Method for removing impurities in metallurgic silicon
A technology of metallurgical grade silicon and impurities, applied in the field of silicon purification, to achieve the effect of less acid consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
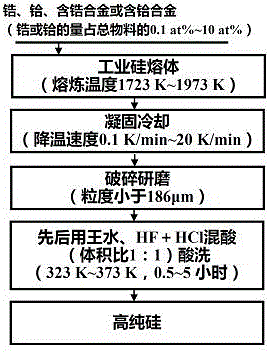
[0022] Such as figure 1 As shown, a method for removing impurities in metallurgical grade silicon, the specific steps are as follows:
[0023] (1) Add Zr to industrial silicon (the amount of added Zr accounts for 10% of the total molar number of materials) and put it into a high-purity dense graphite crucible for melting. The melting temperature is 1723K, and the melting atmosphere is argon protective gas;
[0024] (2) Cool down the completely melted silicon melt in step (1) to room temperature at a rate of 20K / min;
[0025] (3) Grinding the silicon obtained in step (2) into silicon powder smaller than 186 μm;
[0026] (4) Pickling the silicon powder obtained in step (3) with aqua regia, HF+HCl mixed acid (the volume ratio of HF and HCl is 1:1) to obtain high-purity silicon, the pickling temperature is 323K, and the pickling time is 5h.
[0027] After step (4), the content changes of main impurity elements in silicon are shown in Table 1, where the added Zr is reduced from ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Such as figure 1 As shown, a method for removing impurities in metallurgical grade silicon, the specific steps are as follows:
[0033] (1) Add Si-30at%Zr alloy to industrial silicon (the amount of Zr added accounts for 0.1% of the total molar number of materials) and put it into a high-purity dense graphite crucible for melting. The melting temperature is 1973 K and the melting atmosphere is Argon protective gas;
[0034] (2) Cool down the completely melted silicon melt in step (1) to room temperature at a rate of 0.1K / min;
[0035] (3) Grinding the silicon obtained in step (2) into silicon powder smaller than 186 μm;
[0036] (4) The silicon powder obtained in step (3) was pickled successively with aqua regia, HF+HCl mixed acid (the volume ratio of HF and HCl was 1:1) to obtain high-purity silicon. The pickling temperature was 353 K, and the pickling time was 0.5h.
[0037] After step (4), the content changes of main impurity elements in silicon are shown in Table...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Such as figure 1 As shown, a method for removing impurities in metallurgical grade silicon, the specific steps are as follows:
[0043] (1) Add Hf to industrial silicon (the amount of added Hf accounts for 10% of the total molar number of materials) and put it into a high-purity dense graphite crucible for melting. The melting temperature is 1803K, and the melting atmosphere is argon protective gas;
[0044] (2) Cool down the completely melted silicon melt in step (1) to room temperature at a speed of 10K / min;
[0045] (3) Grinding the silicon obtained in step (2) into silicon powder smaller than 186 μm;
[0046] (4) The silicon powder obtained in step (3) was pickled successively with aqua regia, HF+HCl mixed acid (the volume ratio of HF and HCl was 1:1) to obtain high-purity silicon. The pickling temperature was 333 K, and the pickling time was for 3h.
[0047] After step (4), the content changes of main impurity elements in silicon are shown in Table 3, where the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com