Rice field non-point source pollution emission reducing and rice yield increasing method
A non-point source pollution and paddy field technology, applied to water pollutants, soil preparation methods, rice cultivation, etc., can solve the problems of low biochar utilization efficiency, increase crop yield, and biochar loss, so as to reduce the risk of non-point source pollution and improve Crop yield, effect of promoting growth and development
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
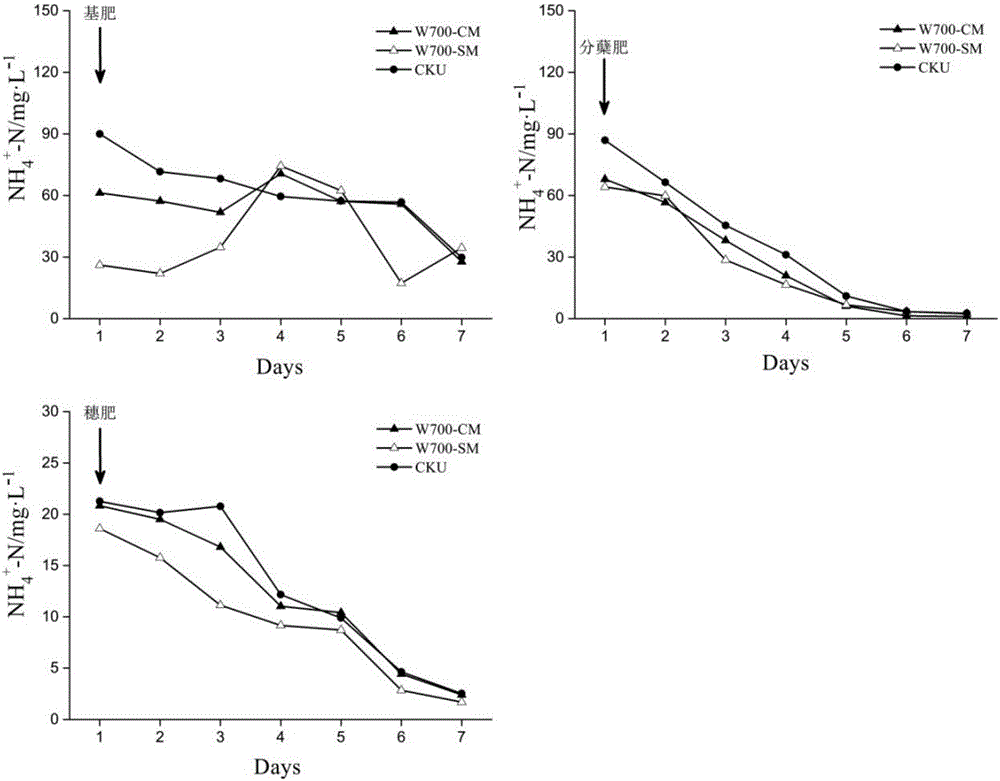
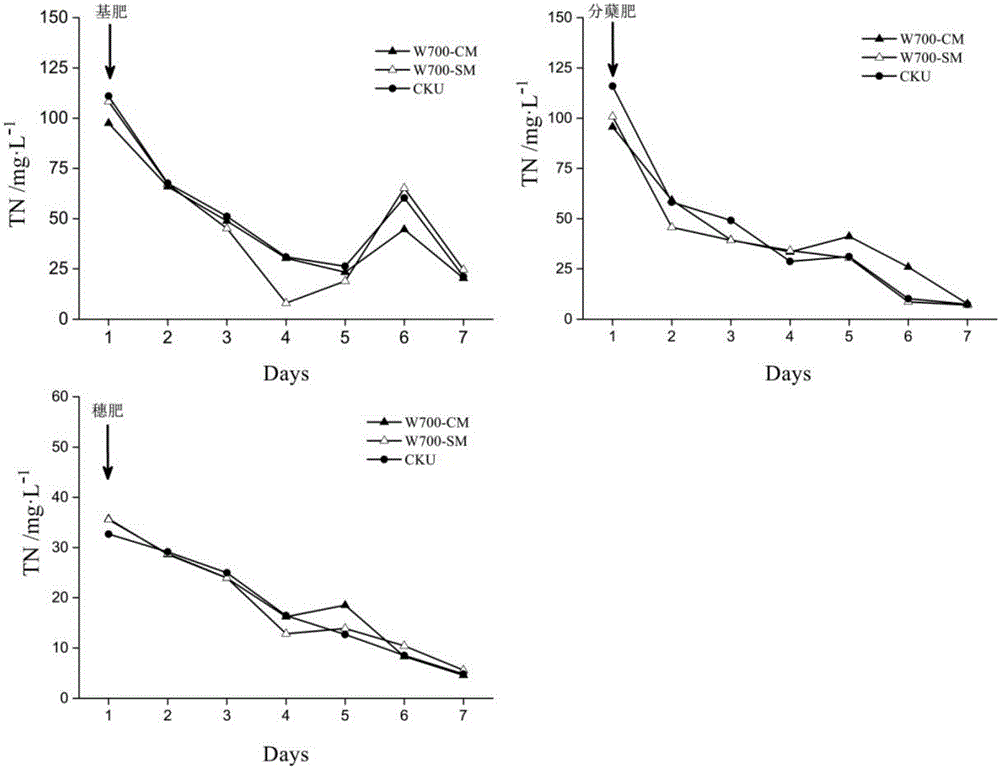
[0039] Embodiment 1 investigated the impact of a kind of paddy field non-point source pollution reduction and rice production increase measures on paddy field surface water nitrogen concentration (ammonia nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen and total nitrogen). In 2015, a rice pot experiment was established at the test field of Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences, and three treatments were set up, namely no application of biochar (CKU), conventional application of biochar (W700-CM, biochar application rate 0.5% w / w, The depth of application is 15cm), the biochar application scheme of the present invention (W700-SM, biochar application rate 0.5%w / w, soil-biochar buffer layer is 5cm, and wood vinegar pH=4.0, active ingredient 5% , the amount of wood vinegar to be applied is 100L / ha, the shallow plowing depth is 5cm, and the biochar is prepared from wheat straw at a preparation temperature of 700°C, and the specific surface area of biochar is 80m 2 / g, biochar covering layer 3cm). ...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2 Effects of the new rice field non-point source pollution reduction and rice production increase measures on the inhibition and control of ammonia nitrogen in the surface water of paddy fields
[0041] This embodiment has investigated the adsorption effect of a new type of paddy field non-point source pollution reduction and rice production increase measures on ammonia nitrogen ( figure 1 ). The specific operation mode of this embodiment is similar to that of Embodiment 1. After the application of basal fertilizer, tiller fertilizer and panicle fertilizer, compared with the application of fertilizer but no application of biochar, under the treatment of the new biochar application scheme, the ammonia nitrogen in the surface water of the paddy field decreased by an average of 33.57mg / L, while under the conventional application scheme, the surface water of the paddy field decreased by 33.57mg / L. Ammonia nitrogen decreased by an average of 16.1mg / L. The new bioch...
Embodiment 3
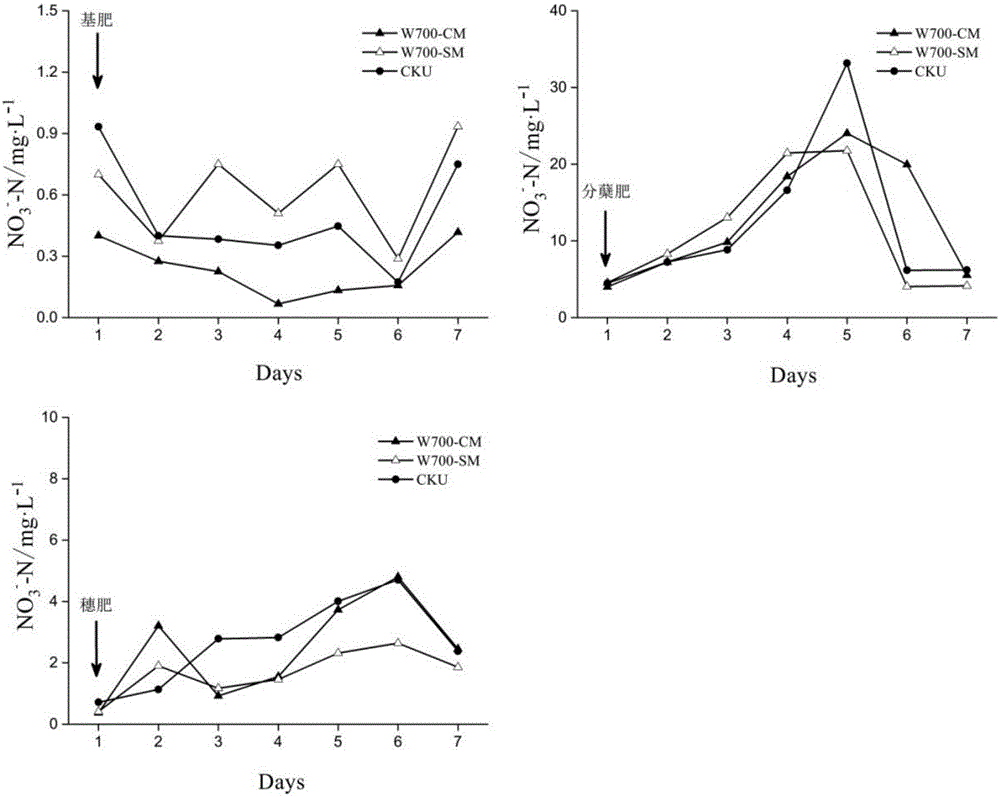
[0042] Example 3 Effects of novel paddy field non-point source pollution reduction and rice production increase measures on the inhibition and control of nitrate nitrogen in paddy field surface water
[0043] This embodiment has investigated the adsorption effect of a new type of paddy field non-point source pollution reduction and rice production increase measures on nitrate nitrogen ( figure 2 ). The specific operation mode of this embodiment is similar to that of Embodiment 1. After the application of basal fertilizer, tillering fertilizer and ear fertilizer, compared with the application of fertilizer but no application of biochar, under the treatment of the new biochar application scheme, the surface water nitrate nitrogen of the paddy field decreased by an average of 1.62mg / L, while under the conventional application scheme, the paddy field The average increase of nitrate nitrogen in field surface water was 0.43mg / L. The new biochar application scheme can significantl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com