Volatile component measuring method for Tibetan medicine heracleum millefolium diels
A technology of volatile components and determination methods, which is applied in the field of medicinal material detection, can solve the problems of cumbersome and complicated extraction and purification operations, easy loss of volatile components, and distortion of sample information, so as to avoid distortion of detection information, high degree of automation, and reliable results. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
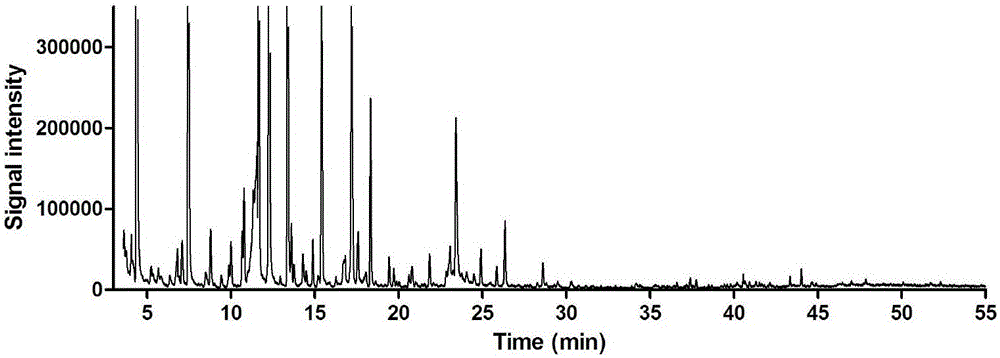
[0037] The method for the determination of volatile components in the root of the Tibetan medicinal material Lola lobata comprises the following steps:
[0038] 1) Sample pulverization: take the root of the lobster leaf and pulverize it into medicinal material powder (through a 200-mesh sieve);
[0039] 2) Headspace sampling: Weigh 0.2000 g of the above medicinal material powder, put it directly into a 20 ml headspace bottle and seal it in a sample tray. The heating temperature of the sample vial is 100 °C, and the equilibration time is 40 min; 1 mL of the gas in the headspace of the vial is injected into the GC-MS system, the temperature of the quantitative loop is 120 °C, and the temperature of the transfer line is 140 °C;
[0040] 3) Separation and detection by GC-MS system: separation by gas chromatography and detection by mass spectrometry.
[0041] Among them, gas chromatography conditions: HP-5 capillary column elastic chromatography column (0.25μm×250μm×30m); carrier ...
Embodiment 2
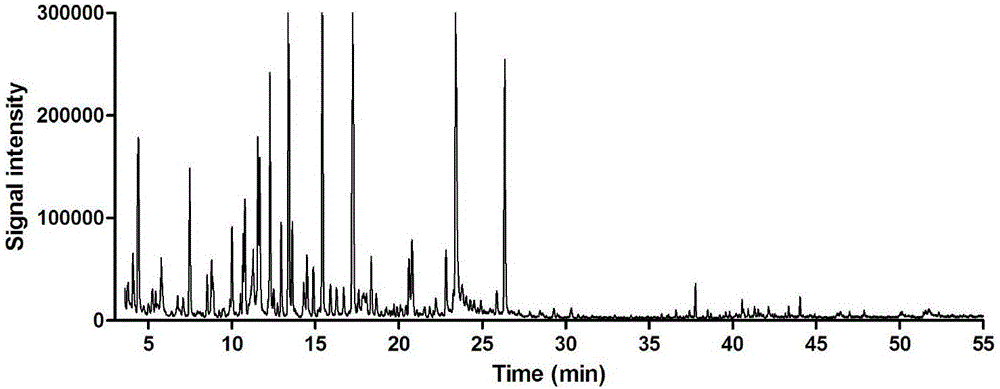
[0046] The determination method of the volatile components in the stems of the Tibetan medicinal herb L. chinensis comprises the following steps:
[0047] 1) Sample pulverization: take the stem of the lobed leaf and pulverize it into medicinal material powder (through a 300-mesh sieve);
[0048]2) Headspace sampling: Weigh 0.2500 g of the above medicinal material powder, put it directly into a 20 ml headspace bottle and seal it in a sample tray. The heating temperature of the sample bottle is 60°C, and the equilibration time is 120min; 1mL of the gas in the headspace of the sample bottle is injected into the GC-MS system, the temperature of the quantitative loop is 80°C, and the temperature of the transfer line is 100°C;
[0049] 3) Separation and detection by GC-MS system: separation by gas chromatography and detection by mass spectrometry.
[0050] Among them, gas chromatography conditions: HP-5 capillary column elastic chromatography column (0.25μm×250μm×30m); carrier gas:...
Embodiment 3
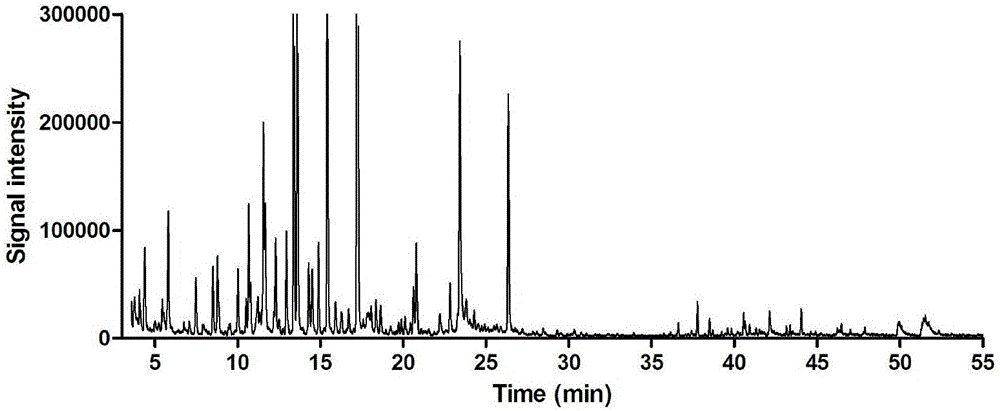
[0054] The method for the determination of volatile components in the leaves of the Tibetan medicinal herb Cracked Leaf, comprises the following steps:
[0055] 1) Sample pulverization: take the leaves of Cracked Leaves and pulverize them into medicinal material powder (pass through a 400-mesh sieve);
[0056] 2) Headspace sampling: Weigh 0.1500 g of the above medicinal material powder, put it directly into a 20 ml headspace bottle and seal it in a sample tray. The heating temperature of the sample vial is 200 °C, and the equilibration time is 10 min; 1 mL of the gas in the headspace of the vial is injected into the GC-MS system, the temperature of the quantitative loop is 180 °C, and the temperature of the transfer line is 180 °C;
[0057] 3) Separation and detection by GC-MS system: separation by gas chromatography and detection by mass spectrometry.
[0058] Among them, gas chromatography conditions: HP-5 capillary column elastic chromatography column (0.25μm×250μm×30m); c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com