Biocompatible cross-linking micro-nano material for drug encapsulation and sustained release and preparation technology of biocompatible cross-linking micro-nano material for drug encapsulation and sustained release
A biocompatible, micro-nano technology, applied in the field of biocompatible cross-linked micro-nano materials for drug loading and sustained release and its construction technology, can solve threats, poor biocompatibility, environment and Human health hazards and other issues, to achieve the effect of easy storage, stable storage, and low energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
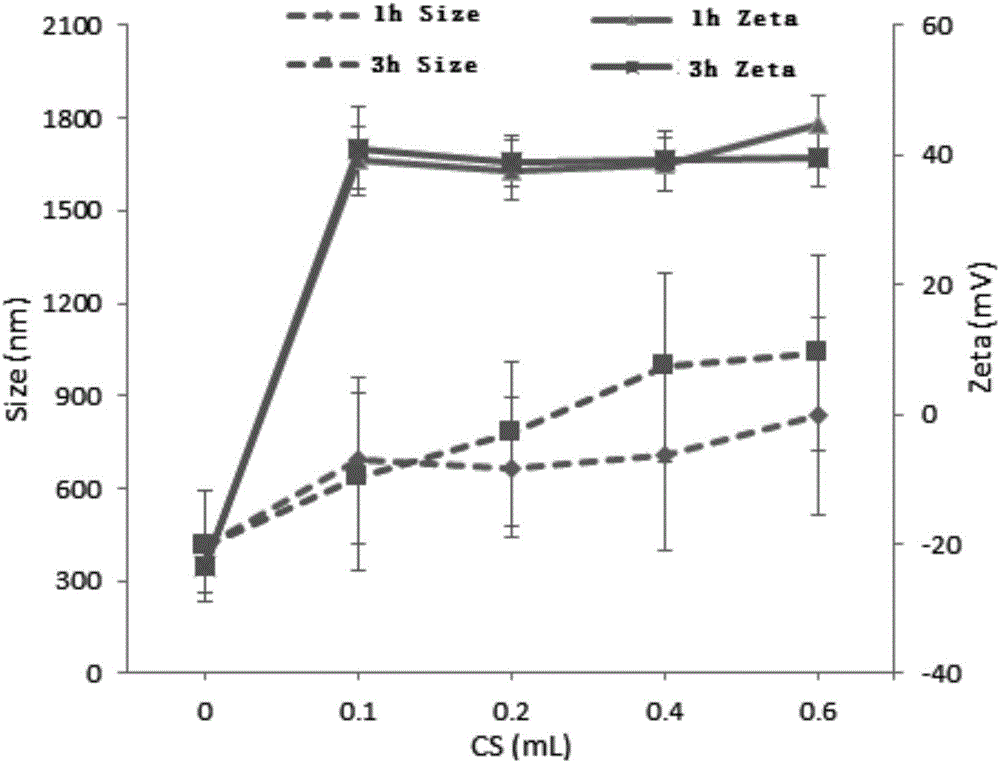
[0031] Example 1: Take 4 tubes of 1 ml polyacrylate nanoparticles, add 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6 ml of 5% chitosan solution in sequence, mix for 1 hour and 3 hours at the same time, and centrifuge to separate the polyacrylate nanoparticles Particles, and the uncoated chitosan was washed with pure water, and after concentration, the polyacrylate nanoparticles were redispersed in phosphate (PPS) buffer for storage. Measure the particle size and potential before and after crosslinking with a particle size analyzer, and the results are shown in the attached figure 1 As shown, the particle size and surface potential of polyacrylate nanoparticles changed to varying degrees after encapsulation.
Embodiment 2
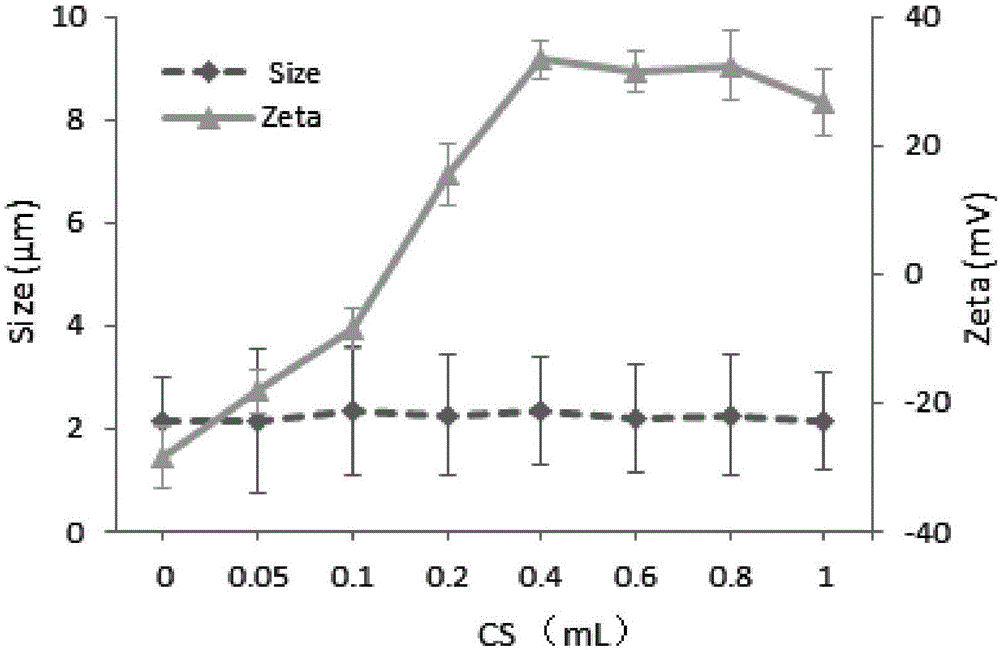
[0032] Example 2: Take 7 tubes of 1 ml polyacrylate microbubbles respectively, add 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0 ml of 5% chitosan solution in sequence, and mix for 3 hours at the same time, then centrifuge to separate the microbubbles Bubble, and wash the uncoated chitosan with pure water, redisperse the polyacrylate microbubbles in phosphate (PPS) buffer after concentration, and store them. Measure particle size and potential before and after crosslinking with particle counter and particle size analyzer, the results are as attached figure 2 The particle size and potential of polyacrylate microbubbles changed to varying degrees after encapsulation.
Embodiment 3
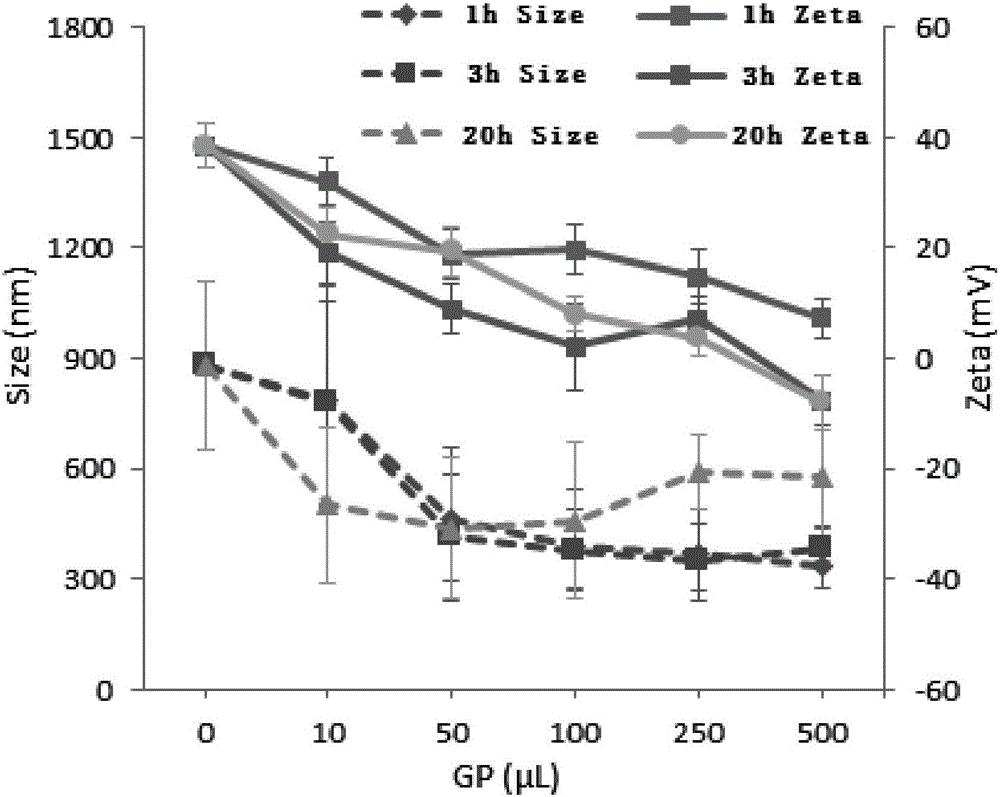
[0033] Example 3: Take 5 tubes of 1 ml chitosan-wrapped polyacrylate nanoparticles, add 10, 50, 100, 250, 500 microliters of 0.1 moles per liter of genipin solution in sequence, and mix for 1 hour, 3 hours and 20 hours Finally, the polyacrylate nanoparticles were separated by centrifugation, and the uncrosslinked genipin was washed with pure water, and after concentration, the polyacrylate nanoparticles were redispersed in phosphate (PPS) buffer for storage. Measure the particle size and potential before and after crosslinking with a particle size analyzer, and the results are shown in the attached image 3 As shown, the particle size and surface potential of polyacrylate nanoparticles changed to varying degrees after crosslinking.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com