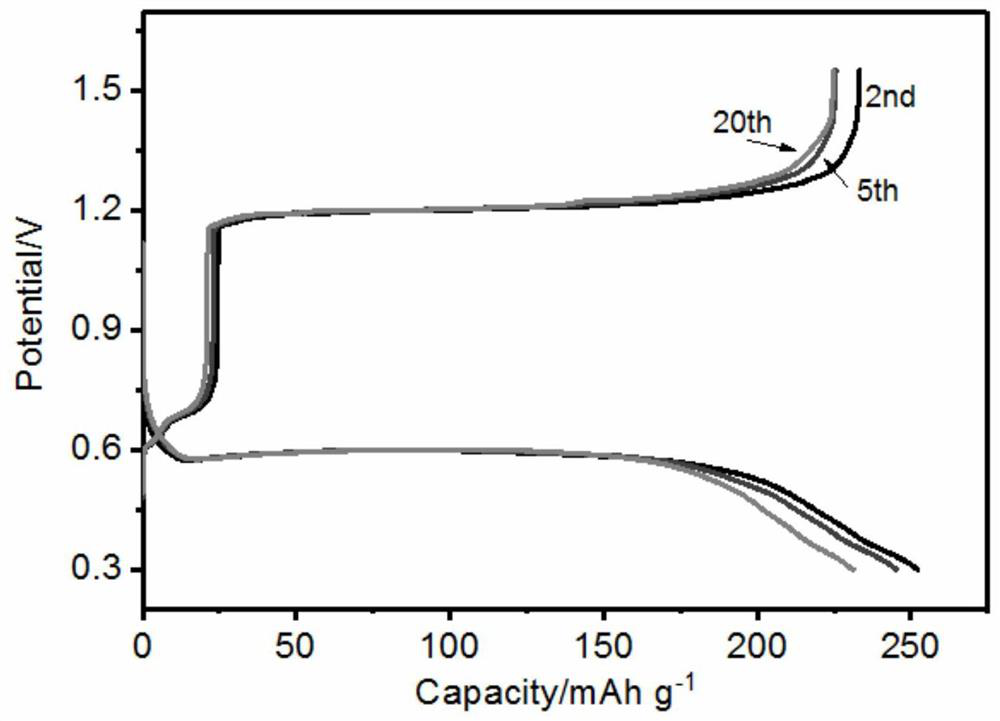
A kind of aqueous zinc-tellurium secondary battery
ActiveCN110034342BEfficient electrochemical solid-solid phase conversion reactionIncrease capacityFinal product manufactureCell electrodesElectrical batteryTellurium compounds
The invention belongs to the field of secondary batteries, in particular to an aqueous secondary battery based on zinc-tellurium. An aqueous secondary battery, the positive electrode contains tellurium; the negative electrode contains zinc; and an aqueous electrolyte and a separator are arranged between the positive electrode and the negative electrode. The invention is mainly based on the redox reaction of elemental tellurium and tetravalent tellurium compounds (tellurium dioxide or tellurite) in the aqueous electrolyte in the positive electrode and the dissolution (oxidation) / deposition (reduction) reaction of zinc ions in the negative electrode for energy storage Therefore, the aqueous zinc-tellurium secondary battery of the present invention has the advantages of high capacity, long cycle life, safety and environmental protection, etc., and can be widely used in consumer electronic equipment, intelligent devices, electric vehicles, communications, aerospace and large-scale energy storage, etc. important areas.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Indium-doping tellurous acid lead quantum dot sensitized solar cell and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104681292AImprove short-circuit current density and photoelectric conversion efficiencyImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyLight-sensitive devicesElectron holeValence band
The invention relates to an indium (In)-doping tellurous acid lead (PbTeO3) quantum dot sensitizer for a solar cell and a preparation method of the sensitizer. The method comprises the following step of doping In impurity atoms into PbTeO3 quantum dots to form the sensitizer to assemble the quantum dot sensitized solar cell. Transmission paths of electron holes inside the cell are optimized, so that the electron holes can be more quickly separated and can be more effectively injected into valence bands of NiO, dark current is reduced, and the short-circuit current and the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the solar cell are improved. The method is simple and easy to operate and low in cost, and can be used for large-area manufacturing.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
Rubidium molybdenum fluorine tellurite second-order nonlinear optical crystal material and preparation thereof, and application of rubidium molybdenum fluorine tellurite second-order nonlinear optical crystal material in laser frequency conversion
ActiveCN113481599ALarge frequency doubling effectWide transmission rangePolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsNonlinear optical crystalHolographic storage
The invention relates to a rubidium molybdenum fluoride tellurite second-order nonlinear optical crystal material and preparation thereof, and application of rubidium molybdenum fluorine tellurite second-order nonlinear optical crystal material in laser frequency conversion. The chemical formula of the crystal material is RbTeMo2O8F; the molecular weight of the crystal material is 551.95; the crystal material belongs to a monoclinic system; the space group of the crystal material is Pn; the cell parameters of the crystal material are that a is equal to 5.55 to 5.73 angstroms, b is equal to 9.18 to 9.30 angstroms,c is equal to 7.44 to 7.57 angstroms, alpha is equal to gamma and equal to 90 degrees, beta is equal to 95.13 to 95.32, and Z is equal to 2; and the cell volume V of the crystal material is equal to 379.1 to 403.4 angstroms<3>.The rubidium molybdenum fluoride tellurite crystal material has excellent optical performance; under irradiation of laser with a wavelength of 1064 nm, the powder frequency doubling strength of the rubidium molybdenum fluoride tellurite crystal material is about 27 times the powder frequency doubling strength of a monopotassium phosphate crystal; and under laser with a wavelength of 2100 nm, the powder frequency doubling strength of the rubidium molybdenum fluoride tellurite crystal material is 2.2 times the powder frequency doubling strength of a potassium titanyl phosphate crystal. In addition, the crystal material has a wide transmission range in a visible light-infrared light region (0.34-5.4 [mu]m), and has wide application prospects in the fields of laser frequency conversion, photoelectric modulation, laser signal holographic storage and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Preparing method for cow mammitis staphylococcus culture fluid and its use
InactiveCN100345977CRapid selective expansionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyAntibiotic sensitivity
The preparation process of cow mammitis staphylococcus culture fluid and its use belongs to the field of animal epidemic disease diagnosing, preventing and treating technology. The preparation process includes dissolving peptone 10 g, yeast powder 5 g, sodium pyruvate 10 g, glycin 12 g and lithium chloride 5 g in water of 980 ml; regulating pH to 7.3 with sodium hydroxide; sterilizing at 121 deg.c; cooling to 50+ / -10 deg.c; adding bacteria-free 1% concentration potassium tellurite water solution in 10 ml and Tween-80 in 7 ml, and preservation at 4 deg. c. The culture fluid may be used in the fast identification of cow mammitis staphylococcus and antibiotic sensitivity test.
Owner:兆丰华生物科技(南京)有限公司
Chromogenic medium used for detecting esherichia coli O157:H7
ActiveCN102424832BHigh detection sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyThio-
The invention discloses a chromogenic medium used for detecting esherichia coli O157:H7. The medium comprises agar, peptone, beef extract powder, sodium chloride, sorbitol, inositol, neutral red, beta-galactosidase chromogenic substrate, beta-glucuronidase chromogenic substrate, isopropyl-beta-D- thiogalactopyranoside, natrium taurocholicum, potassium tellurite and cefixime. The chromogenic medium used for detecting esherichia coli O157:H7 of the present invention has the advantages of high sensitivity, good specificity, direct bacterial strain discrimination according to colony color, short detection period and strong operationality, is suitable for treating high-reflux samples, is capable of comprehensively, systematically and accurately detecting and preliminarily identifying the esherichia coli O157:H7 in food production and environment, and provides a novel approach for rapidly detecting the microbes.
Owner:GUANGDONG HUANKAI MICROBIAL SCI & TECH
Devices for reducing radionuclide emissions during extreme accidents in nuclear power plants
ActiveCN105869692BReduce concentrationEmission reductionRadioactive decontaminationSulfate radicalsNuclear power
A device for reducing radionuclide emission in extreme accidents of nuclear power plants comprises an adsorption tank, three water tanks, three electromagnetic valves, three float valves and a remote controller. The adsorption tank is filled with a high-temperature-resistant inorganic adsorption material is preset in a containment sump, the three water tanks filled with different solutions are preset in a containment, and the remote controller is mounted outside the containment of the nuclear power plant. The solution in the first water tank comprises, by weight, 0.5%-5% of strontium ions, 0.1%-2% of iodide ions, 0.1%-2% of tellurous acid radicals and the balance water or comprises, by weight, 0.5%-5% of strontium ions, 0.1%-2% of iodide ions, 0.1%-2% of tellurous acid radicals, 1%-4% of boric acid and the balance water. The solution in the second water tank comprises, by weight, 0.1%-4% of silver ions and the balance water or comprises, by weight, 0.1%-4% of silver ions, 1%-4% of boric acid and the balance water. The solution in the third water tank comprises, by weight, 0.5%-5% of sulfate radicals and the balance water or comprises, by weight, 0.5%-5% of sulfate radicals, 1%-4% of boric acid and the balance water.
Owner:HENGYANG NORMAL UNIV
A method for controlling the content of tellurium dioxide and tellurite in tellurite products
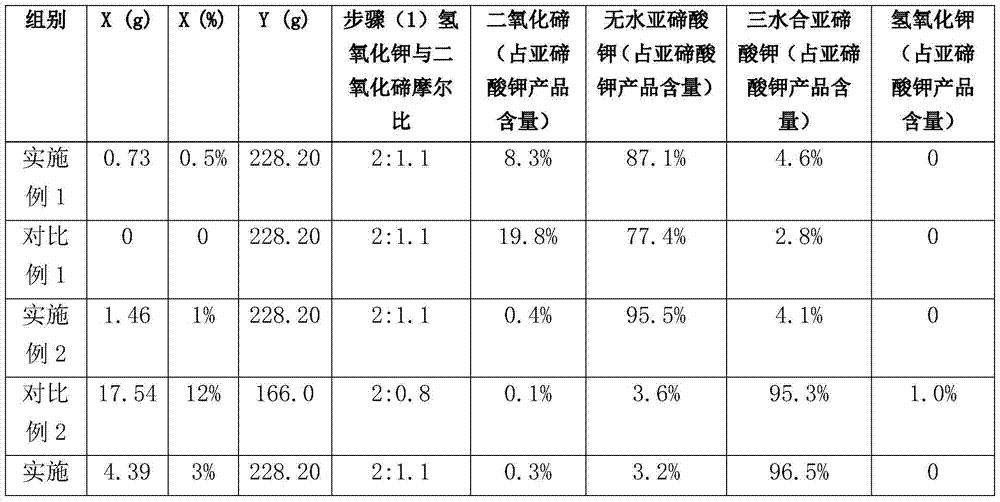
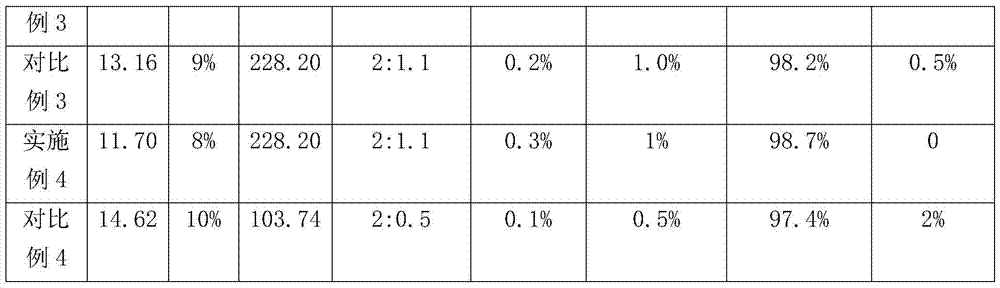
ActiveCN105480956BControl of tellurite trihydrate contentAvoid decompositionSelenium/tellurium oxyacid saltsMetalTellurium dioxide
The invention discloses a method for controlling the content of tellurium dioxide, the content of anhydrous tellurite and the content of trihydrate tellurite in a tellurite product. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, alkali metal hydroxide and tellurium dioxide are reacted in an aqueous solution with the mole ratio of 2.00:(1.00-1.15) to obtain a tellurite solution; secondly, alkali metal hydroxide is added in the tellurite solution, wherein the adding amount of alkali metal hydroxide accounts for X of alkali metal hydroxide in the first step by weight, different numerical value ranges are selected from X to control the content of tellurium dioxide, the content of anhydrous tellurite and the content of trihydrate tellurite in the tellurite product, and X is larger than zero and smaller than or equal to 8.00%. By means of the method, high-purity potassium tellurite can be prepared, and high-purity needle-like trihydrate potassium tellurite can also be prepared in an industrialized mode.
Owner:广东先导稀贵金属材料有限公司
Isolation medium for detecting Escherichia coli O157 and preparation method thereof
PendingCN113293193AStrong specificityIncrease contentMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyCefixime
The invention provides an isolation medium for detecting Escherichia coli O157 and a preparation method of the isolation medium. The separation medium for detecting the escherichia coli O157 comprises peptone, rhamnose, inositol, sorbitol, peptone, agar, cholate 3, neutral red, crystal violet, potassium tellurite, cefixime and a [beta]-galactosidase chromogenic substrate. The peptone, the rhamnose, the inositol, the sorbitol and the 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indole-[beta]-galactoside are added into the separation medium provided by the invention, and the content of each component is optimized, so that not only is the false positive rate reduced, but also the Escherichia coli O157:H7 can be quickly distinguished through the color difference, and the specificity of the culture medium is improved, and the cost is not obviously increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST FOR FOOD & DRUG CONTROL
High tellurite tolerant bacterium-mediated synthesized biological tellurium nano-particles and antibacterial application of high tellurite tolerant bacterium-mediated synthesized biological tellurium nano-particles
ActiveCN114426990AStable biological functionStrong tellurite reducing abilityAntibacterial agentsFungiBiotechnologyTellurate
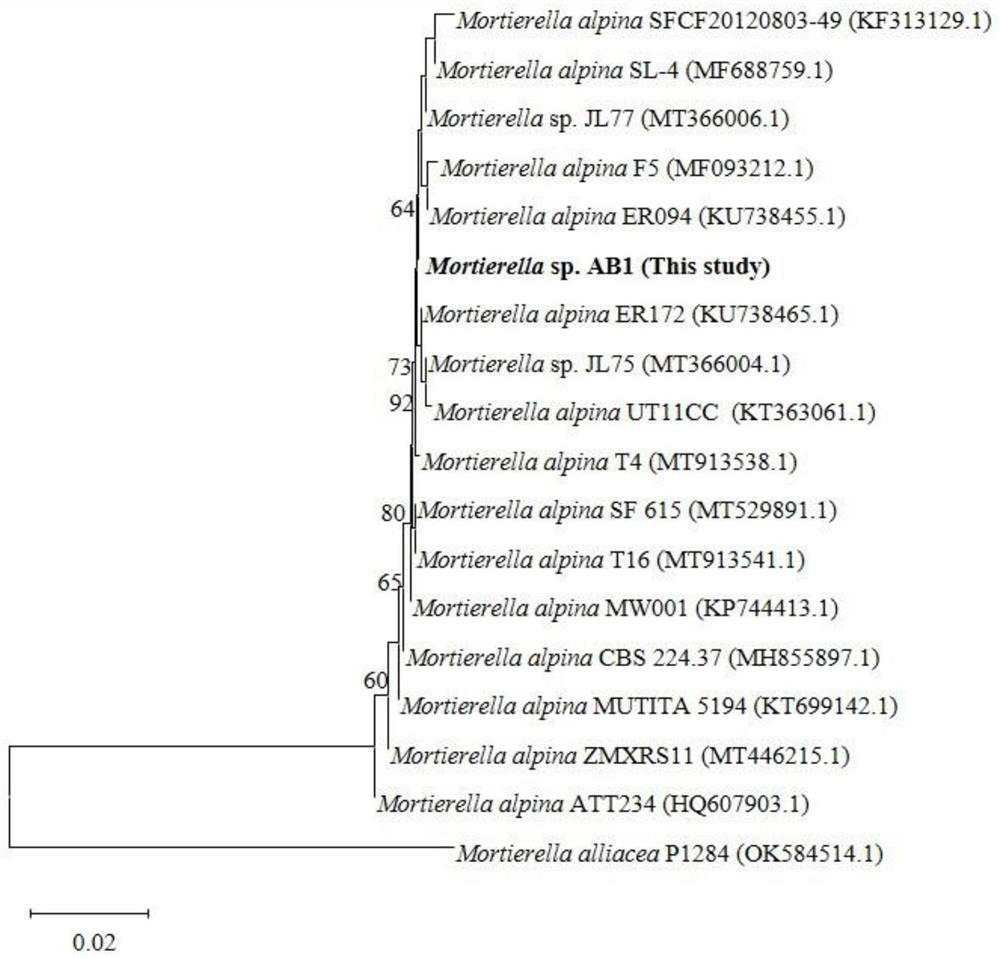
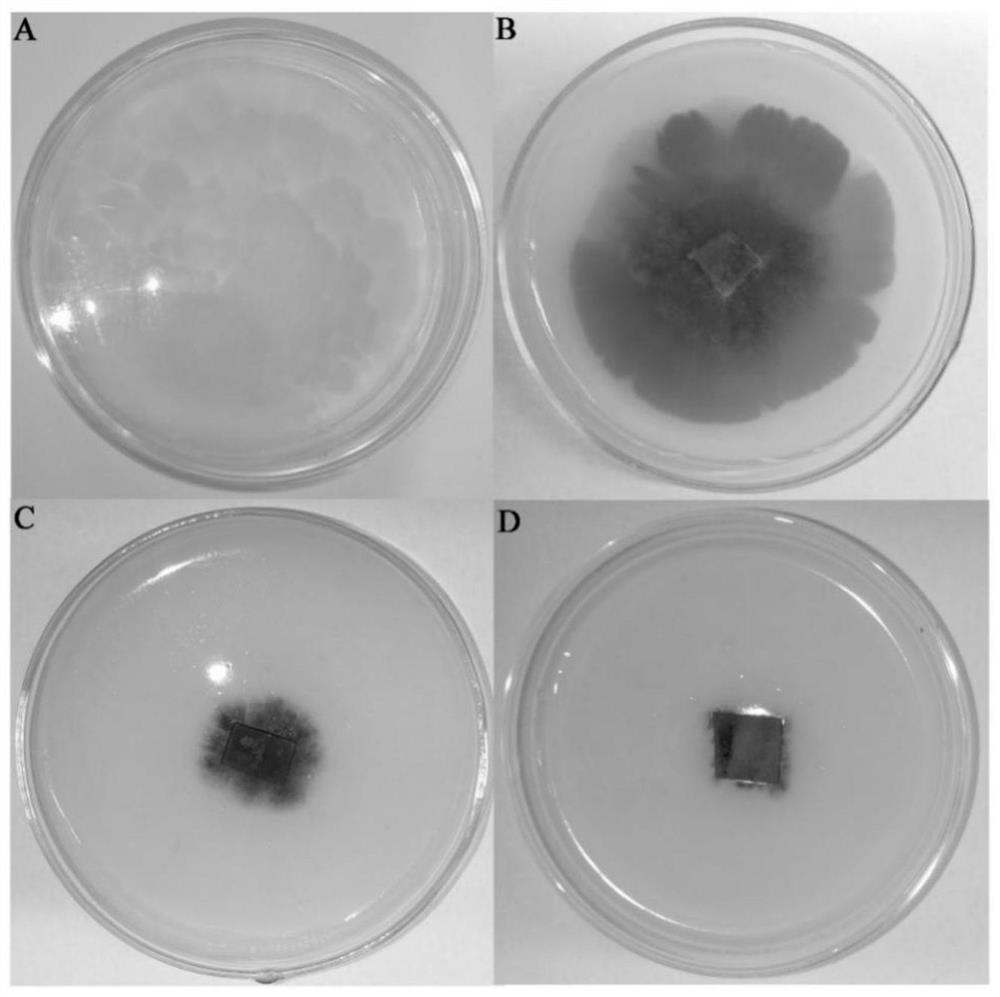
The invention provides a high tellurite tolerant bacterium mediated synthesized biological tellurium nanoparticle, which is prepared by the following steps: 1) obtaining a strain mortierella sp.AB1 (Mortierella sp.AB1), and preserving in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) with the preservation number of CCTCC M 20211177); 2) fermenting; 3) adding a tellurite solution into the improved PDA for continuous growth; 4) collecting thalli, performing suction filtration, washing, performing suction filtration, freezing, grinding and resuspending; and 5) washing with Tris-HCl and n-caprylic alcohol, washing with deionized water in sequence, and re-suspending. The invention further provides antibacterial application of the biological tellurium nano-particles. The strain is stable in biological function, and the tellurite reducing capacity and the biological tellurium nano-particle synthesis capacity are high; the product is low in production raw material price, simple in synthesis process condition, safe and controllable, simple in preservation mode, high in stability and strong in antibacterial ability.
Owner:HUBEI NORMAL UNIV
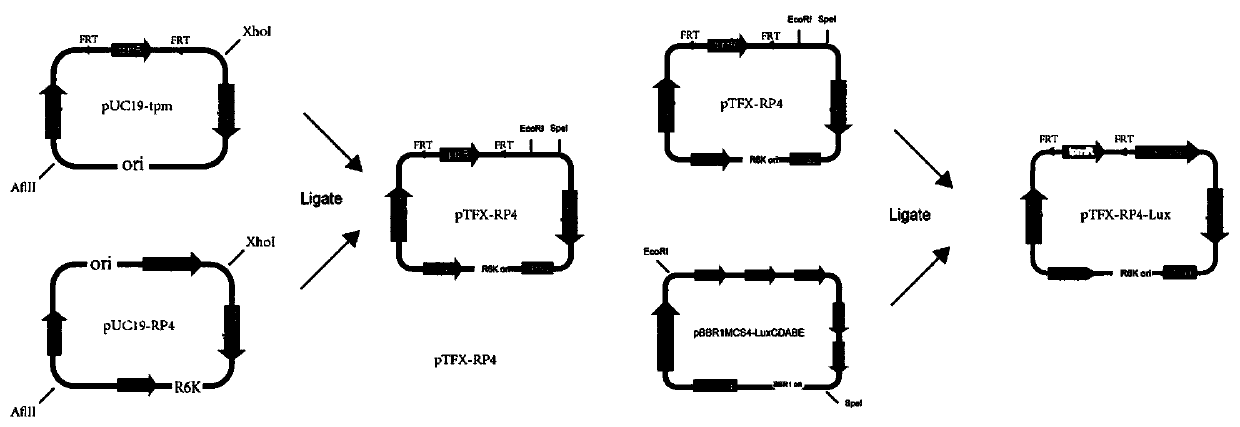
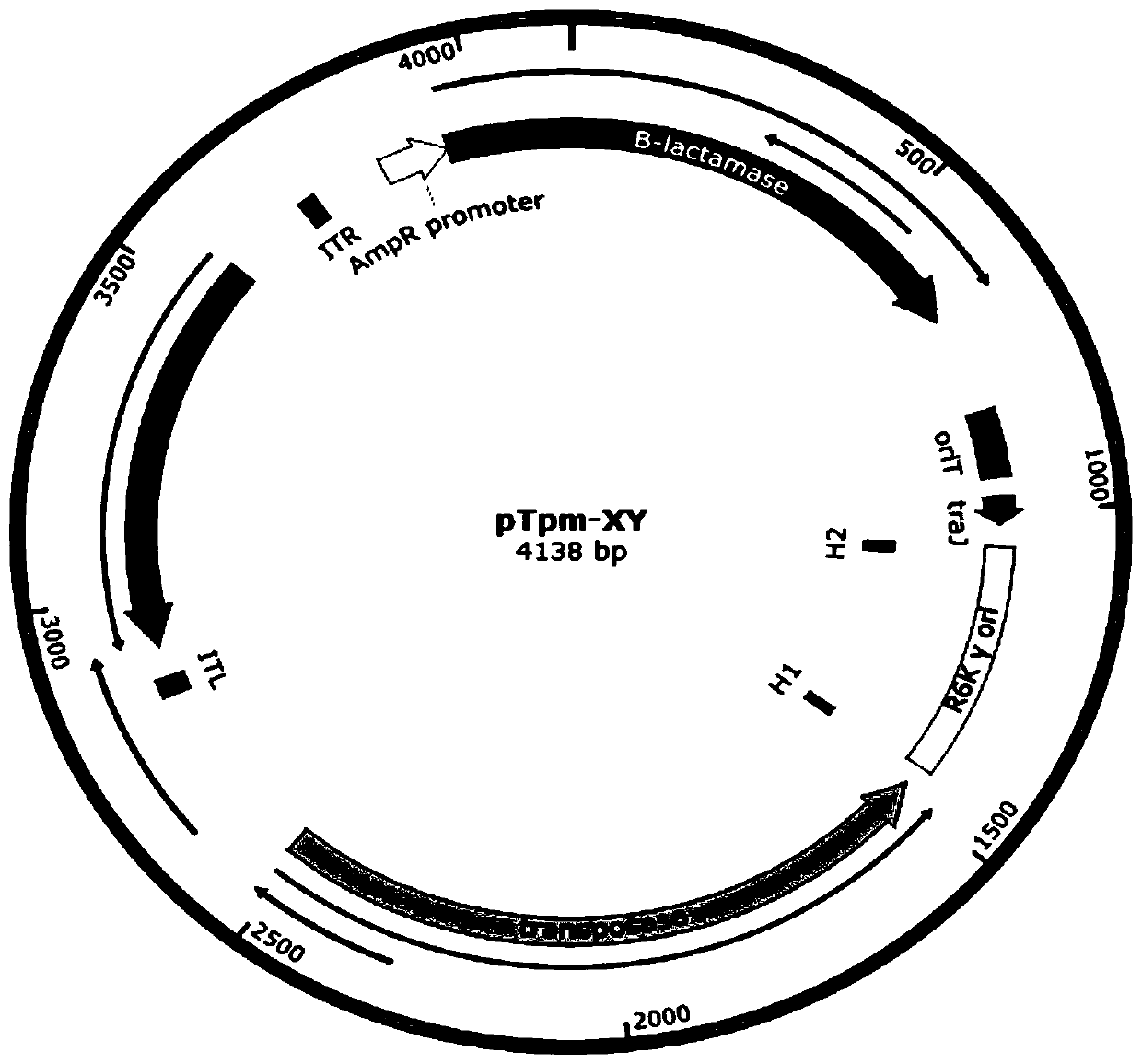
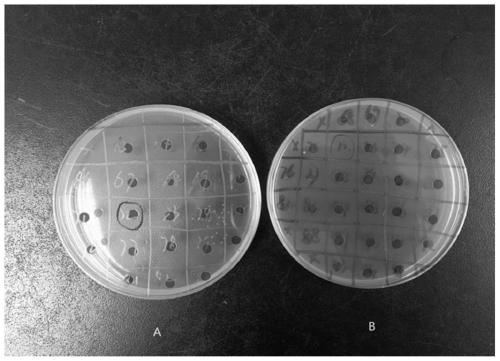
Method for constructing suicide plasmid and drug-resistant mutant strain based on mariner transposon
ActiveCN110079540BEfficient screeningIncrease workloadBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPharmaceutical SubstancesMutant strain
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Bismuth base hydrogen storage material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101513994BUniform sizeSingle formCell electrodesBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsTe elementSolvent
The invention relates to a bismuth base (bismuth selenide, bismuth telluride) hydrogen storage material and a preparation method thereof, relating to low temperature liquid phase synthesis of bismuth base material and the application thereof on hydrogen storage, lithium storage and electrode material. The invention is characterized in that water is taken as solvent, bismuth salts such as bismuth nitrate, bismuth chloride and the like as a bismuth source, and water-soluble tellurium (selenium) acid salts (such as sodium tellurite, selenium substituted sodium sulfate, sodium selenite) or tellurium (selenium) acids (such as orthotelluric acid, tellurous acid and selenous acid) as a tellurium source (selenium) source; proper coordination agents (such as nitrilotriacetic acid, hexamethylene diamine tetraacethyl and the like) and reducing agents (such as vitamin C, sodium borohydride and the like) are added for liquid phase reaction synthesis at the low temperature of 60-80 DEG C. The bismuth selenide crystal grains prepared by the invention take on flower shapes with the sphere diameter of 1-6mum, and the bismuth telluride crystal grains take on sheet shapes with nanometer diameter; the hydrogen storage performance reaches over 100mAh.g<-1>. The method has the advantages of cheap raw material, simple technique, convenient operation, easy mass production, etc.
Owner:江苏先进无机材料研究院
Device for reducing radionuclide emission in extreme accidents of nuclear power plants
ActiveCN105869692AReduce concentrationEmission reductionRadioactive decontaminationSulfate radicalsNuclear power
A device for reducing radionuclide emission in extreme accidents of nuclear power plants comprises an adsorption tank, three water tanks, three electromagnetic valves, three float valves and a remote controller. The adsorption tank is filled with a high-temperature-resistant inorganic adsorption material is preset in a containment sump, the three water tanks filled with different solutions are preset in a containment, and the remote controller is mounted outside the containment of the nuclear power plant. The solution in the first water tank comprises, by weight, 0.5%-5% of strontium ions, 0.1%-2% of iodide ions, 0.1%-2% of tellurous acid radicals and the balance water or comprises, by weight, 0.5%-5% of strontium ions, 0.1%-2% of iodide ions, 0.1%-2% of tellurous acid radicals, 1%-4% of boric acid and the balance water. The solution in the second water tank comprises, by weight, 0.1%-4% of silver ions and the balance water or comprises, by weight, 0.1%-4% of silver ions, 1%-4% of boric acid and the balance water. The solution in the third water tank comprises, by weight, 0.5%-5% of sulfate radicals and the balance water or comprises, by weight, 0.5%-5% of sulfate radicals, 1%-4% of boric acid and the balance water.
Owner:HENGYANG NORMAL UNIV
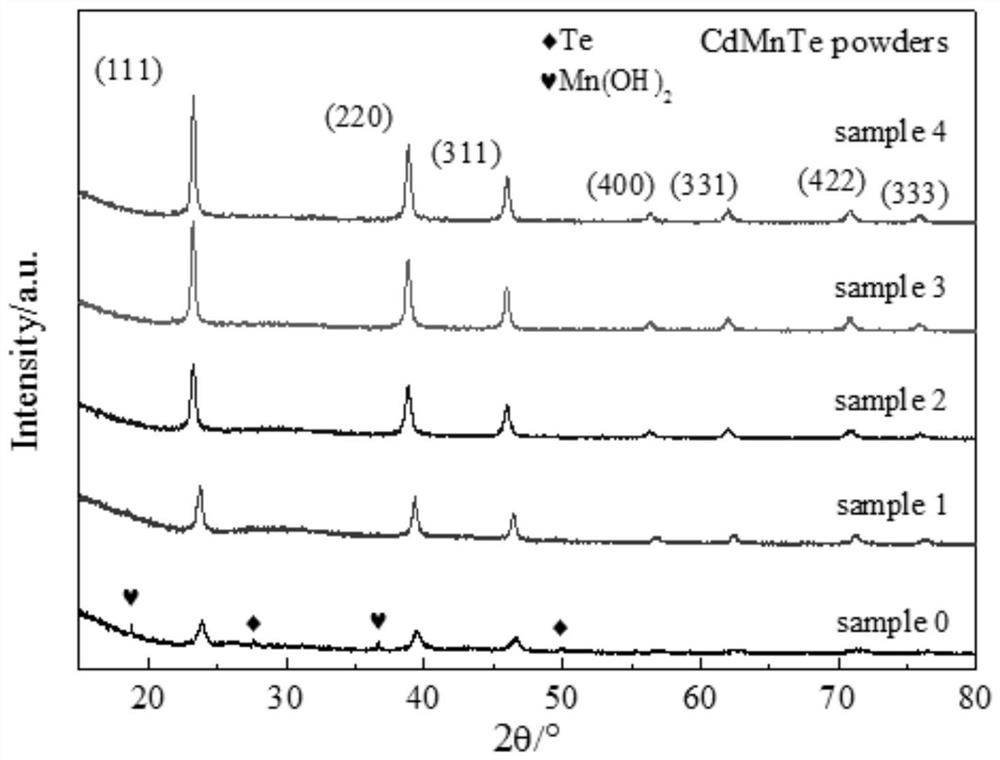
Tellurium-manganese-cadmium nano-powder and preparation method thereof
PendingCN113428842AUniform sizeLow toxicityMaterial nanotechnologyMetal selenides/telluridesManganeseSolar battery
The invention relates to a tellurium-manganese-cadmium nano-powder and a preparation method thereof. The nano-powder is prepared by taking a cadmium salt, a manganese salt and a tellurite as reaction raw materials, adding sodium citrate and thiohydracrylic acid as stabilizers and a hydroboron as a reducing agent through a hydrothermal reaction. The molar ratio of Cd to Mn to Te in the cadmium salt, the manganese salt and the tellurite is 1: (0.1-0.5): (1.1-1.5); the molar ratio of the cadmium salt to the sodium citrate to the thiohydracrylic acid is 1: (0.1-1): (1-5). The process method is simple to operate, does not need a protective atmosphere, is controllable in powder size and low in reaction temperature, and the prepared product is of a pure-phase sphalerite structure. The powder can be used in the fields of radiation detectors, solar cell raw materials, photocatalysis and the like.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com