A kind of cutting propagation method of Kudingcha holly seedlings
A Kudingcha holly cutting technology, applied in the agricultural field, can solve the problem of low rooting rate and transplanting survival rate of seedling cuttings, unguaranteed yield and quality of Kudingcha products, and great differences in agronomic and quality traits, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of high rooting rate, strong growth, and short seedling cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Embodiment 1: cutting propagation method of the present invention
[0028] Cut the semi-lignified branches of the current year on the mother plant of Kudingcha holly as cuttings, and cut the cuttings into cuttings of appropriate specifications. The length of the cuttings is about 15-20cm, and the diameter is about 0.6-1.0cm. Keep 3-4 leaves for each cutting, subtract 1 / 3 of the area of each leaf and keep the petiole. Each cutting contains more than 2 axillary buds (2-4). The upper cut of the cutting is 2.0 cm above the bud, and the lower cut is 5-10 cm below the bud. The cut of the cutting is neat and unbroken. Cuttings do not use branches with a higher degree of lignification at the base or tender parts at the top.
[0029] Wash the prepared cuttings in clean water for 5 minutes, bundle about 30 cuttings into a small bundle, and then soak the bundled cuttings in 300mg / L naphthaleneacetic acid solution for more than 8 hours. The pH of the naphthaleneacetic acid solut...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Embodiment 2: the cutting method using the branches at the higher part of the lignified part of the base and the branches at the tender part of the top as cuttings
[0036] Except that the selection of cuttings is different, all the other steps and environment are the same as in Example 1.
[0037] Test results: The cuttings grew callus after 50 days of cutting seedlings, rooting was visible after 60 days, and the average root length was 4.1cm after 70 days, the rooting rate was only 48.1%, and the survival rate after transferring to the arched shed for hardening was only 43.2%.
Embodiment 3
[0038] Embodiment 3: the cutting method of different kinds and concentration hormone treatment
[0039] In addition to selecting hormones according to the type and concentration in Table 1, other steps and environments refer to Example 1 and each treatment is consistent. The test results are shown in Table 1.
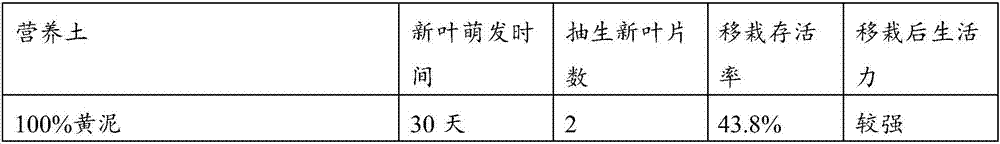
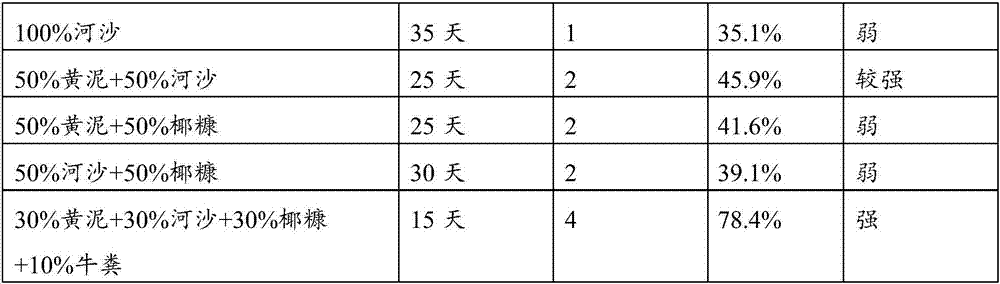
[0040] Table 1 Cutting breeding seedlings treated with different hormones
[0041] hormone healing time rooting time average root length Rooting rate Transplanting survival rate clear water 60 days 80 days 3.7cm 11.3% 9.91% 50mg / L naphthaleneacetic acid 45 days 55 days 4.8cm 57.3% 45.9% 100mg / L naphthaleneacetic acid 45 days 50 days 5.3cm 63.2% 55.4% 200mg / L naphthaleneacetic acid 40 days 50 days 6.7cm 71.5% 66.3% 300mg / L naphthaleneacetic acid 40 days 50 days 8.1cm 86.3% 80.7% 100mg / L indole butyric acid 50 days 60 days 4.9cm 56.1% 49.7% 200mg / L indole butyric acid 50 d...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com