High resistant starch rice milk and preparation method thereof
A high-resistant starch and starch rice technology, applied in the field of deep processing of grains, can solve the problems of restricting the development of rice and bread, and achieve the effects of improving nutritional value and edible value, wide application value, and simple preparation methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
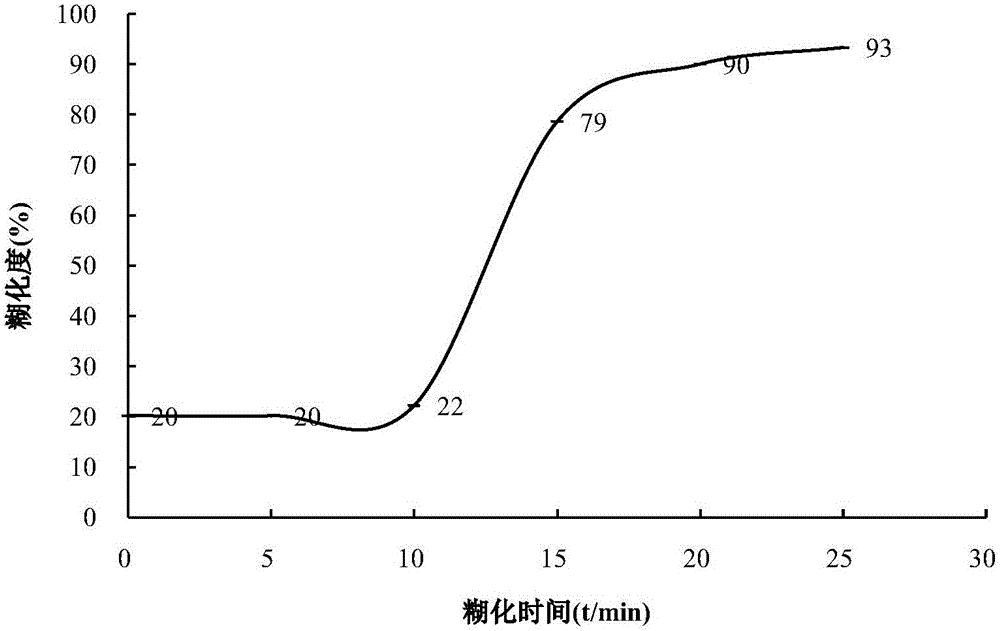
[0019] Example 1: Effect of pre-gelatinization treatment on rice gelatinization degree
[0020] Weigh 10g of indica rice, add water according to the weight ratio of 1:2 (indica rice: water), without independent soaking, steam it in a rice cooker for 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, and 40 minutes. The rice was used as a blank control, and the degree of gelatinization of rice was measured with the cooking time.
[0021] The degree of gelatinization is measured: transfer the samples treated with different cooking times to a beaker, add 40 mL of citric acid buffer with a pH of 5.6, water bath at 50°C for 5 minutes, and add 5 mg / mL amylase (3300 U / mL, enzymatic hydrolysis) The conditions are pH 4.5, 40°C, and the substrate is soluble starch) solution 2.0mL, in a water bath at 50°C for 15min, shaking intermittently, and then immediately adding 4mL 1mol / L hydrochloric acid to terminate the reaction. After cooling, transfer to a 100mL volumetric flask, and dilute to the mark with distilled water; afte...
Embodiment 2
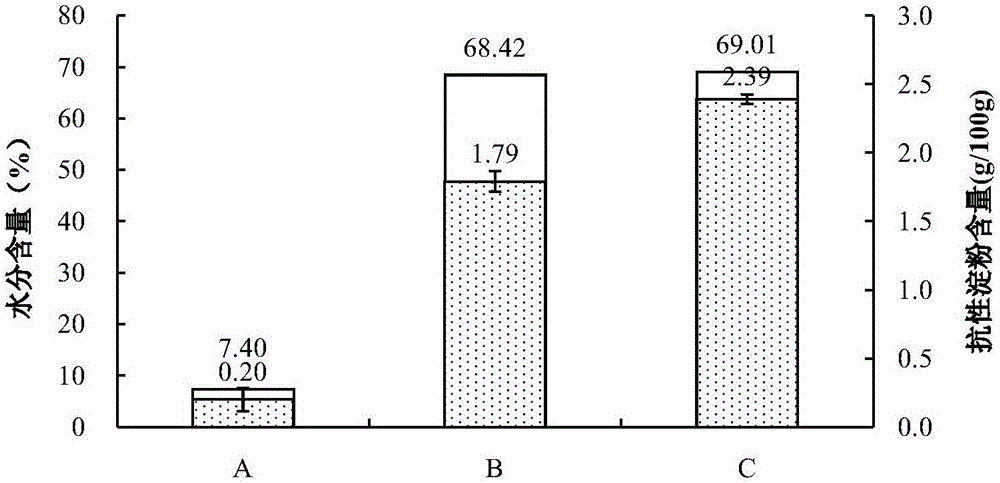
[0031] Example 2: The effect of aging treatment process on rice moisture and resistant starch content
[0032] (1) Sample processing
[0033] The untreated rice sample is labeled as sample A; the weight ratio of rice to water is 1:2, and it is cooked and gelatinized for 20 minutes, and stored at 5°C for 24 hours. It is labeled as sample B; the weight ratio of rice to water is 1:2, cooking Gelatinized for 20 minutes, frozen at -18°C for 24 hours, labeled as sample C;
[0034] (2) Determination of moisture
[0035] According to GB5009.3-2010, the moisture content of samples A, B and C is determined by the direct drying method, and the results are as follows figure 2 Shown.
[0036] 1) Instrument preparation: Put the petri dish to be used in an oven at 105°C, dry to constant weight, weigh the mass of the petri dish, and record it as m 0 ;
[0037] 2) Sample preparation: Weigh 4-6g (accurate to 0.0001g) of the above samples in a dried petri dish with an analytical balance, weigh the total ...
Embodiment 3
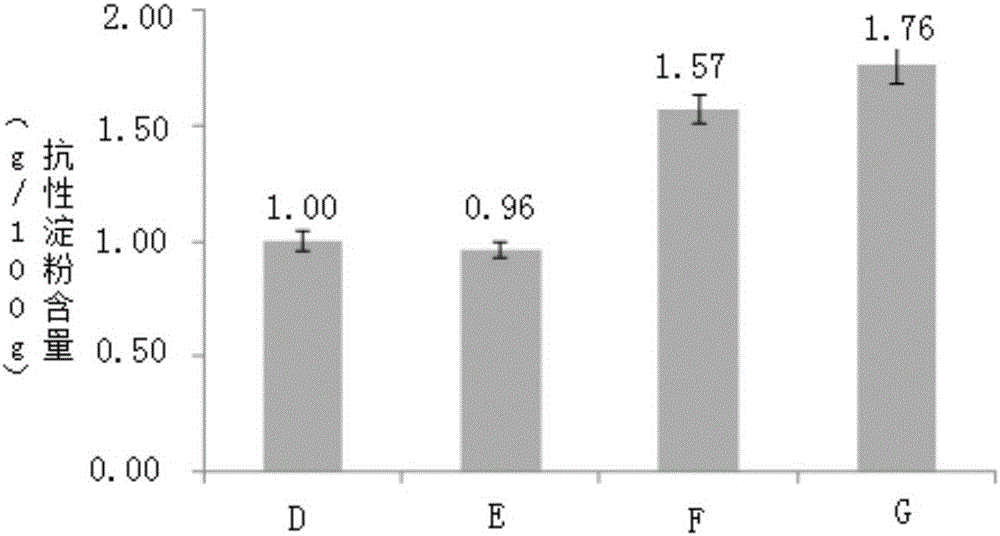
[0059] Example 3: Effect of different treatments on resistant starch content in rice bread
[0060] Preparation of bread samples: blank control (sample D): bread made with basic formula without adding rice; rice flour bread (sample E): raw rice crushed and passed through a 100-mesh sieve, and the ratio of rice flour: flour = 1:3 Bread made after mixing; rice bread (Sample F): High-resistant starch rice milk is obtained after gelatinization and refrigerated rice beating. The amount of high-resistant starch rice milk is the same as dry rice: flour = 1:3. Bread; rice bread (Sample G): high-resistant starch rice milk is obtained after gelatinized and frozen rice is beaten. The amount of high-resistant starch rice milk is a rice bread made of dry rice: flour=1:3.
[0061] The content of resistant starch in the above samples was determined, and the results were as follows image 3 Shown. From image 3 It can be seen that the content of resistant starch in sample F and sample G is high...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com