Identification of animal-derived food pathogens and its drug resistance and virulence gene detection composite chip
A drug resistance gene and virulence gene technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of heavy laboratory workload, low test detection sensitivity, long test cycle, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0089] Embodiment 1, the preparation of composite detection gene chip
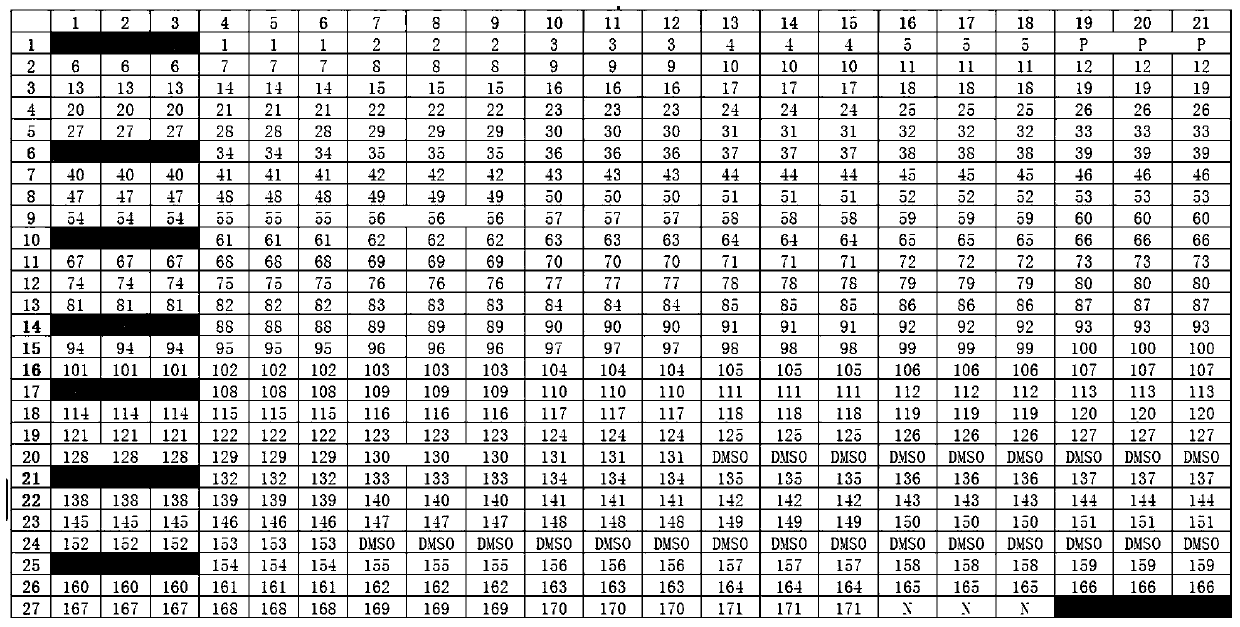
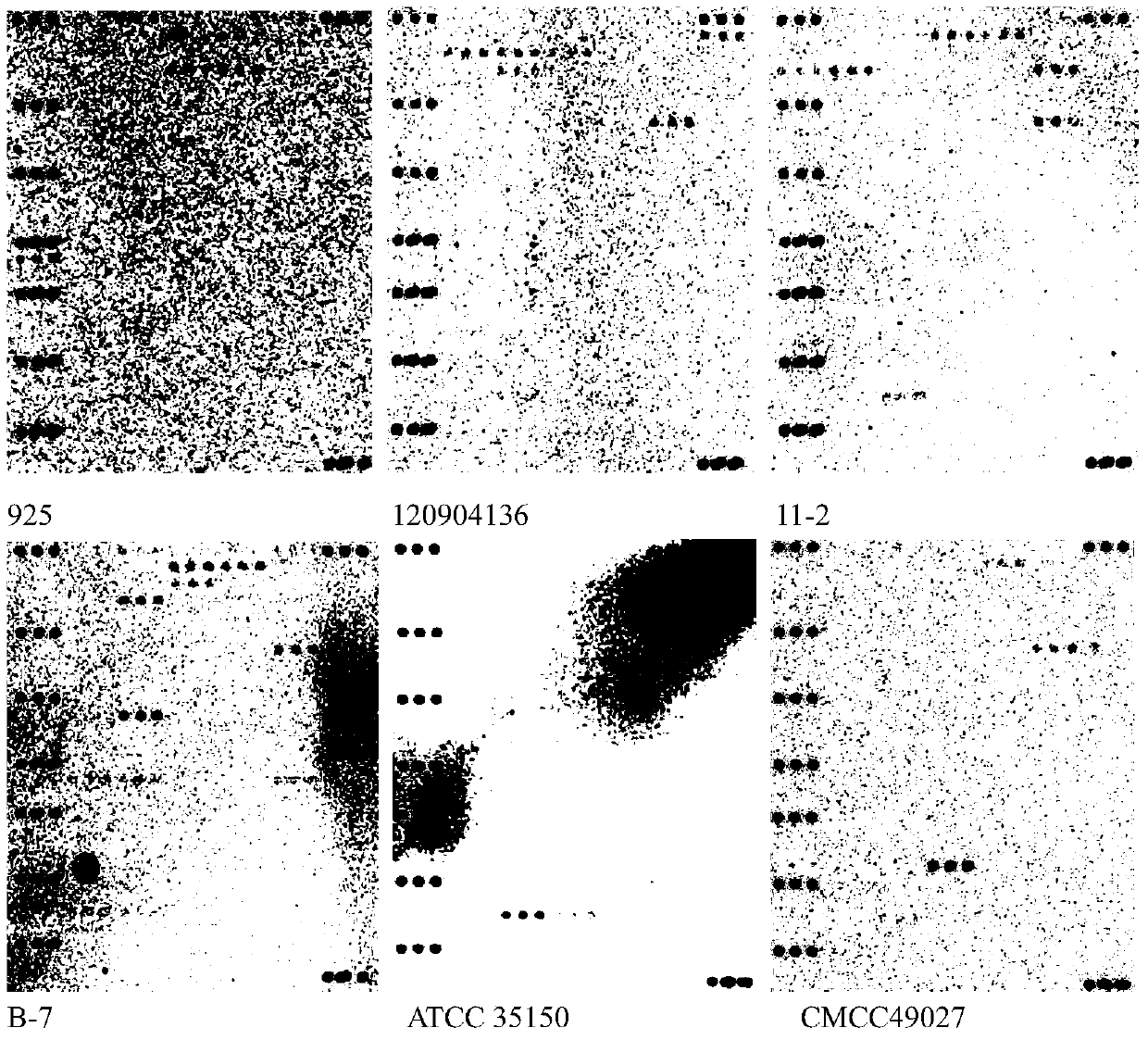
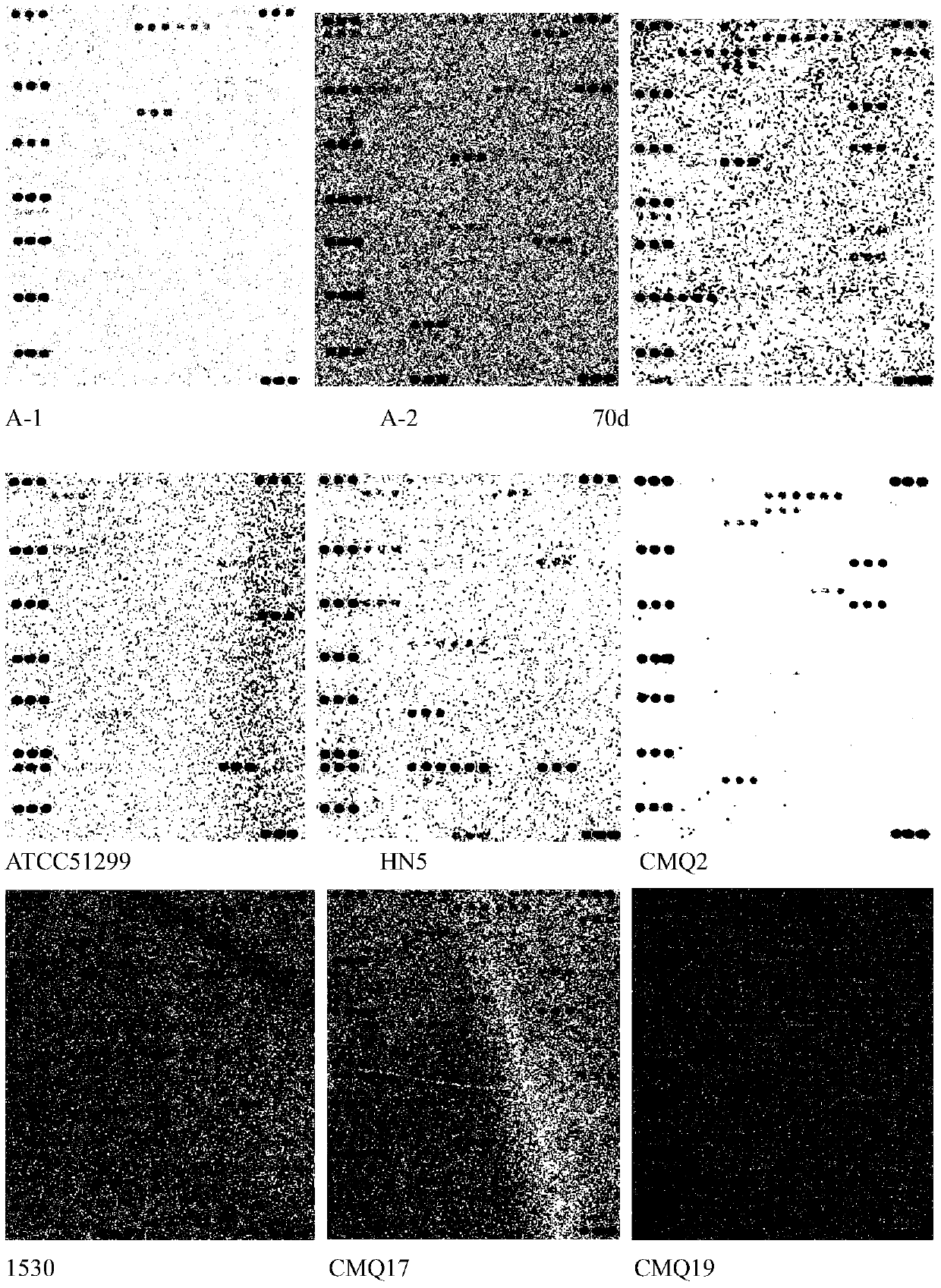
[0090] In order to simultaneously achieve the triple purpose of pathogenic bacteria identification, virulence gene identification and drug resistance gene identification, a microarray detection platform for simultaneous detection of pathogenic bacteria and their related virulence and drug resistance genes in 14 animal-derived foods was established. The 171 oligonucleotide probes placed on the composite detection gene chip involved and included specific genes for identification of pathogenic bacteria in 14 common animal-sourced foods, 16S rRNA genes of 11 pathogenic bacteria, and the 16S rRNA genes of some bacteria. Virulence genes, as well as common drug resistance genes involved in the field of drug resistance surveillance in my country. Some of the detection probes can be flexibly applied to high-sensitivity multiplex PCR amplification and 16SrRNA-PCR single-amplification chip detection. The characterist...
Embodiment 2
[0123] Embodiment 2, the application of composite detection gene chip
[0124] 1. Obtaining samples to be hybridized
[0125] 1. Extraction of sample nucleic acid
[0126] According to the determination of the pre-detection object of the gene chip, the The Genomic DNA Purification Kit was used to extract the DNA of the bacteria to be tested shown in Table 2 according to the research instructions to obtain the genomic DNA of each bacteria.
[0127] The genomic DNA of each bacterium was subjected to the following experiments:
[0128] 2. Random primer PCR amplification of samples to be hybridized
[0129] 1) PrimerA reaction:
[0130] DNA reaction solution 1: 400ng of genomic DNA, 2.5 μL of PrimerA (PrimerA: GTTTCCCAGTCACGATCNNNNNNNNNN (sequence 172)), 6 μL of MQ H 2 After O mixing, pre-denature at 95°C for 5 minutes, and then place it on ice immediately to obtain DNA reaction solution 1;
[0131] Mixture 2: Mix 2.5 μL dNTP (Takara Company Code: R001A)), 23 μL MQ H 2 O m...
Embodiment 3
[0192] Embodiment 3, compound detection gene chip carries out blind test test
[0193] 1. Obtaining samples to be hybridized
[0194] 1. Extraction of sample nucleic acid
[0195] The detection strain used for the blind test was a strain of MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) isolated from commercial pigs, and another strain was a strain of Salmonella isolated from the chicken processing chain.
[0196] Genomic DNA of MRSA and Salmonella was extracted.
[0197] 2. Random primer PCR amplification of the sample to be hybridized: the same as in Example 2.
[0198] 3. Fluorescent labeling: the same as in Example 2.
[0199] 2. Chip hybridization: the same as in Example 2.
[0200] 3. Chip detection
[0201] Method is identical with embodiment 2, and result is as image 3 As shown in A.
[0202] According to the chip detection results, the identification of the two bacteria was accurately identified, and at the same time, the detection results of the drug-resi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com