A kind of method for preparing rare earth permanent magnet material
A rare-earth permanent magnet and rare-earth-rich alloy technology, which is applied in the direction of magnetic materials, inorganic materials, magnetic objects, etc., can solve the problems of small magnet grains, low material utilization rate, and high material utilization rate, and achieve small product deformation and high material utilization. High utilization rate and good fluidity of magnetic powder
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] 1. Change the composition to Nd 26.25 PR 8.75 Fe 64 B 1 (mass percentage content) of sintered NdFeB blank mechanically crushed into particles with an average particle diameter of 200 μm;
[0027] 2. Apply a magnetic field of 1T, the size of the green body is R8.1×R3.6×10, and the weight of the green body is 29.97g;
[0028] 3. Put the green body in the cavity of the pressure sintering mold, the pressure sintering mold is in a closed space, first evacuate to 8×10 -3 Pa, then filled with argon to 8×10 4 Pa, then raise the temperature to 850°C, pressurize 200MPa along the thickness direction of the sintered NdFeB green body, hold the pressure for 6 minutes, and then cool it out;
[0029] 4. Put the pressure-sintered magnet into a vacuum furnace for heat treatment, and heat-treat the hot-pressed blank by using 900°C for 4 hours and 500°C for 4 hours to obtain a specification of R8.1×R3.6×5.3 High-quality magnets have a material utilization rate of 100%, no corner crac...
Embodiment 2
[0031] will be composed as Nd 26.25 PR 8.75 Fe 64 B 1 (mass percent content) sintered NdFeB blanks are mechanically broken into particles with an average particle size of 50 μm. Add 5% Nd to polycrystalline NdFeB particles 70 Cu 30 (mass percent content) rare earth-rich alloy powder, wherein the average particle diameter of the neodymium-copper alloy powder is 3 μm. The temperature during pressure sintering was 700° C., and other processes were the same as in Example 1.
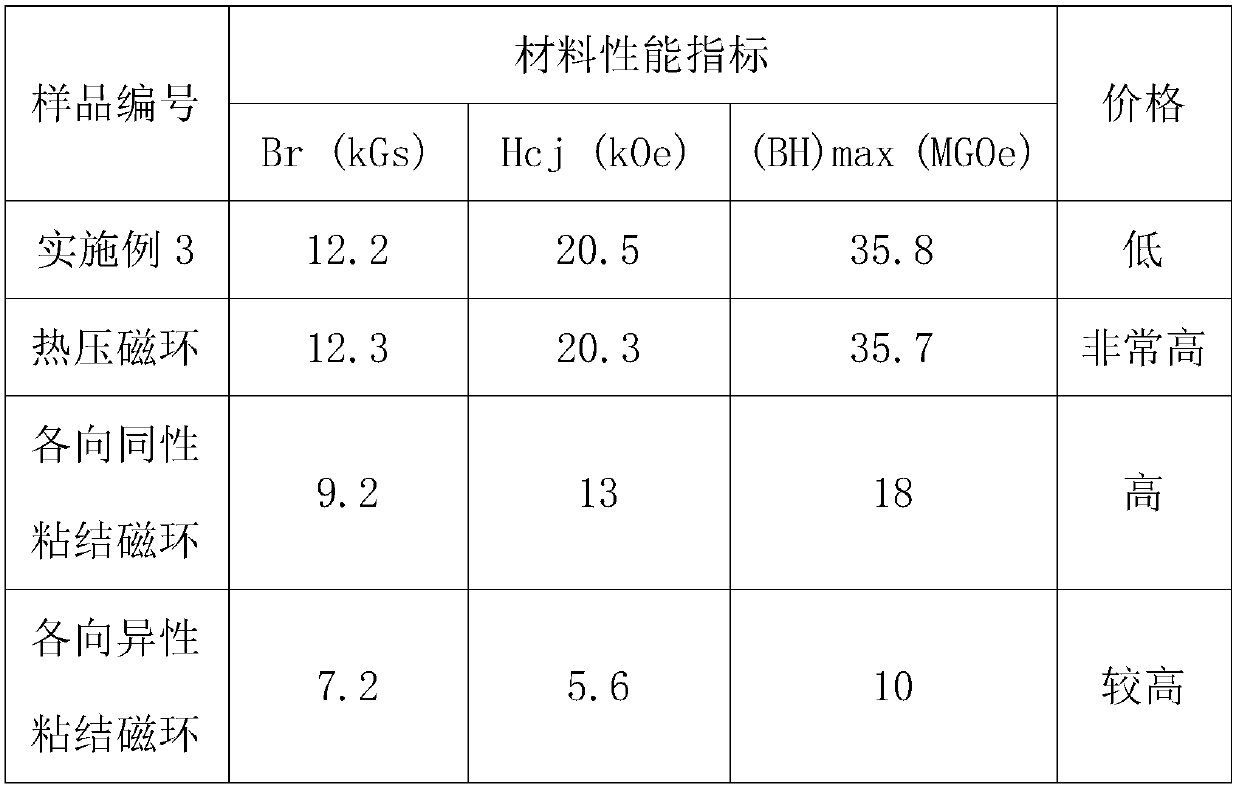
Embodiment 3
[0033] Wash and dry the leftovers of sintered NdFeB and break them into 300μm polycrystalline particles, then add 5% Nd 70 Cu 30 (mass percentage content) the rare earth-rich alloy powder, the average particle diameter of the neodymium-copper alloy powder is 3 μm. A circular green body of φ30×φ24×20 was prepared by orientation with a 0.5T radiation magnetic field. The temperature during pressure sintering is 650 degrees centigrade, and other processes are the same as in embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com