Multifunctional regenerative blood purification system
A kind of blood purification and multi-functional technology, applied in dialysis system, blood circulation treatment, drug equipment and other directions, can solve the problems of high price of liver support system, adsorption of particles into the human body, loss of self-albumin, etc., to achieve reuse, The effect of shortening the treatment time and balancing the electrolyte concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
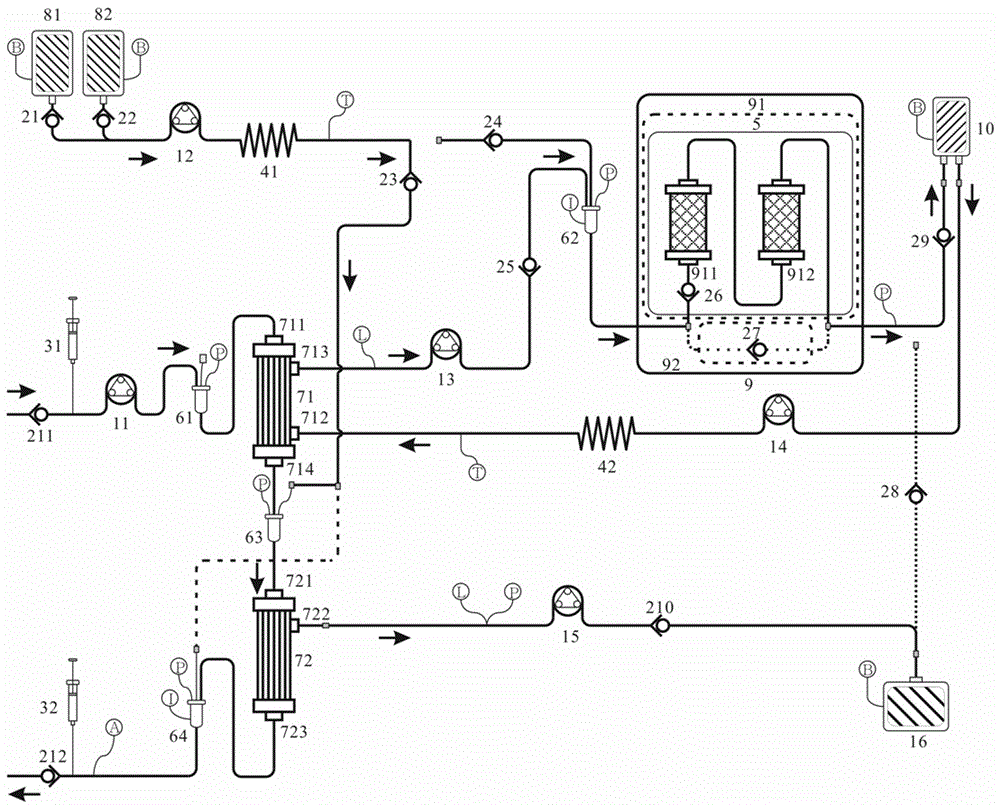
[0081] Used to remove toxins from the blood while requiring regeneration of toxin-bound albumin, see figure 1 , figure 2 and Figure 4 ;
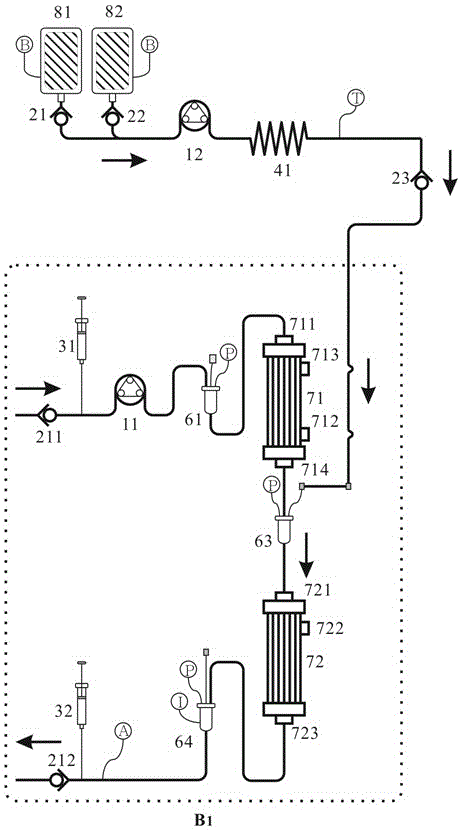
[0082] Depend on Figure 4 It can be seen that in step (6) when removing excess water and water-soluble medium and small molecular toxins in the blood through the blood purification module, the B2 post-dilution mode is adopted, and the blood that has been adsorbed or not adsorbed to remove albumin-bound toxins can also be processed The third arterial jug 63 directly flows into the second high-flux dialyzer 72 to remove excess water and water-soluble small and medium molecular toxins in the blood, and then flows into the venous jug 64 while the dialysate replenishment mechanism replenishes the dialysate.
[0083] Other steps (1), step (2), step (3), step (4), and step (5) are the same as those in embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0085] Used to remove toxins from the blood while requiring regeneration of toxin-bound albumin, see figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3 and Figure 4 .
[0086] Depend on image 3 and Figure 4 It can be seen that in step (6) when removing excess water and water-soluble medium and small molecular toxins in the blood through the blood purification module, the B1 pre-dilution mode and the B2 post-dilution mode are adopted at the same time, and the adsorption or non-adsorption removal is combined with albumin Toxic blood passes through the third arterial jug 63 and replenishes the dialysate through the dialysate replenishment mechanism, then flows into the second high-flux dialyzer 72 to remove excess water and water-soluble small and medium molecular toxins in the blood, and then flows into the venous jug 64 At the same time, the dialysate is replenished by the dialysate replenishment mechanism.
[0087] Other steps (1), step (2), step (3), step (4), and step (5) are the same...
Embodiment 4
[0089] For blood purification only, without regeneration of toxin-bound albumin, see figure 1 , figure 2 and image 3 , dialysis check valve 21, replacement check valve 22, purification check valve 23, first drug intake check valve 25, bypass check valve 27, third drug intake check valve 29, waste liquid check valve 210, input The one-way valve 211 and the output one-way valve 212 are opened, and the working principle is as follows:
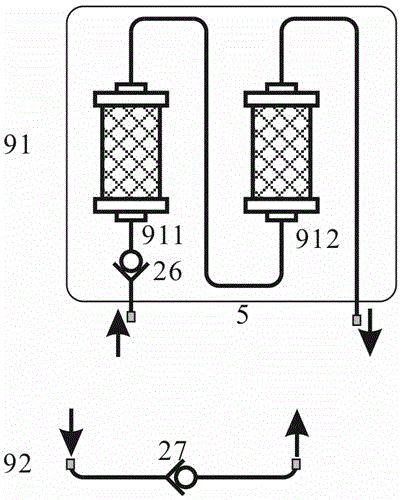
[0090] see figure 2 , after step (1) in Example 1, when it is not necessary to recover the albumin bound to the toxin, step (2) then the toxin-containing solution flows into the toxin adsorption device 9 through the second arterial pot 62, and in the toxin adsorption device In 9, the toxin in the toxin solution directly flows through without being adsorbed in the working mode in which the bypass check valve 27 is connected in series.
[0091] Other steps (1), step (3), step (4), step (5), and step (6) are the same as in embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com