Microcellular-foamed high-strength polypropylene composite material
A composite material, polypropylene technology, applied in the field of micro-foamed high-strength polypropylene composite materials, can solve the problems of high price, and achieve the effects of low cost, uniform cell distribution, and excellent physical and mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Weigh by weight: 100 parts of polypropylene, 0.001 part of tert-butyl peroxylaurate, 10 parts of K resin, NaHCO coated with polyurethane modified silicone resin 3 2 parts of foaming agent, 5 parts of talcum powder, 1 part of nonionic surfactant, cell stabilizer of propylene glycol fatty acid esters and calcium stearate, the particle size of talcum powder is 1000 mesh.
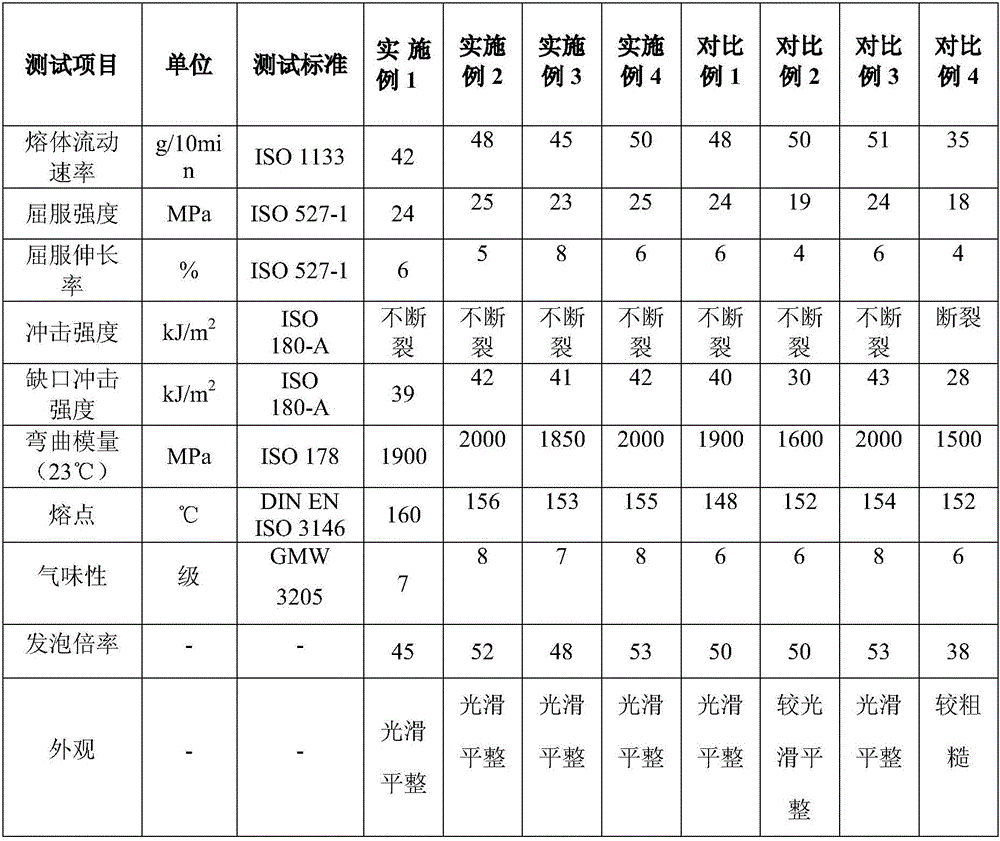
[0022] The polypropylene is melted first, then organic peroxide is added, and then the components other than the foaming agent are added to melt and blend to obtain the polypropylene matrix, and then the polypropylene matrix and the foaming agent are made into microplastics by injection molding. The foamed high-strength polypropylene composite material was subjected to a performance test of the prepared foamed material, and the test results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 2
[0024] Weigh in parts by weight: 100 parts of polypropylene, 0.006 parts of 2,5-dimethyl-2,5-bis(benzoylperoxy)hexane, 12 parts of K resin, polyalkylacrylate-coated NaHCO 3 3 parts of foaming agent, 10 parts of talcum powder, 3 parts of cell stabilizers of ethylene glycol and propylene glycol fatty acid esters and barium stearate, the particle size of talcum powder is 500 mesh.
[0025] The polypropylene is melted first, then organic peroxide is added, and then the components other than the foaming agent are added to melt and blend to obtain the polypropylene matrix, and then the polypropylene matrix and the foaming agent are made into microplastics by injection molding. The foamed high-strength polypropylene composite material was subjected to a performance test of the prepared foamed material, and the test results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0027] Weigh by weight: 100 parts of polypropylene, 0.003 parts of tert-butylperoxyisopropyl monocarbonate, 10 parts of K resin, NaHCO coated with polyurethane modified silicone resin 3 5 parts of foaming agent, 15 parts of talcum powder, 3 parts of pentaerythritol glycerol, cell stabilizer of propylene glycol fatty acid esters and calcium stearate, the particle size of talcum powder is 3000 mesh.
[0028] The polypropylene is melted first, then organic peroxide is added, and then the components other than the foaming agent are added to melt and blend to obtain the polypropylene matrix, and then the polypropylene matrix and the foaming agent are made into microplastics by injection molding. The foamed high-strength polypropylene composite material was subjected to a performance test of the prepared foamed material, and the test results are shown in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Cell diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com