Method for degrading sulfonamide compound by using pycnoporus sanguineus
A technology of Microporus hemoglobinus and sulfonamides, which is applied in the field of environmental pollution control, can solve the problems of poor repeatability, cumbersome procedures, high cost, etc., and achieves the effects of accurate repeatability, shortened fermentation time, and improved degradation rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] The method for degrading sulfonamides by Pycnoporus sanguineus includes the following steps:
[0026] (1) Seed culture: Pycnoporus sanguineus with the preservation number CGMCC 5.815 was cultured in potato dextrose agar solid medium at 28°C for 7 days; then transferred to potato dextrose liquid medium and cultured at 28°C For 48 hours, get the first-grade seeds of Pycnoporus sanguineus;
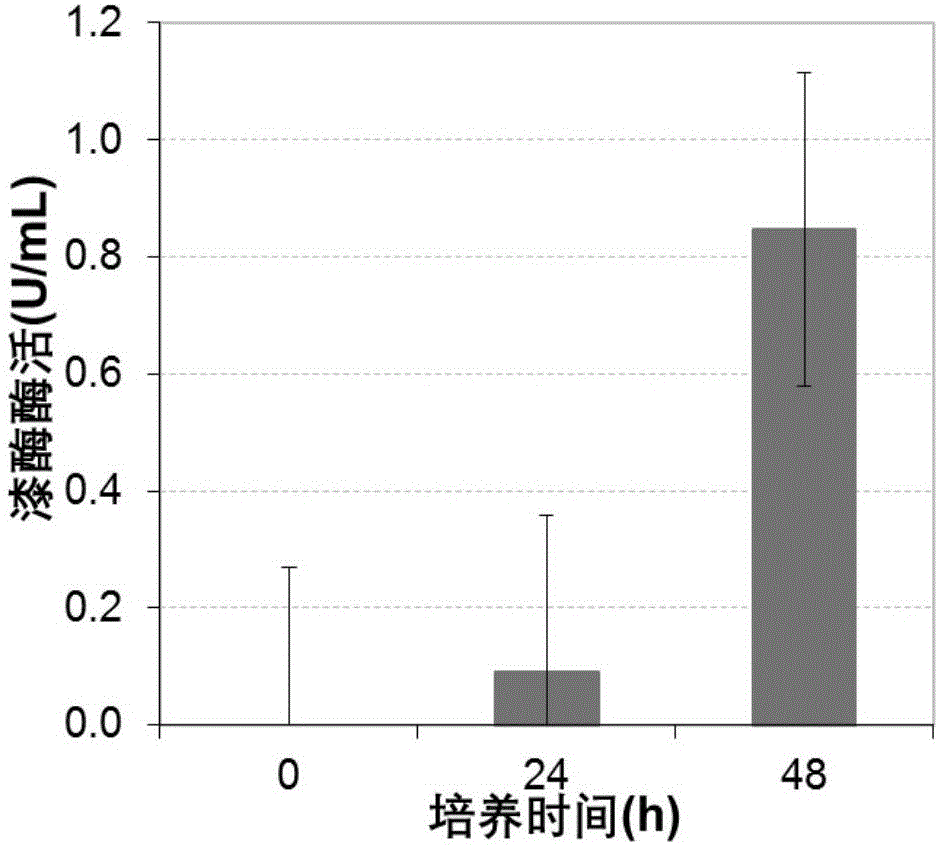
[0027] (2) Fermentation culture: Take 40 mL of the first-grade seed of P. sanguineus obtained in step (1), centrifuge at 8000 rpm for 10 min, discard the supernatant, and resuspend the bacteria in 460 mL fermentation medium at 28° C., 130 rpm, After 48 hours of fermentation, the laccase activity is 0.85U / mL, see figure 1 ;
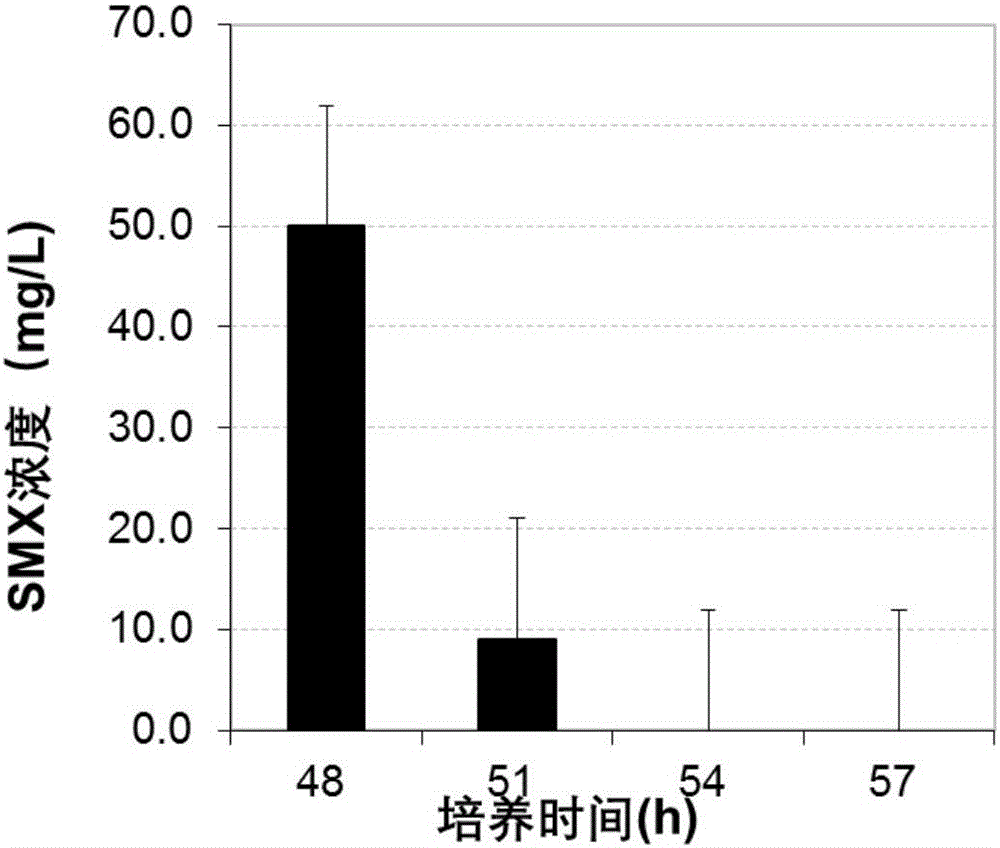
[0028] (3) Degradation of sulfa compounds: Mix sulfamethoxazole production wastewater with the fermentation broth obtained in step (2) to make the concentration of sulfamethoxazole 50mg / L, and add 2,2-diazo-bis(3) -Ethyl-benzothiazole-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt, m...
Embodiment 2
[0030] The method for degrading sulfonamide compounds with Pycnoporus sanguineus includes the following steps:
[0031] (1) Seed culture: Pycnoporus sanguineus with the deposit number CGMCC 5.815 was cultured in potato dextrose agar solid medium at 25°C for 8 days; then transferred to potato dextrose liquid medium at 25°C for 50 1 hour, get first-grade seeds of Pycnoporus sanguineus;
[0032] (2) Fermentation culture: Take 45 mL of the primary seeds of P. sanguineus obtained in step (1), centrifuge at 6000 rpm for 12 min, discard the supernatant, and resuspend the bacteria in 450 mL of fermentation medium. At 25° C., 100 rpm, Fermentation for 50h; laccase activity is 0.78U / mL;
[0033] (3) Degradation of sulfadiazine compounds: Mix the sulfadiazine production wastewater with the fermentation broth obtained in step (2) to make the concentration of sulfadiazine 20mg / L, and add 2,2-hydrazine-bis(3-ethyl- Benzothiazole-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt, the concentration is 0.4mM, and t...
Embodiment 3
[0036] The method for degrading sulfonamides by Pycnoporus sanguineus includes the following steps:
[0037] (1) Seed culture: Pycnoporus sanguineus with the preservation number CGMCC 5.815 was cultured in potato dextrose agar solid medium at 30°C for 6 days; then transferred to potato dextrose liquid medium and cultivated at 30°C 45 1 hour, get first-grade seeds of Pycnoporus sanguineus;
[0038] (2) Fermentation culture: Take 40 mL of the first-grade seed of P. sanguineus obtained in step (1), centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 8 min, discard the supernatant, and resuspend the bacteria in 500 mL of fermentation medium. At 30° C., 150 rpm, Fermentation for 40h; laccase activity is 0.92U / mL;
[0039] (3) Degradation of sulfa compounds: Mix sulfaisoxazole production wastewater with the fermentation broth obtained in step (2) to make the concentration of sulfisoxazole 35mg / L, and add 2,2-diazo-bis(3) -Ethyl-benzothiazole-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt, the concentration is 0.6mM, and the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com