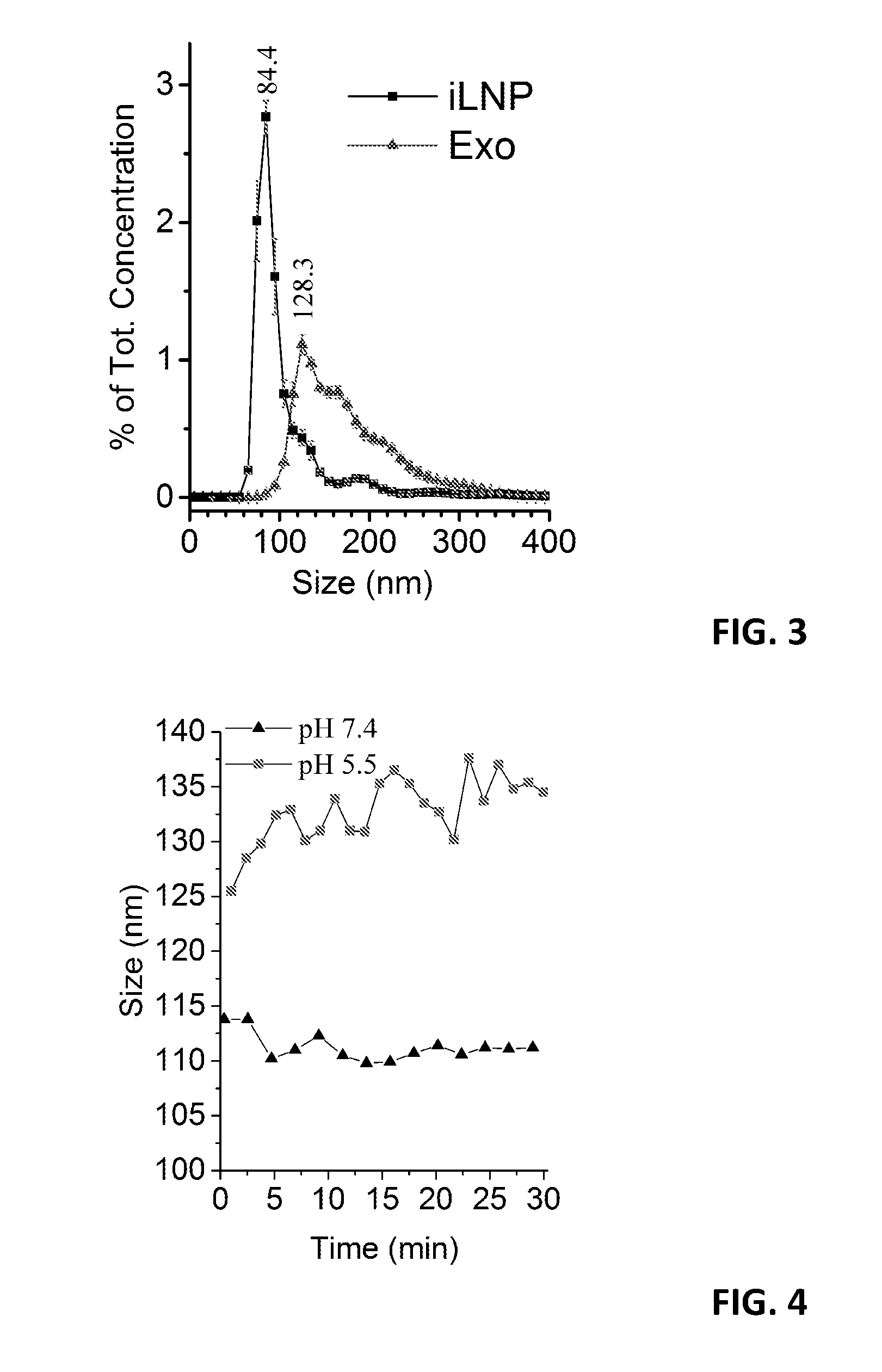
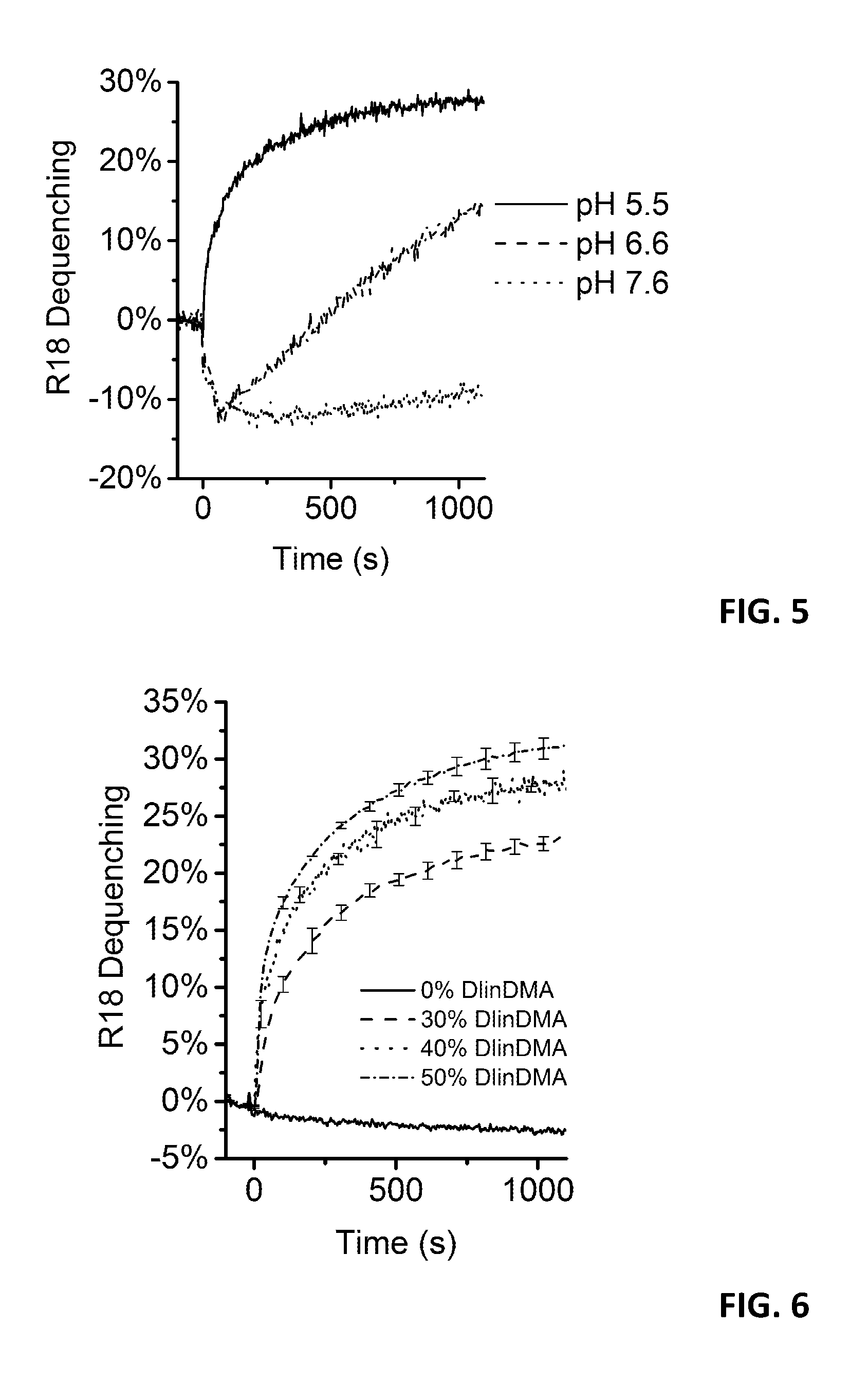
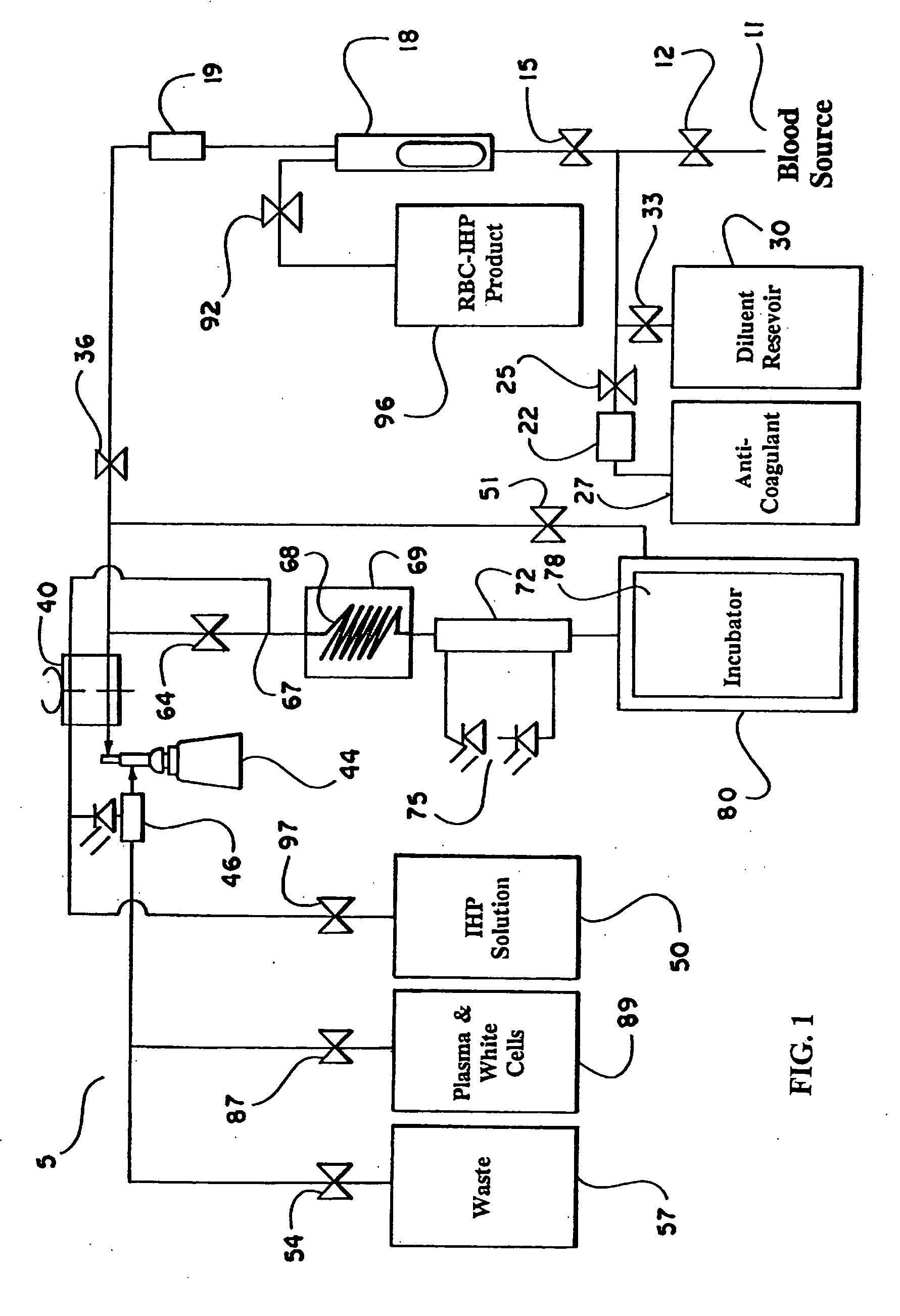
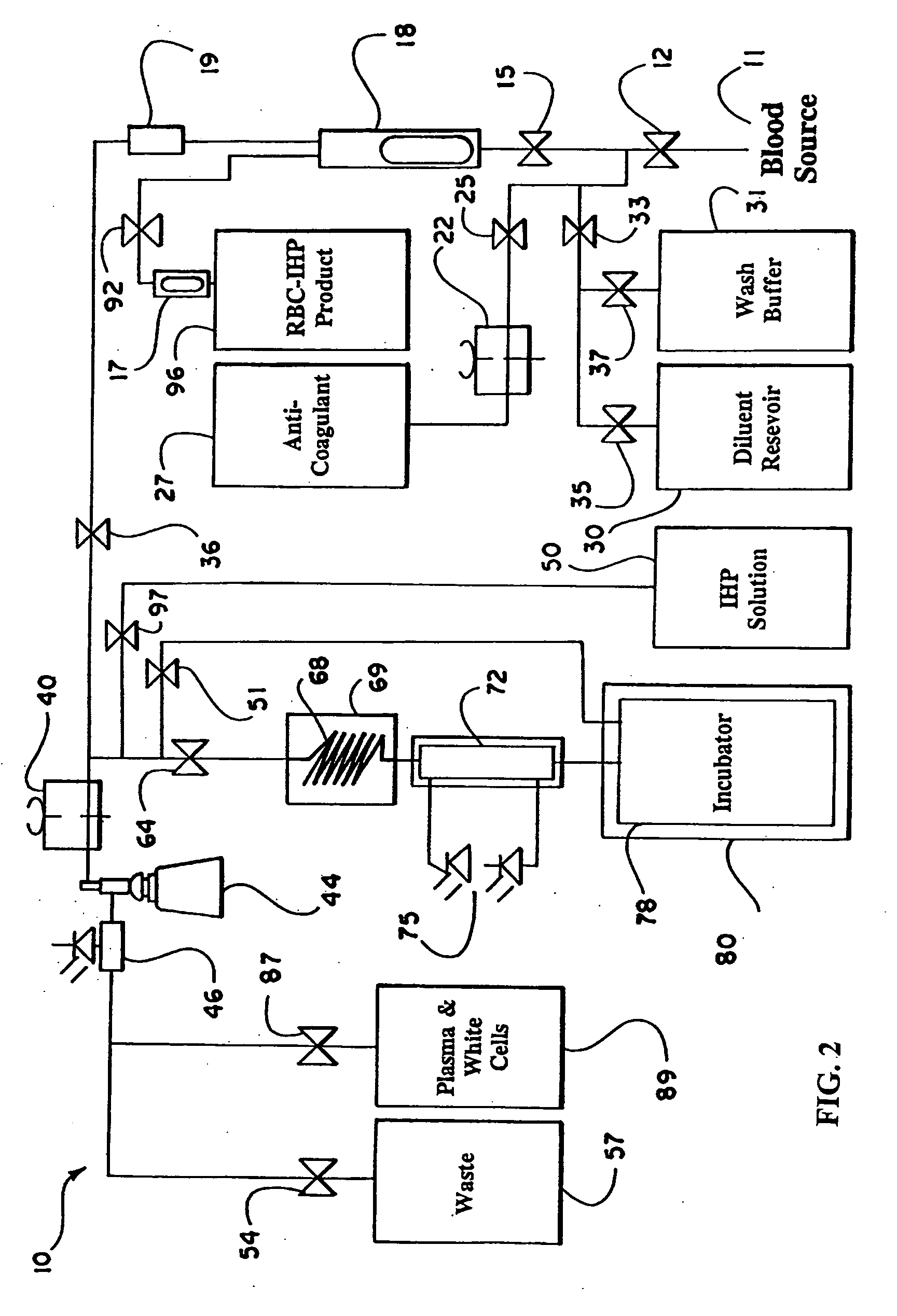
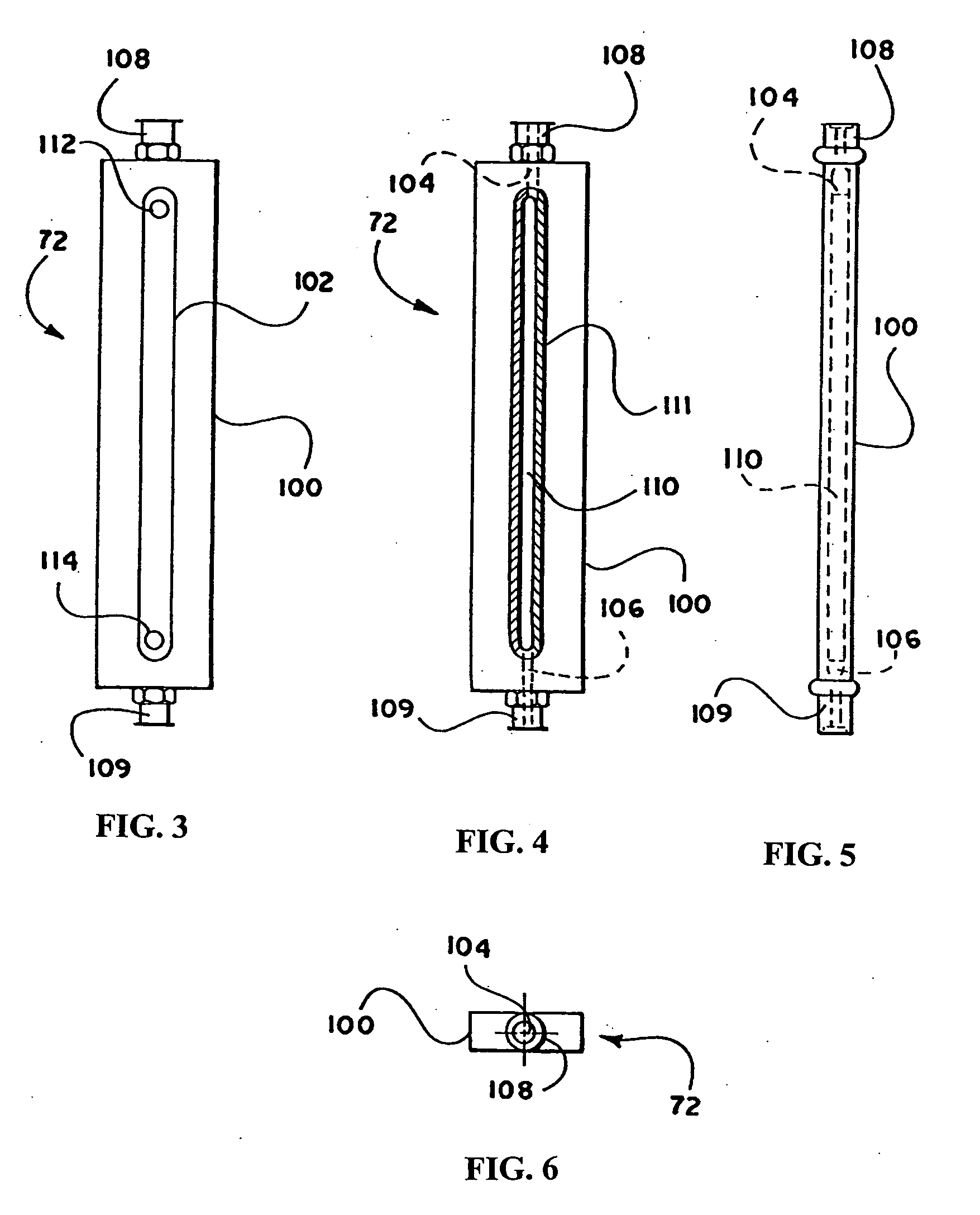
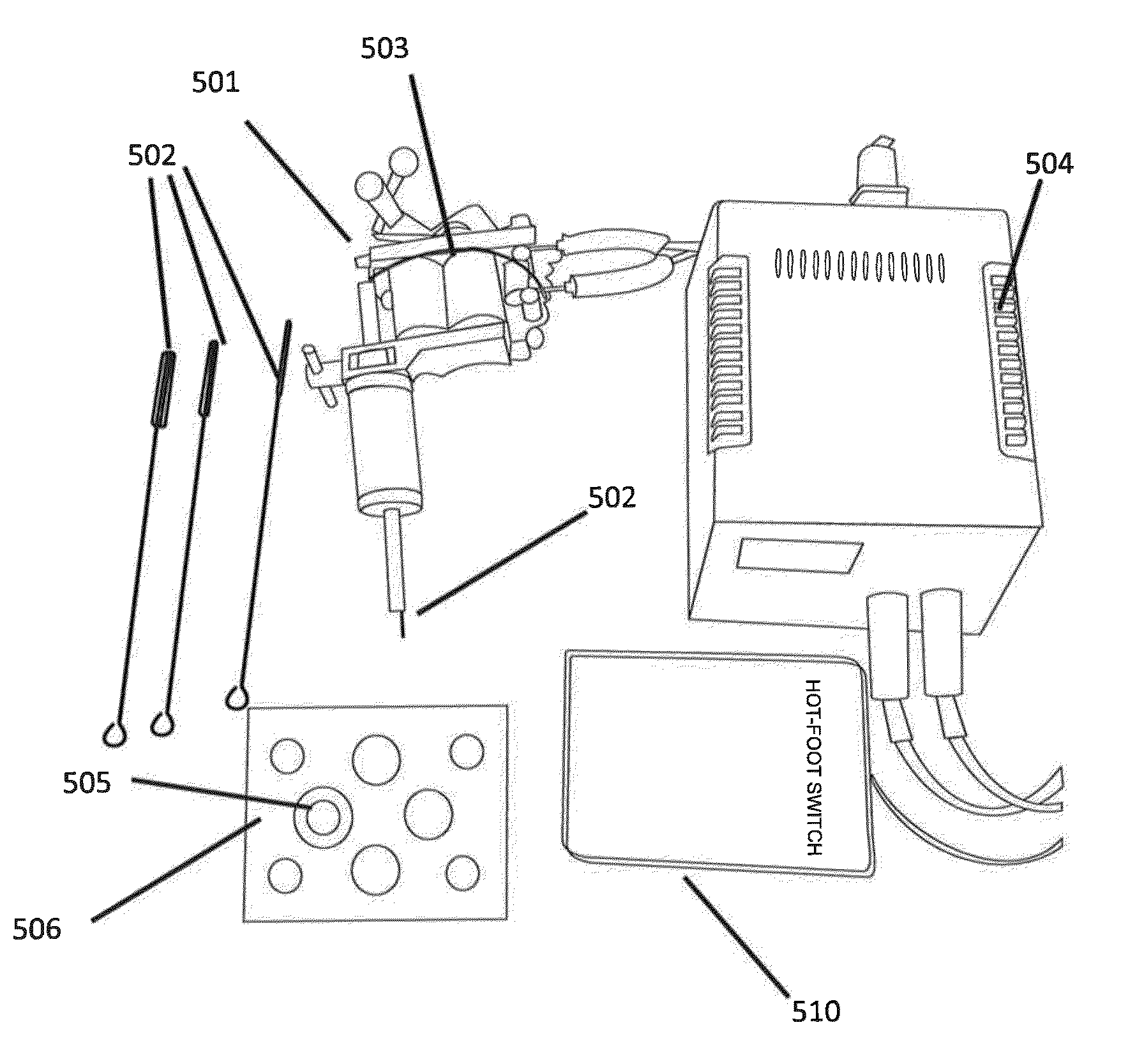
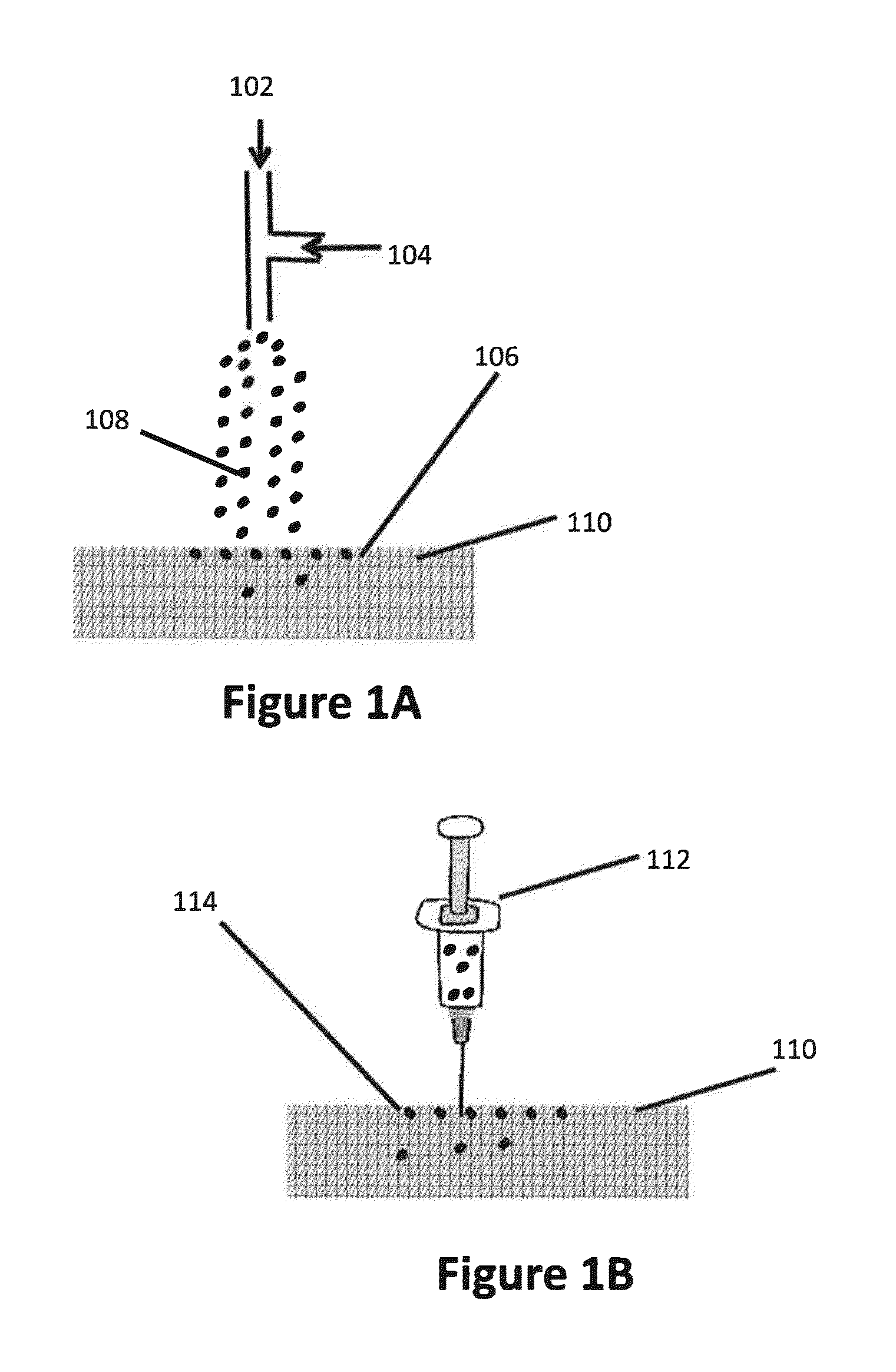
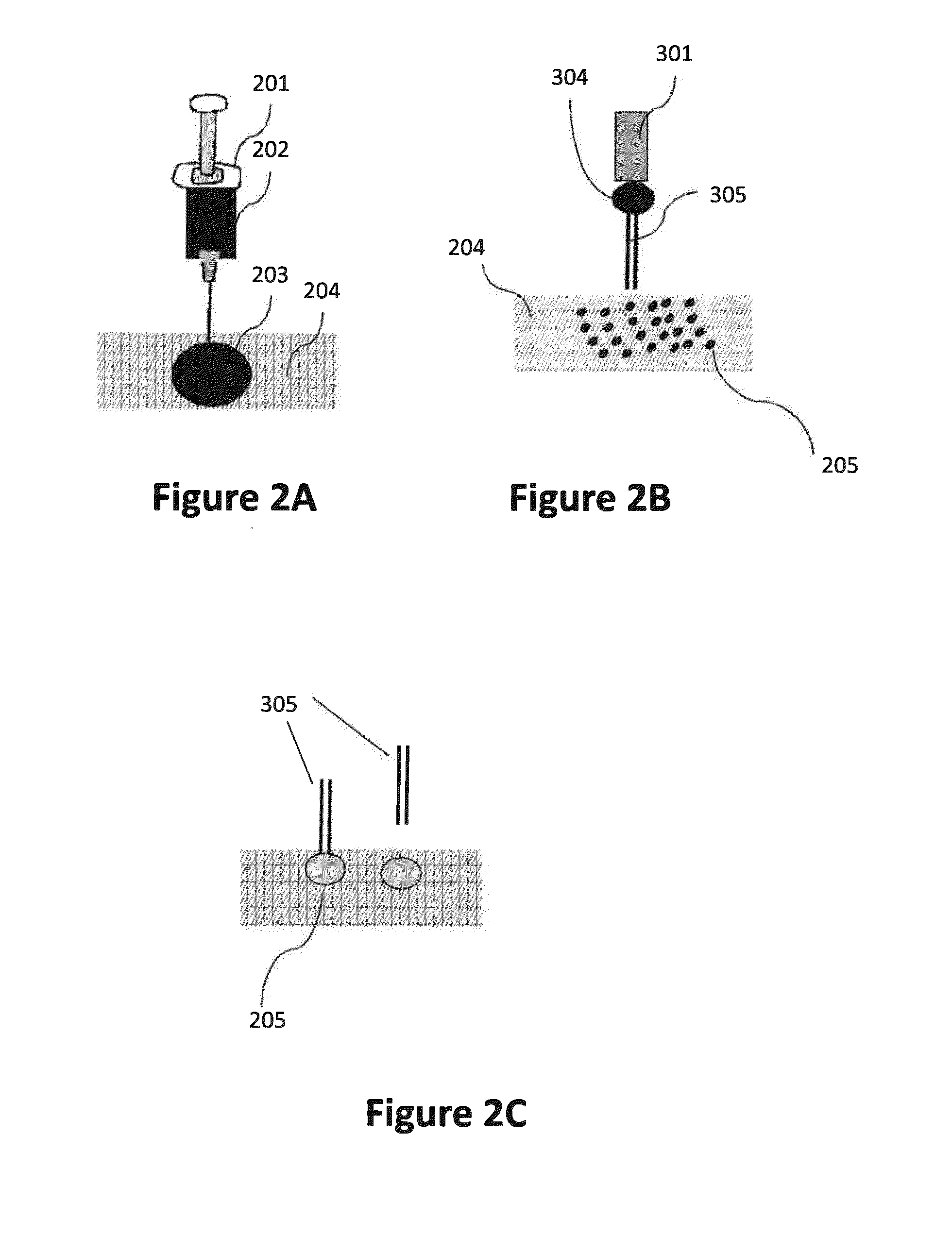
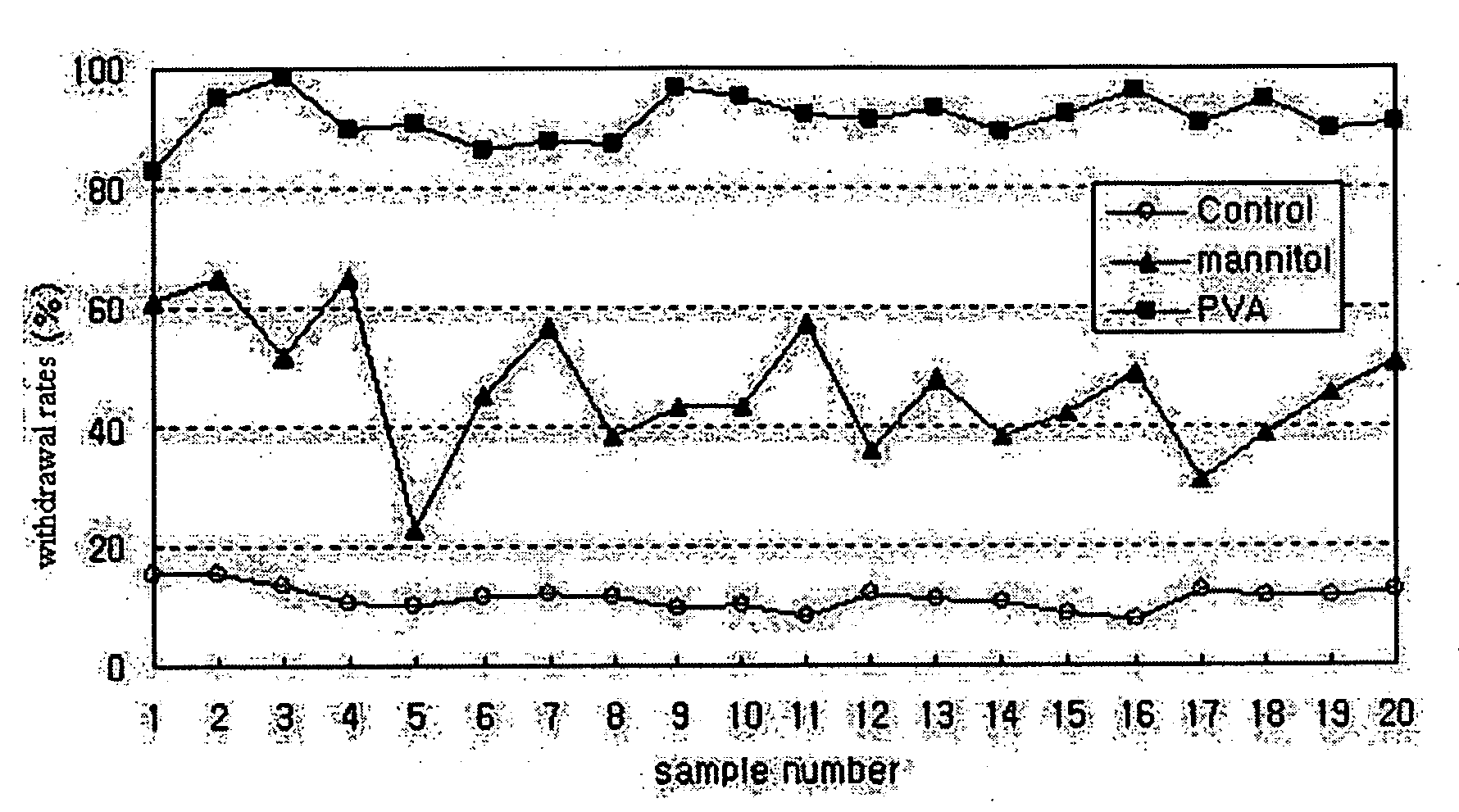
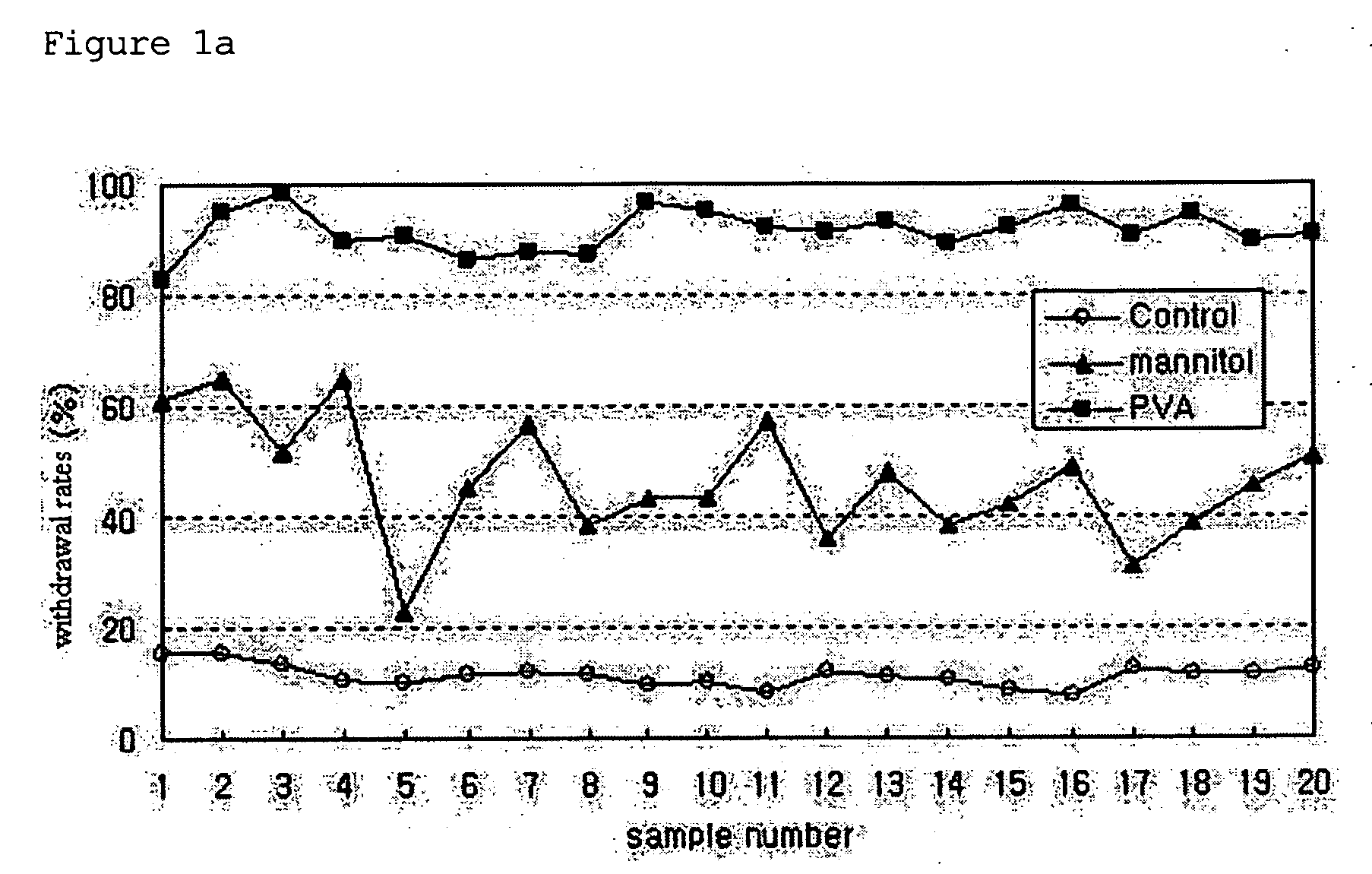
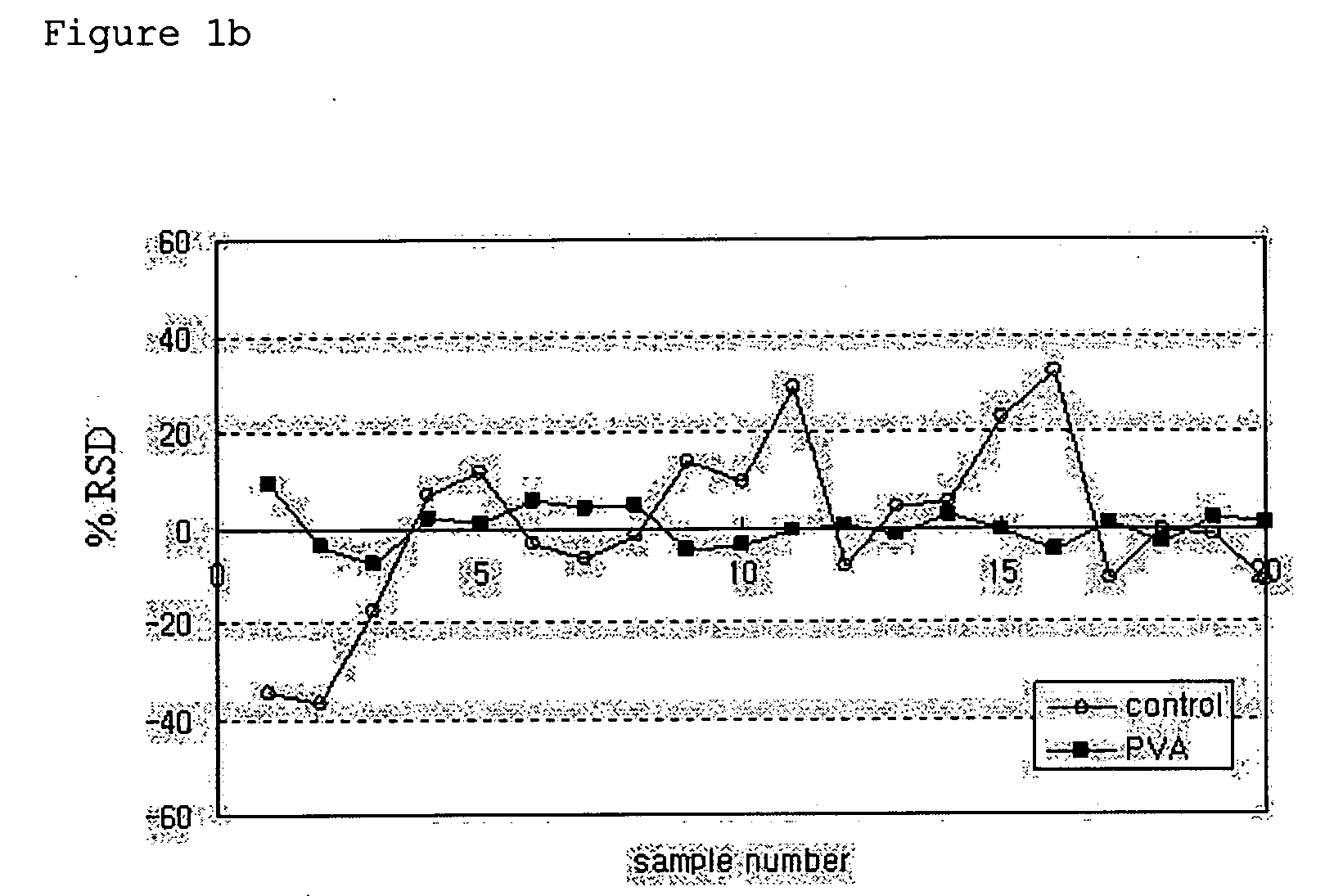
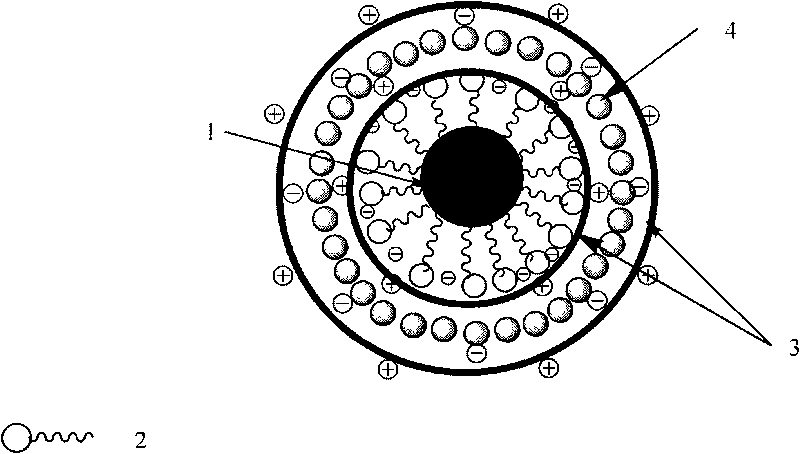
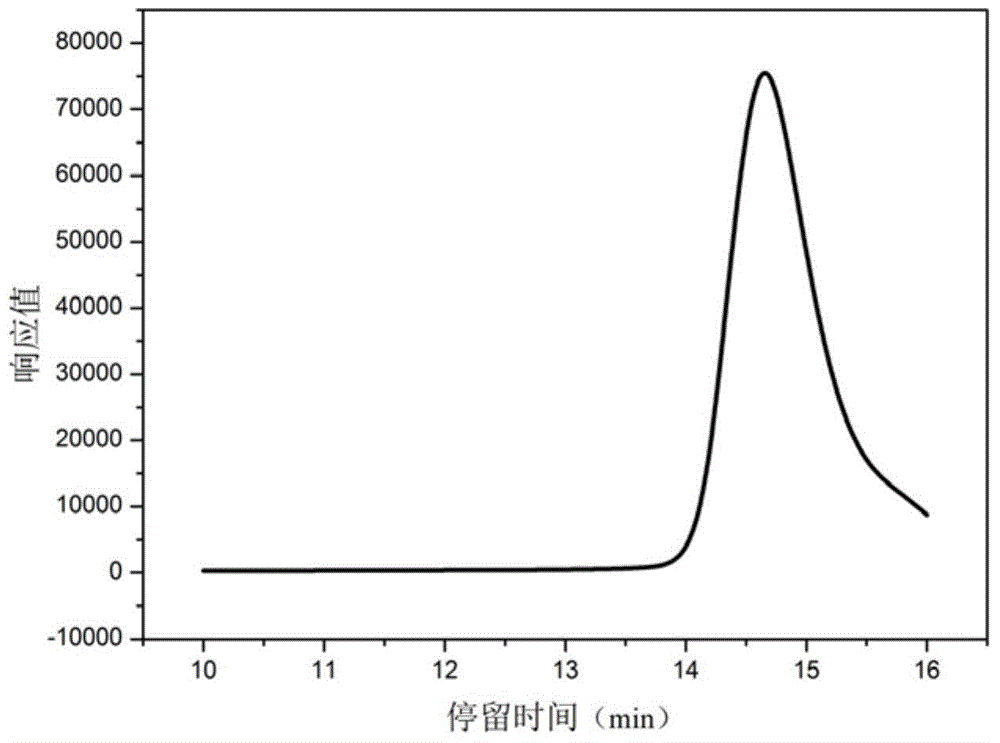
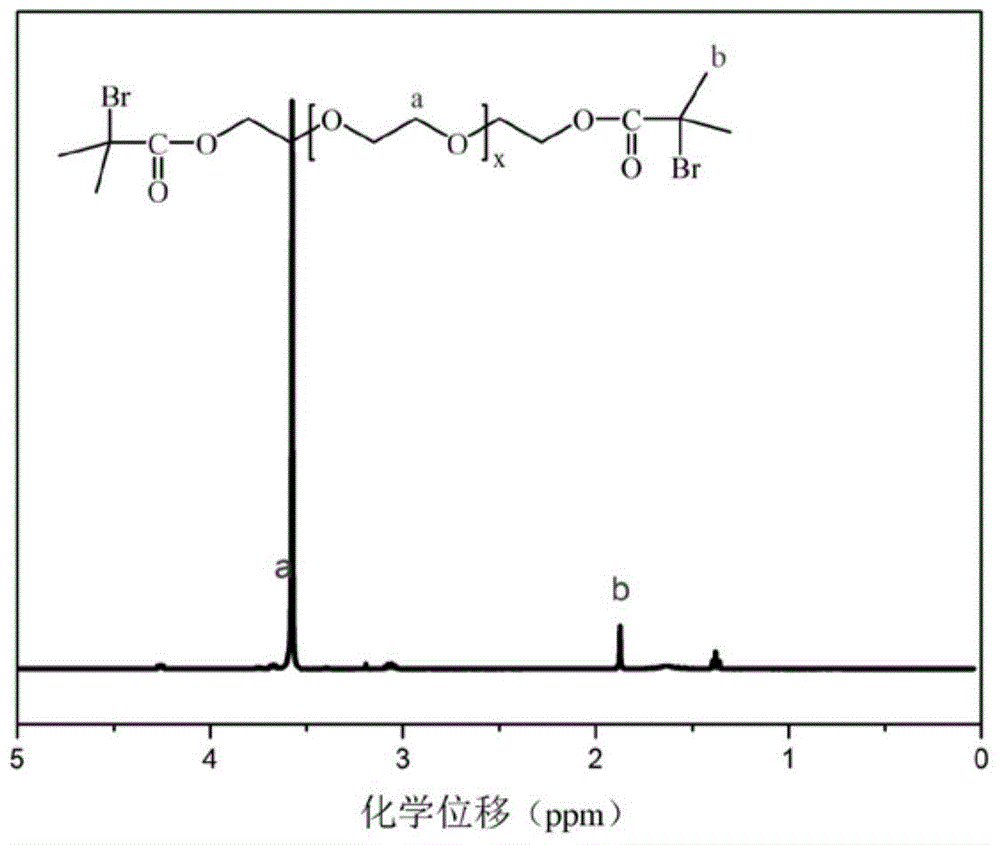
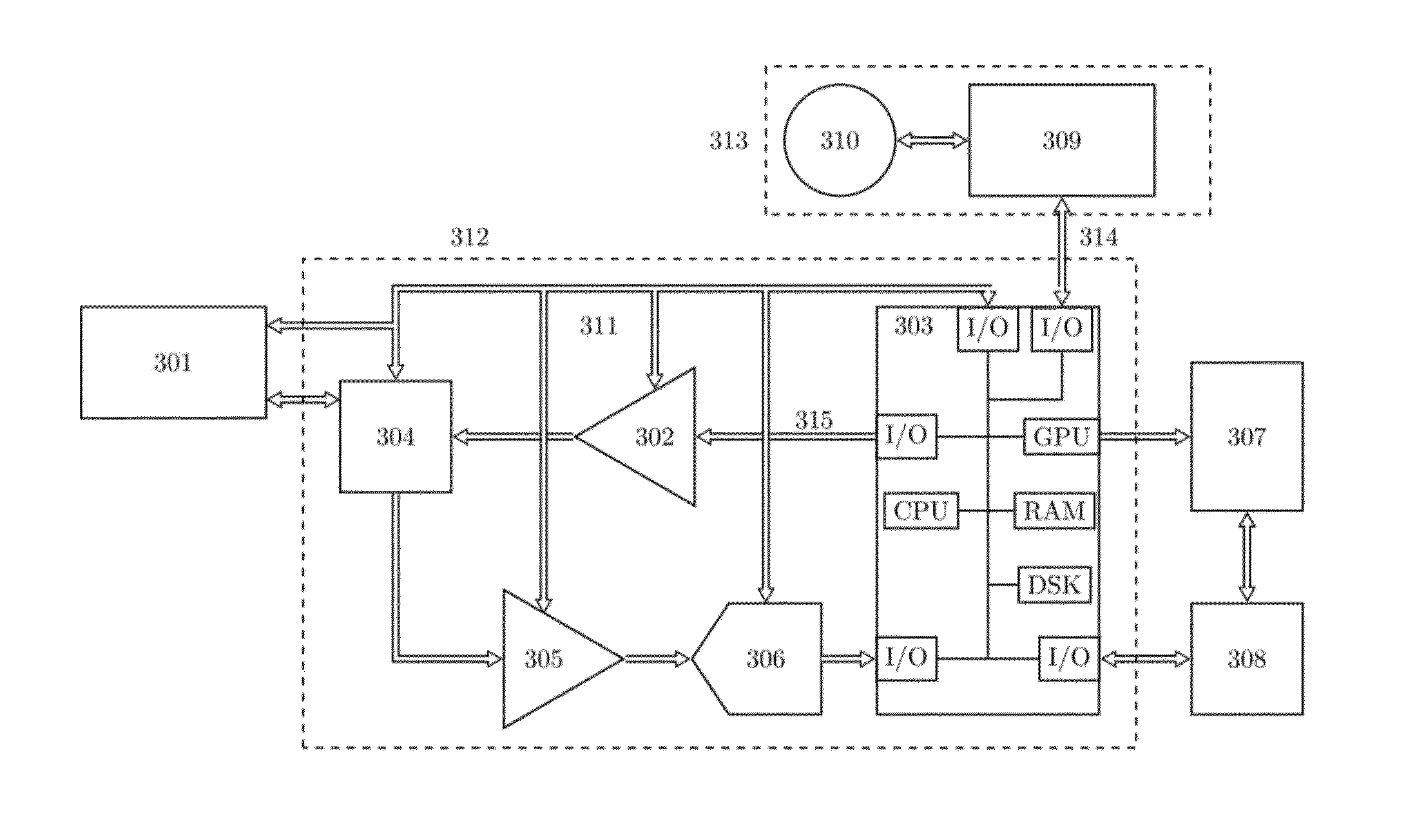
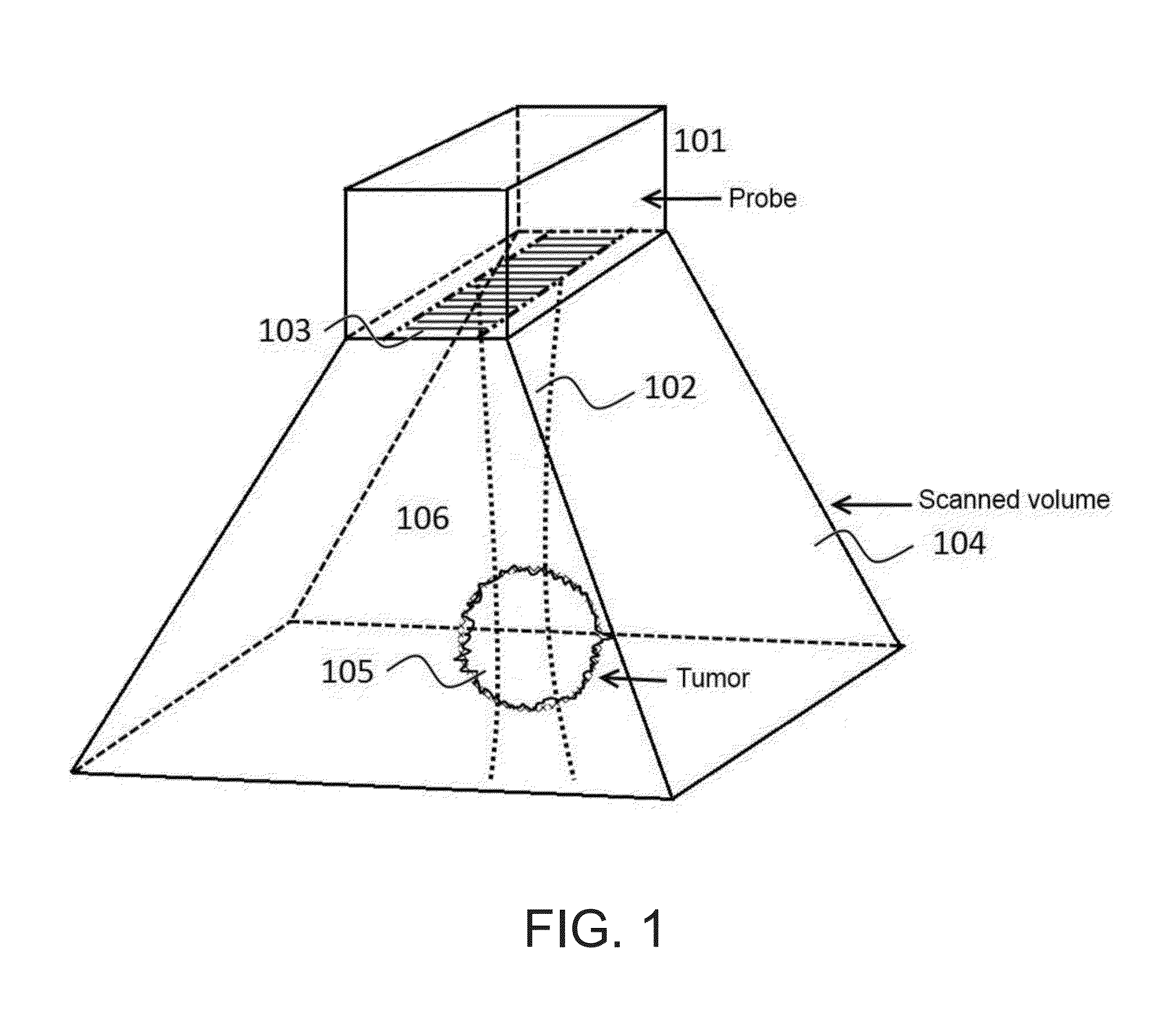
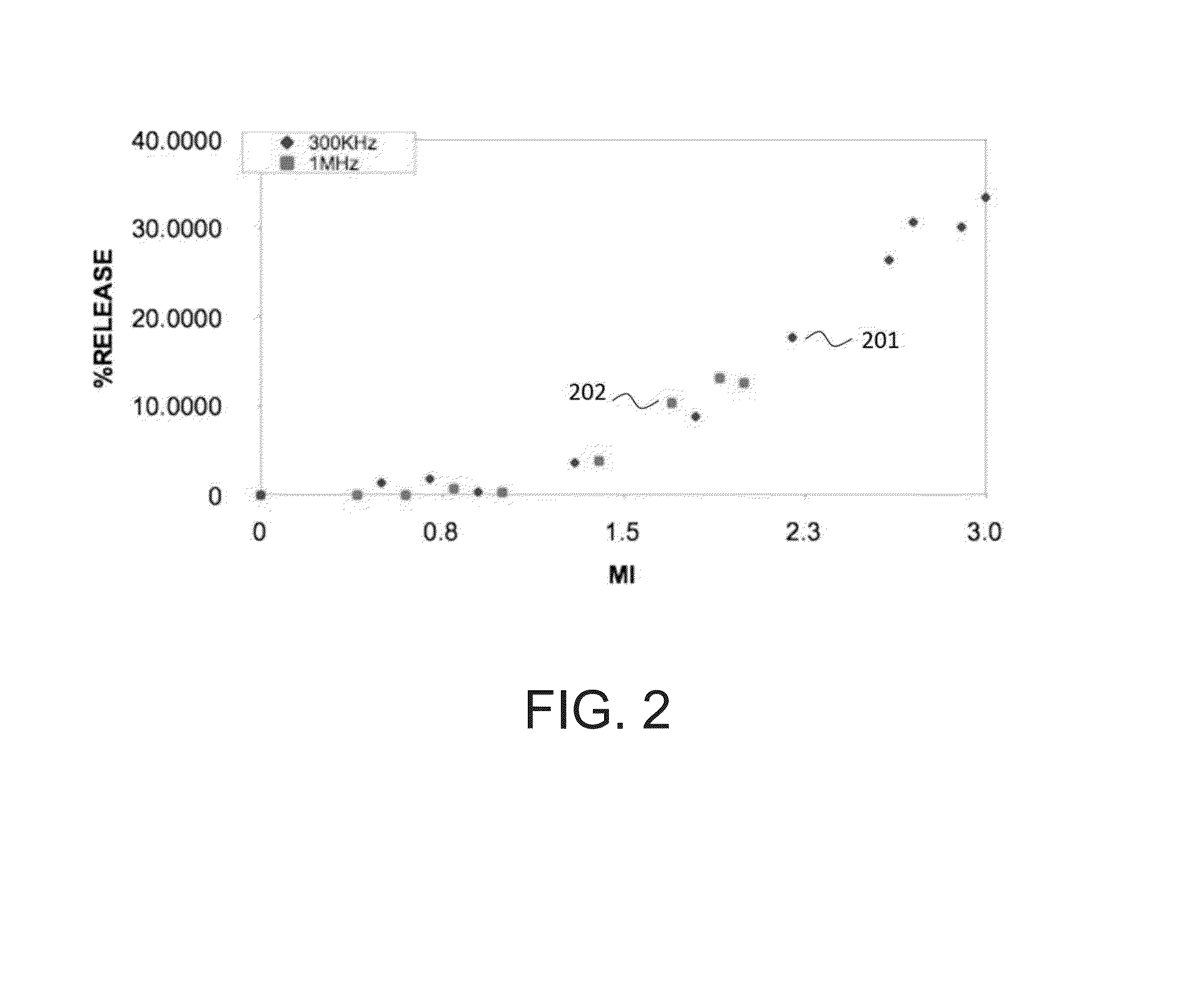
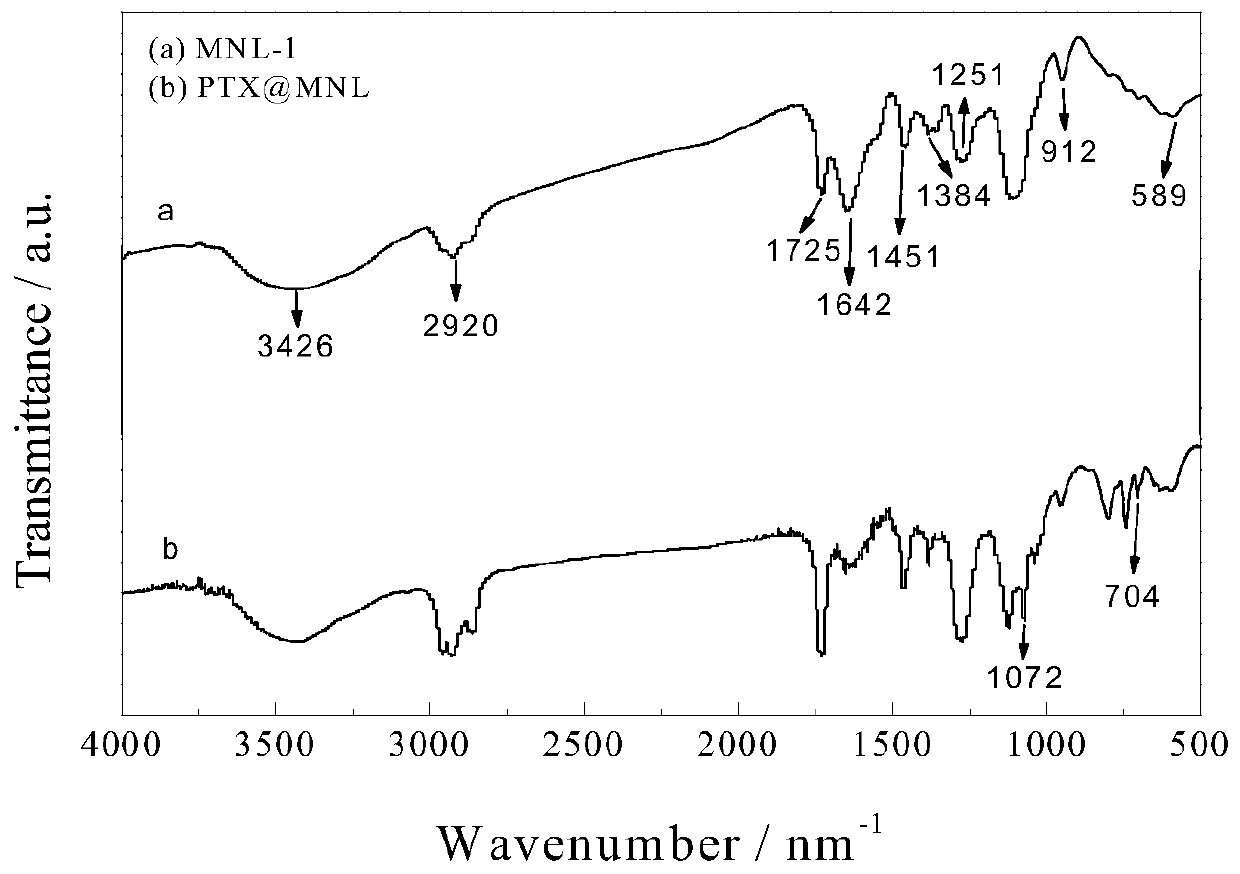
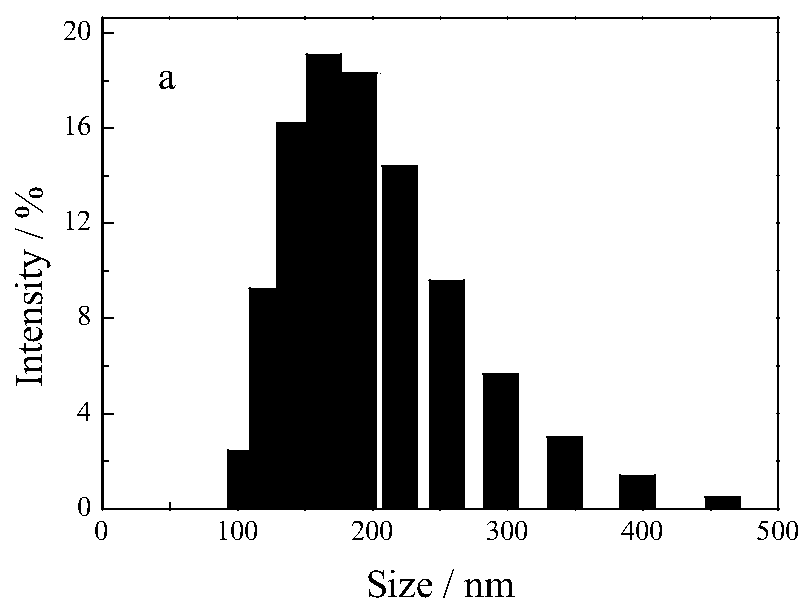
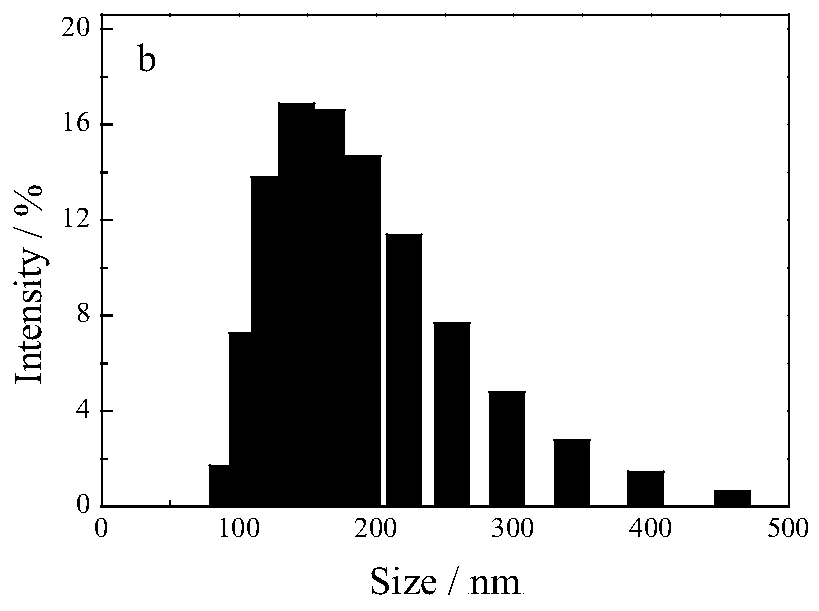
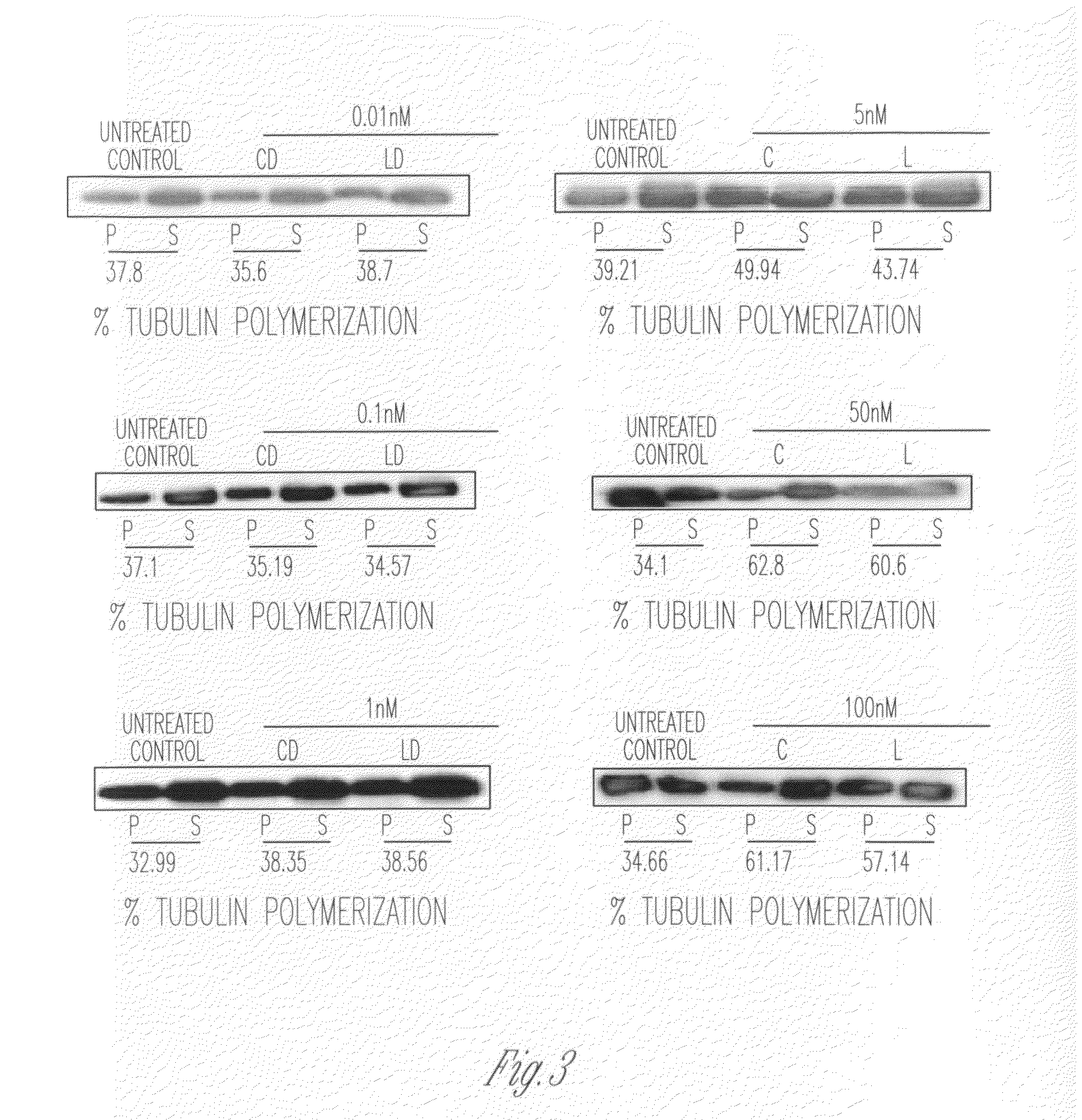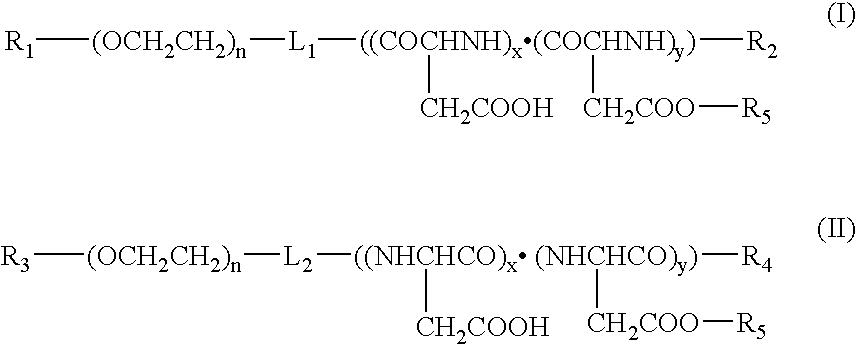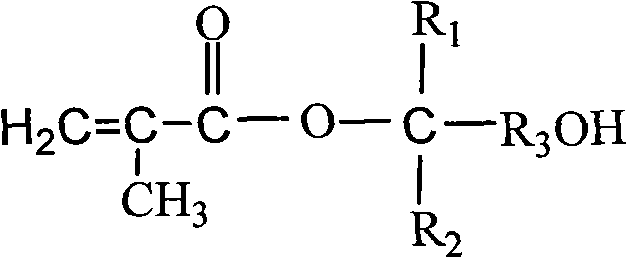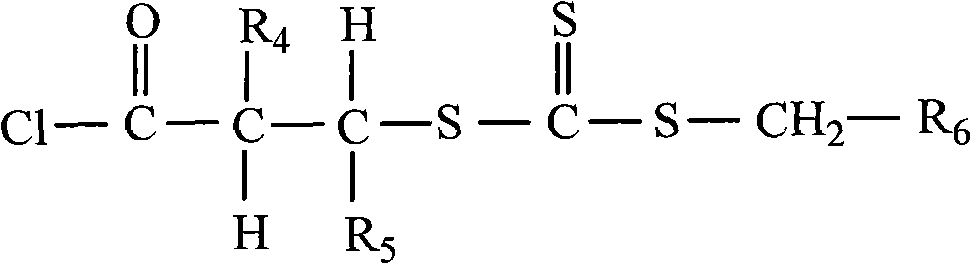Patents
Literature
171 results about "Drug encapsulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
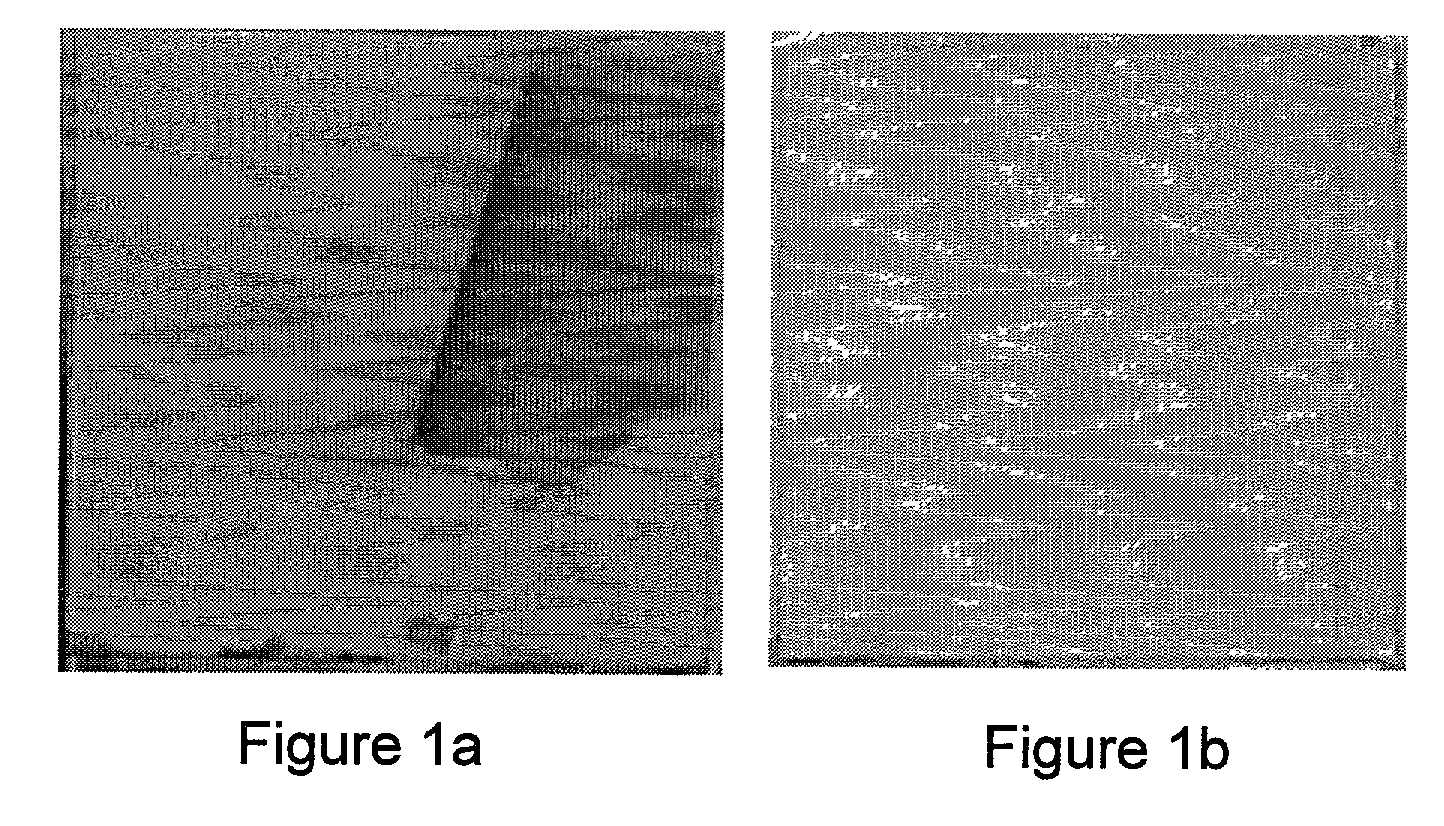
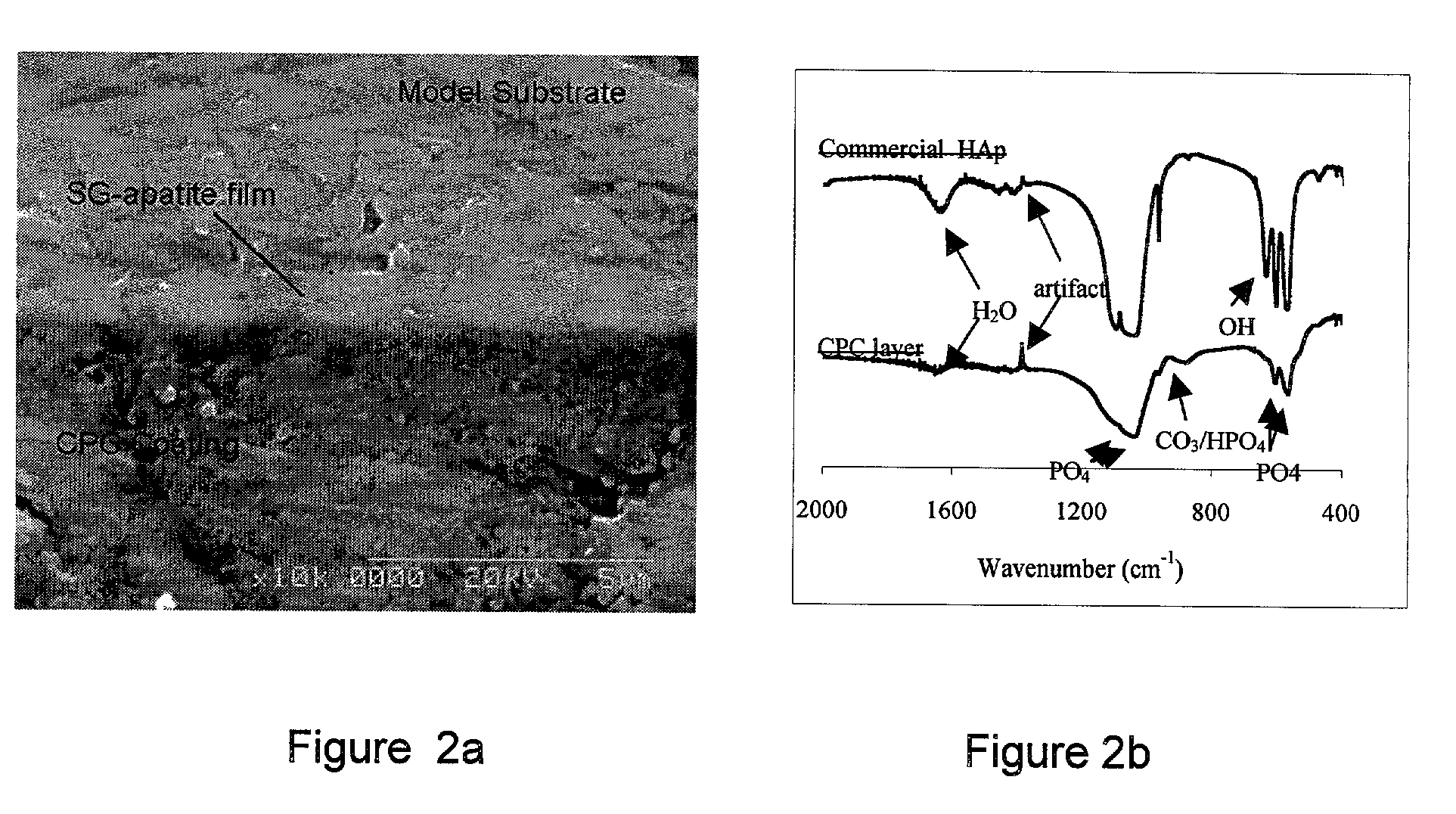
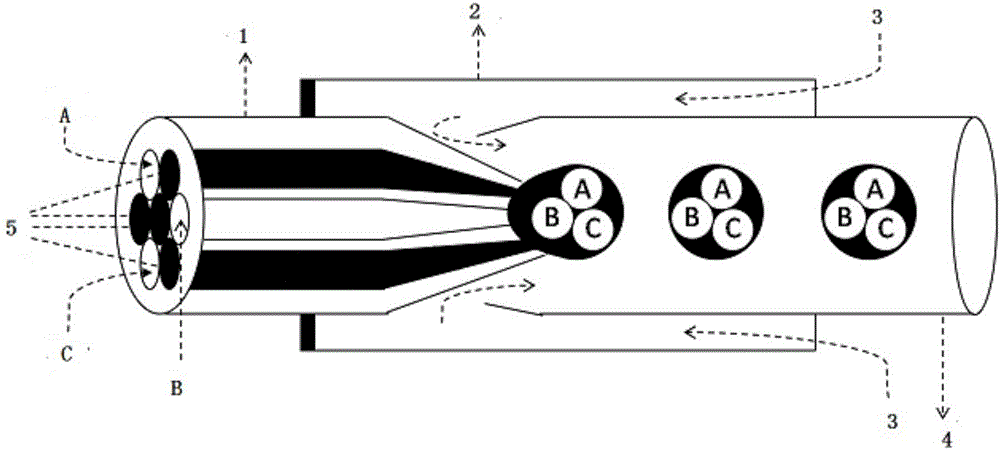
Biofunctional hydroxyapatite coatings and microspheres for in-situ drug encapsulation
InactiveUS20020155144A1Improve relationshipImprove interface strengthPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsGene deliverySide effect
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Biocompatible polymers and Methods of use
InactiveUS20100254900A1Alter propertyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPeptide/protein ingredientsPorosityNatural source
Compositions and methods for manufacturing polymers are disclosed. Compositions include novel plastics, including films and shaped forms comprising polymer matrices that are biologically compatible and biodegradable. Such plastics may comprise polymers derived from natural sources. Further, such plastics are useful in biological systems for wound repair, implants, stents, drug encapsulation and delivery, and other applications. The disclosed methods comprise mild manufacturing processes such that various additives, such as biologically active proteins, sugars, lipids, and the like may be incorporated into the polymer matrix without subsequent loss of bioactivity during processing. Additionally, methods of manufacture for controlling mechanical properties, such as elasticity, pliancy, and the porosity of such plastics are disclosed.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Biofunctional hydroxyapatite coatings and microspheres for in-situ drug encapsulation
InactiveUS6730324B2High strengthEasy to makePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsGene deliverySide effect
This invention relates to novel room-temperature process for obtaining calcium phosphate, in particular hydroxyapatite, coatings and microspheres that encapsulate drugs, proteins, genes, DNA for therapeutical use. The coatings and microspheres are designed to perform a defined biological function related to drug delivery, such as gene therapy through gene delivery. A novel method for encapsulation, and subsequent controlled release of therapeutically active agents from such biofunctional coatings and microspheres is disclosed. Such coatings and microspheres are useful for side-effects free, long-term, targeted, controlled release and delivery of drugs, proteins, DNA, and other therapeutic agents.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Method of Biomolecule Immobilization On Polymers Using Click-Type Chemistry
ActiveUS20090297609A1Improve efficiencyProcess environmental protectionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsFuranAlkyne
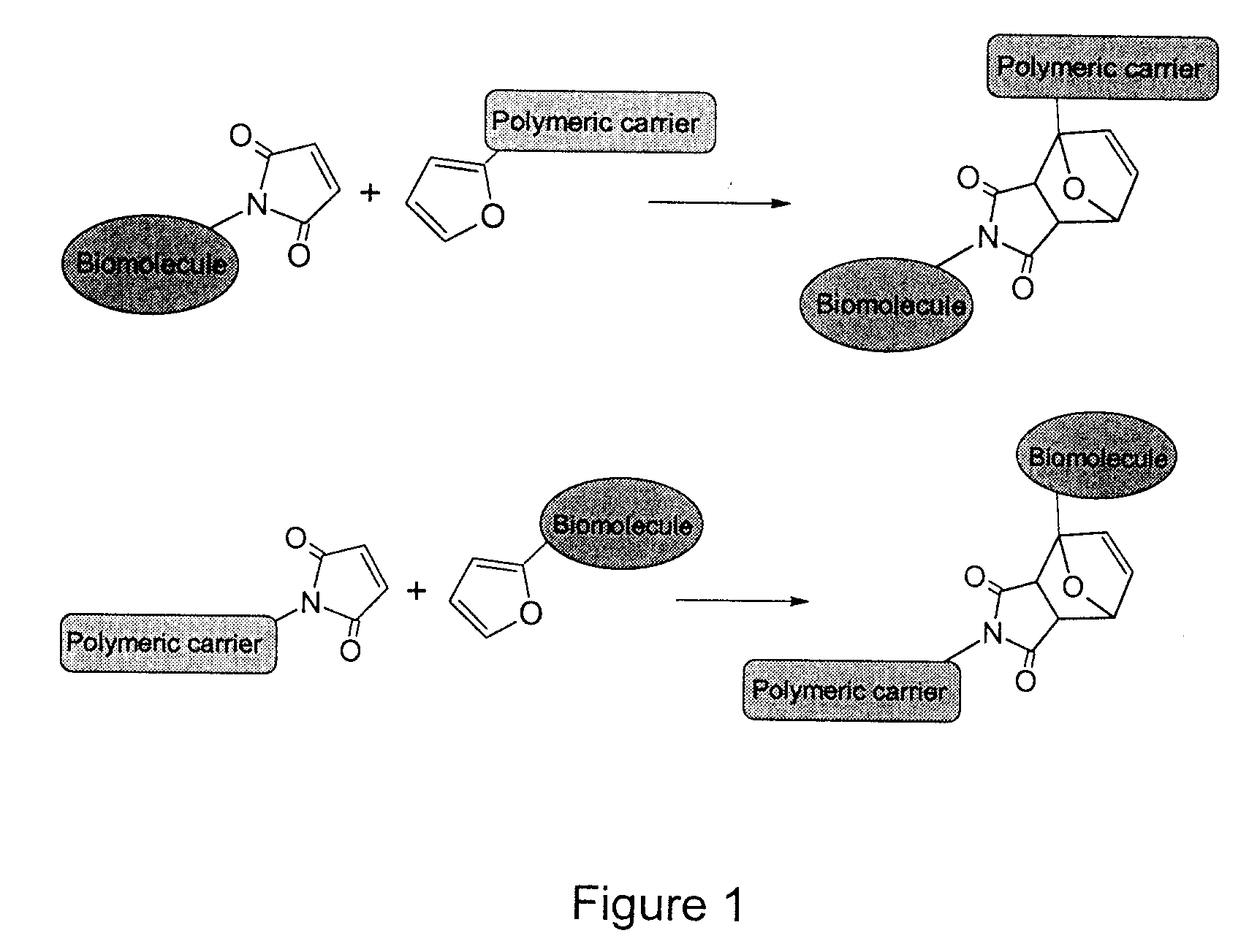
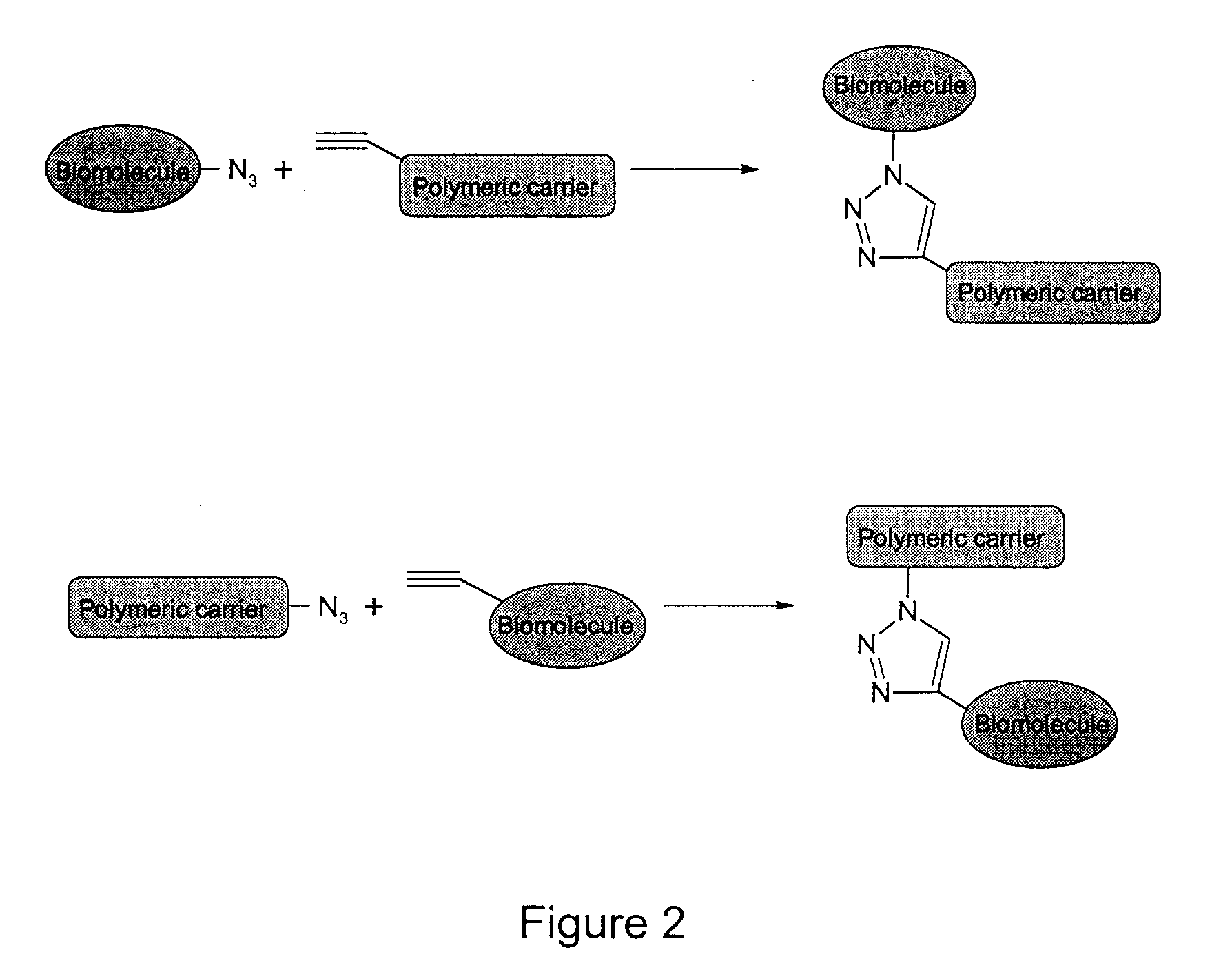
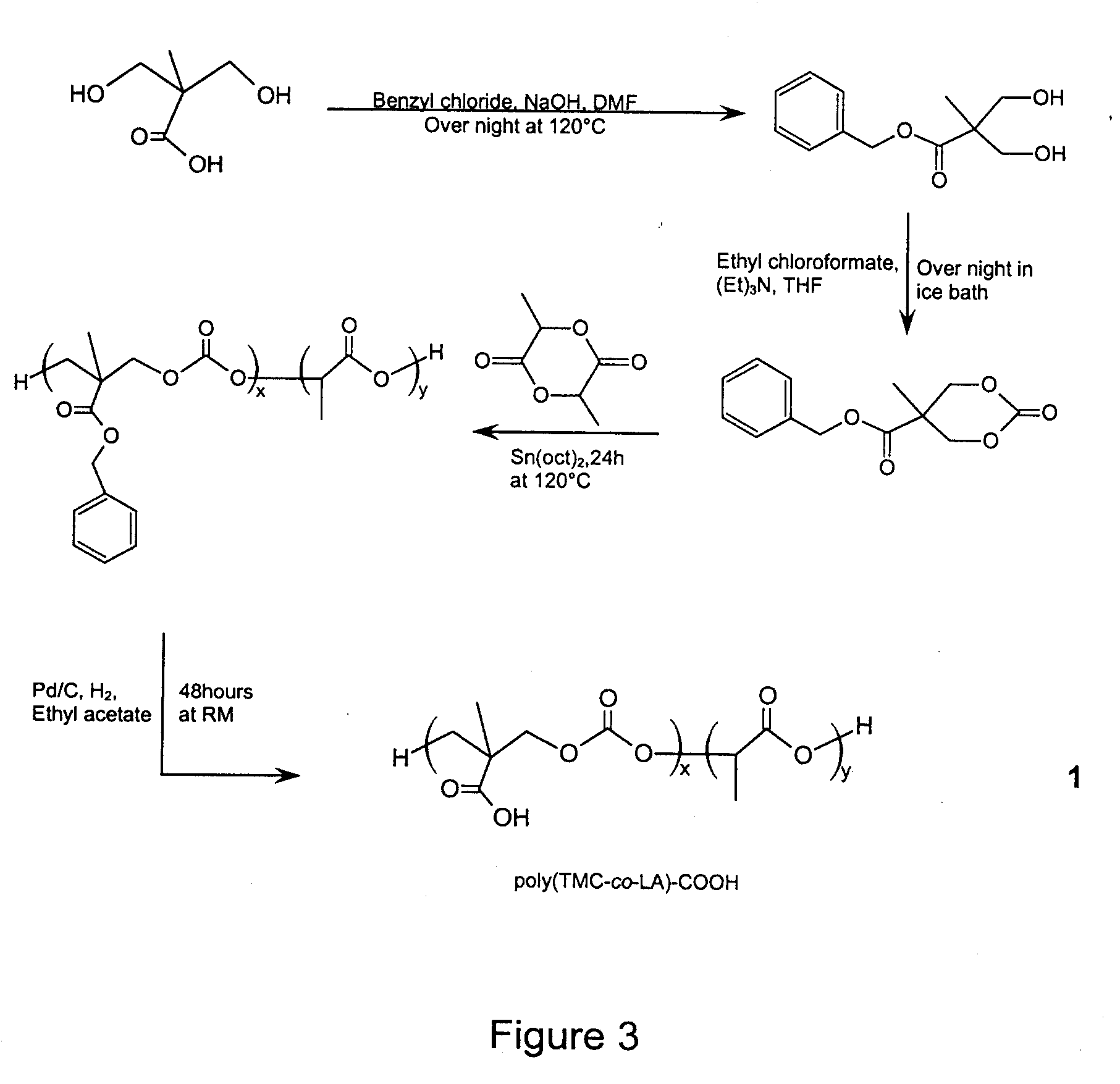
The present invention provides a method for the covalent immobilization of biomolecules on polymers for delivery of the biomolecules, which has the advantage of being simple, highly efficient, environmentally friendly and free of side products relative to traditional immobilization techniques. The invention provides a modified micro / nanoparticle system, which uses a functionalized polymer formed into micro or nanoparticles to bind a molecule to the particles using uses facile chemistry, the Diels-Alder cycloaddition between a diene and a dienophile with the polymer being functionalized with one of them and the molecule with the other, or the Huisgen 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between a terminal alkyne and an azide to bind the molecule to the particle. The molecules and / or other therapeutic agents may be encapsulated within the polymer particles for intravenous therapeutic delivery. The invention also provides a novel synthetic biodegradable polymer, a furan / alkyne-functionalized poly(trimethylene carbonate) (PTMC)-based polymer, whose composition can be designed to meet the defined physical and chemical property requirements. In one example, the particle system self-aggregates from functionalized PTMC-based copolymers containing poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) segments. The composition of the copolymers can be designed to meet various particle system requirements, including size, thermodynamic stability, surface PEG density, drug encapsulation capacity and biomolecule immobilization capacity.
Owner:SHOICHET MOLLY S +2
Nanometer composite porous gel microsphere and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102617769APharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMicroballoon preparationMicrospherePickering emulsion
The invention relates to a nanometer composite porous gel microsphere and a preparation method thereof, which are characterized in that the nanometer composite porous gel microsphere is prepared by the steps of using double Pickering emulsion (O / W / O) as a template, using a water-soluble polymerizable monomer and an initiator as aqueous phase, and adding hydrophilic moderate nanometer particles in the aqueous phase to form oil-in-water type emulsion through emulsification; adding hydrophobic nanometer particles in outer oil phase, adding colostrums into a dispersing agent of the outer oil phase to perform emulsification once again to obtain water-in-oil and oil-in-water type double Pickering emulsion. An aqueous monomer of intermediate phase of the obtained double Pickering emulsion is polymerized to obtain the nanometer composite porous gel microsphere. By means of the preparation method, a large amount of independent gel microspheres with holes insides can be simply prepared. Due to the fact that the functionalization of the nanometer particles can further endow special responsiveness of the microsphere, the nanometer composite porous gel microsphere has wide application prospect in drug encapsulation, targeted slow release, cell culture and other fields.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Proliposomal and liposomal compositions of poorly water soluble drugs
InactiveUS20090017105A1Good storage stabilityGood potencyOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsLipid formationAntioxidant
Concentrates or proliposomal compositions of poorly water-soluble drugs and compounds, comprising of one or more membrane forming lipids, a membrane stabilizing agent, in a suitable vehicle, and optionally containing a Polyethylene Glycol (PEG)-coupled phospholipid or a mixture thereof and further, optionally containing pharmaceutically acceptable excipients such as antioxidants, buffering agents, acidifying agents etc. are provided, which have superior long term stability. The concentrates of proliposomal compositions instantly form liposomes of the said poorly water-soluble drugs and compounds on rapid injection to a diluting fluid, the liposomal composition so obtained, characterized by a physical stability more than 24 hours, ≧95% drug encapsulation and having a particle size diameter of less than 100 nm. The liposomal compositions so obtained can further be directly administered to patients in need of treatment of the poorly water-soluble drugs and compounds.
Owner:FRESENIUS KABI ONCOLOGY LTD
Polypeptide drug sustained-release microsphere preparation and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102688198AUniform particle sizeNarrow particle sizePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderFreeze-dryingMicrosphere
The invention discloses a polypeptide drug sustained-release microsphere preparation and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: dissolving the polylactic acid-glycollic acid copolymer or polylactic acid, a protective agent and a polypeptide drug in an organic solvent to form a completely uniform mixed solution; adding the mixed solution into an oil phase to form emulsion; removing the organic solvent; and performing centrifugal washing and freeze drying to obtain the polypeptide drug sustained-release microsphere. In the invention, an O / O method is adopted, the problem that the drug spreads toward the outer aqueous phase in the multiple-emulsion preparation method is solved, and the drug encapsulation efficiency is improved to 60-95%. The biological active polypeptide drug is degraded in the body and slowly released with the polymer material of the microsphere through the pores on the microsphere surface; the release time can be as long as several weeks and even several months; and the in-vitro release test indicates that the release conforms to similar zero-order release.
Owner:AC PHARMA CO LTD
Preparation method of drug-loaded nanofiber medical dressing
InactiveCN102266582AEasy to absorbGood for growth and regenerationAbsorbent padsBandagesDrugContinuous release
The present invention relates to a method for preparing a drug-loaded biodegradable nanofiber medical dressing. The dressing is a nanofiber membrane that mainly co-spun hyaluronic acid (chitosan) and pore-forming agent to obtain composite nanofibers. The hyaluronic acid (chitosan) is cross-linked using a cross-linking agent, and then selectively The pore-forming agent and cross-linking agent are removed to obtain hyaluronic acid (chitosan) porous nanofibers. Finally, the free binding characteristics of polycations and anions are used to encapsulate therapeutic drugs in hyaluronic acid (chitosan) nanofibers. The obtained drug-loaded biodegradable nanofiber medical dressing can well absorb permeate, maintain moisture around the wound, and can continuously release therapeutic drugs for a long time. It is biodegradable, antibacterial, and hemostatic, and is beneficial to wound tissue. The growth and regeneration can accelerate wound healing and other functions.
Owner:HANGZHOU INST OF ADVANCED MATERIAL BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Hybridosomes, compositions comprising the same, processes for their production and uses thereof
ActiveUS20160354313A1Microencapsulation basedImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsMedicinePharmaceutical drug
The present invention provides a hybrid biocompatible carrier (hybridosome) which comprises structural and bioactive elements originating from at least one biocompatible delivery module (BDM) and at least one engineered drug encapsulation module (EDEM) comprising at least one tunable fusogenic moiety. The invention further provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising said hybridosomes, processes for their manufacture, as well as pharmaceutical uses and pharmaceutical methods based thereon.
Owner:ANJARIUM BIOSCI AG
Flow electroporation chamber and method
InactiveUS20050019311A1Low affinityIncreased oxygen deliveryBiocideOther blood circulation devicesStreptokinaseMedicine
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for the encapsulation of substances and drugs into cells and platelets. The present invention is also related to the incorporation of thrombus dissolving drugs, such as tissue plasminogen activator and streptokinase into platelets using the apparatus described herein. The treated platelets can then be used to treat patients suffering from a thrombus blocking a blood vessel. The present invention is also related to a preparation of red blood cells that has a stable right shift of the oxygen dissociation curve.
Owner:HOLADAY JOHN W +4
Compositions, methods and devices for local drug delivery
ActiveUS20140271897A1Reduce scar tissue formationEasily visualizedBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsMicroparticleDrug encapsulation
This invention provide novel compositions, methods and devices for sustained drug delivery. The microencapsulated sustained drug delivery compositions are deposited using oscillating needle apparatus oscillating at 10-12000 minutes per minutes. The injected compositions may undergo variety of physical chemical changes upon deposition. The physical and chemical changes enables improved drug encapsulation and sustained drug release. Also described are new methods to form polymer microparticles or polymer films / implants in situ inside the tissue. The invention also describes colored biodegradable microparticle based compositions wherein the compositions comprise drug encapsulated microparticles and coloring agent encapsulated microparticles mixed in any proportion. Medical applications of the compositions and methods described in this invention are also described.
Owner:PATHAK HLDG
Process of preparing microspheres for sustained release having improved dispersibility and syringeability
InactiveUS20070264341A1Easy to mass produceHigh encapsulation efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryEmulsionPolyvinyl alcohol
Disclosed is a process of preparing sustained release microspheres, containing a biodegradable polymer as a carrier and a drug, using spray drying. The process comprises preparing a solution, suspension or emulsion containing a biodegradable polymer, a drug and a solvent; spray drying the solution, suspension or emulsion; and suspending spray-dried microspheres in an aqueous solution containing polyvinyl alcohol to remove the residual solvent and increase the hydrophilicity of the microsphere surface. The process enables the preparation of microspheres having high drug encapsulation efficiency, almost not having a toxicity problem due to the residual solvent, and having good syringeability. The microspheres prepared according to the present invention release an effective concentration of a drug in a sustained manner for a predetermined period when administered to the body, and are thus useful in the treatment of diseases.
Owner:DAEWOONG PHARM CO LTD +1
Polysaccharide/inorganic nanoparticles hybrid micron-nano medicine-carrying capsule
ActiveCN101703490AChange in permeabilityTargetedOrganic active ingredientsInorganic non-active ingredientsBiodispersanBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses polysaccharide / inorganic nanoparticles hybrid micron-nano medicine-carrying capsule. The capsule has the following structure characteristics: (1) a water in oil (W / O) microemulsion capsule core is prepared by using fat-soluble drug A or fat-soluble drug B which is dissolved in oily solvent, negative OSA modified polysaccharide derivative and water; (2) the polysaccharide and negative inorganic nanoparticles perform layer-by-layer self-assembly which is based on the electrostatic interaction to form a capsule wall; and (3) the grain size of the micron-nano medicine-carrying capsule is 50-1000nm. The micron-nano medicine-carrying capsule provided by the invention has high drug encapsulation efficiency for drug situ embedding, the raw materials are all adopted from biodegradable materials with good biocompatibility and biodegradability. In addition, the medicine-carrying system has double intelligent functions of targeting and controlled release.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Wettability-guided preparation method of microcapsules and application of microcapsules
ActiveCN106140037ASimple processGood repeatabilityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsOn/in organic carrierWater solubleDrug encapsulation
The invention discloses a wettability-guided preparation method of microcapsules and application of the microcapsules. The wettability-guided preparation method is characterized in that the microcapsules are obtained by controlling the wettability of a microfluidic channel through a one-step method. The microfluidic channel part is formed by coaxially arranging and assembling one porous capillary tube and one single-hole round tube in one square tube, i.e., a tip of the porous capillary tube is inserted into the single-hole round tube, and meanwhile, central axes of the two tubes are mutually superposed. Oil-soluble microcapsules can be prepared by hydrophobic modification of the porous capillary tube; water-soluble microcapsules can be prepared by hydrophilic modification of the porous capillary tube. The obtained microcapsules have a core-shell structure; in addition, a core of each microcapsule can simultaneously contain different components. The microcapsules can be applied to the technical fields of cell culture, drug encapsulation and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
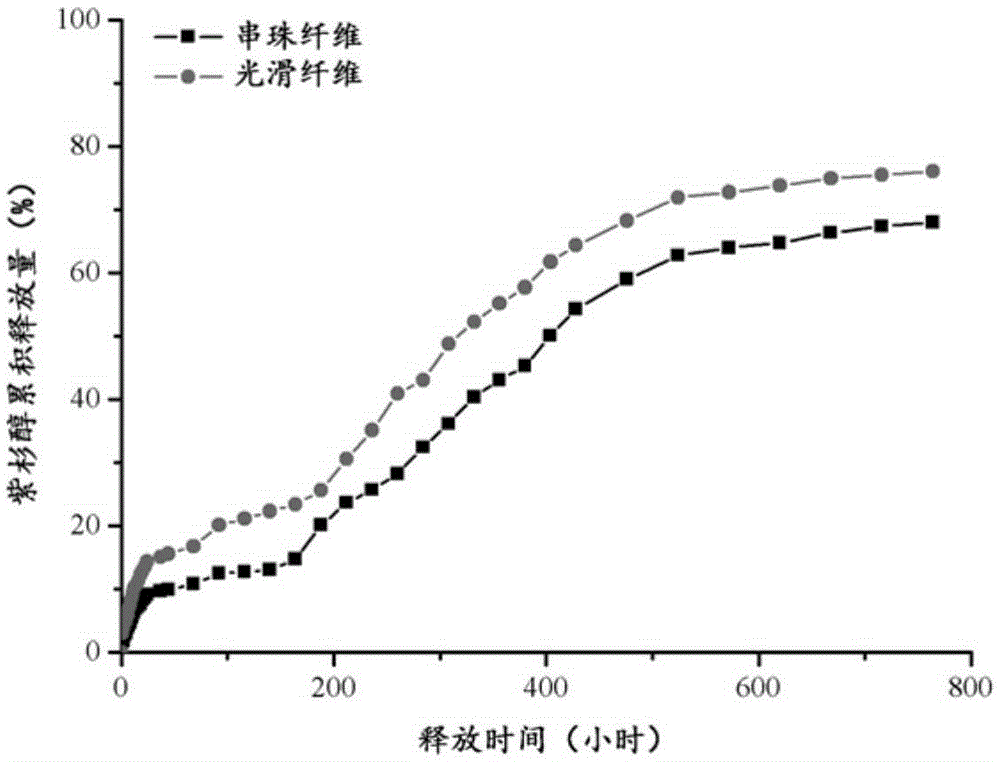
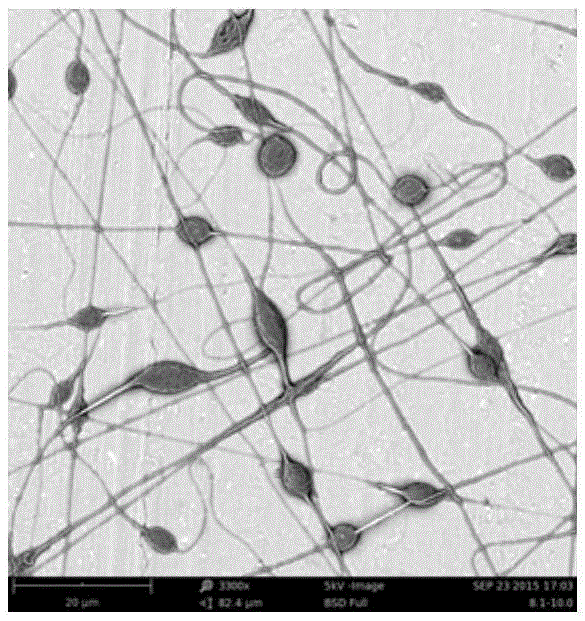
Paclitaxel loaded catenulate nano fiber and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105386155ATo achieve a sustained release effectMaintain biological activityElectro-spinningConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsFiberMedicine
The invention discloses a paclitaxel loaded catenulate nano fiber and a preparation method thereof. At first, catenulate nano fiber is prepared, then paclitaxel is loaded on the beads to form a drug sustain-released system, and thus slow releasing of paclitaxel can be effectively controlled. Furthermore, the biocompatibility is good, the drug encapsulation rate is high, and the activity is strong. The provided dosage form of paclitaxel has the advantages of little side and toxic effect and sustained-release function, and can be applied to preparation of drugs for treating malignant tumors.
Owner:XIAMEN TASMAN BIO TECH
Cell or drug encapsulation device having a wet seal
InactiveUS20070026515A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPorous membraneDrug encapsulation
A biologically implantable containment device having a wet seal, the device being adaptable for drug formulations or cell suspensions. A porous membrane, in a tubular configuration, is formed and can be configured as part of a closed cell-tight system for loading. During loading, the containment device membrane is wet, while the loading system remains cell-tight. The containment device is wet-sealed through a combination of heat and pressure, while the system remains cell-tight. Sealing the containment device substantially or completely eliminates metabolic functioning of any organisms in the vicinity of the closure. The wet-seal is formed by melting a thermoplastic material that is in contact with the membrane. The containment device is separated from the cell-tight loading system, which remains closed after separation.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Micelle based on non-linear polyethylene glycol-polylactic acid block copolymer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101812227AGood biocompatibilityAvoid adsorptionPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsEnd-groupPolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to a micelle based on non-linear polyethylene glycol-polylactic acid block copolymer and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: using a single-end hydroxyl or a double-end-group modified polyethylene glycol to induce lactide for ring-opening polymerization, thereby obtaining a non-linear spindle polyethylene glycol-polylactic acid block copolymer, and then obtaining a micron-sized spindle micelle with high stability through self-assembly in aqueous solution. The particle sizes can be controlled through adjusting the molecular weights of polyethylene glycol and the polylactic acid, the critical micelle concentration is as high as 3.72*10-4g / L, and the drug loading rate and the drug encapsulation rate of the micelle are respectively up to 39.9 percent and 70.8 percent by mass percent, superior to a spherical micelle formed through assembly of a linear polyethylene glycol-polylactic acid block copolymer with an identical molecular weight. Simultaneously, the micelle coated with oil-soluble drugs demonstrates controllable release properties to drug molecules in phosphate buffer saline with the pH value of 7.4. The micelle can be used for slow release and targeted delivery of drugs, enhancement of drug effects and the like.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
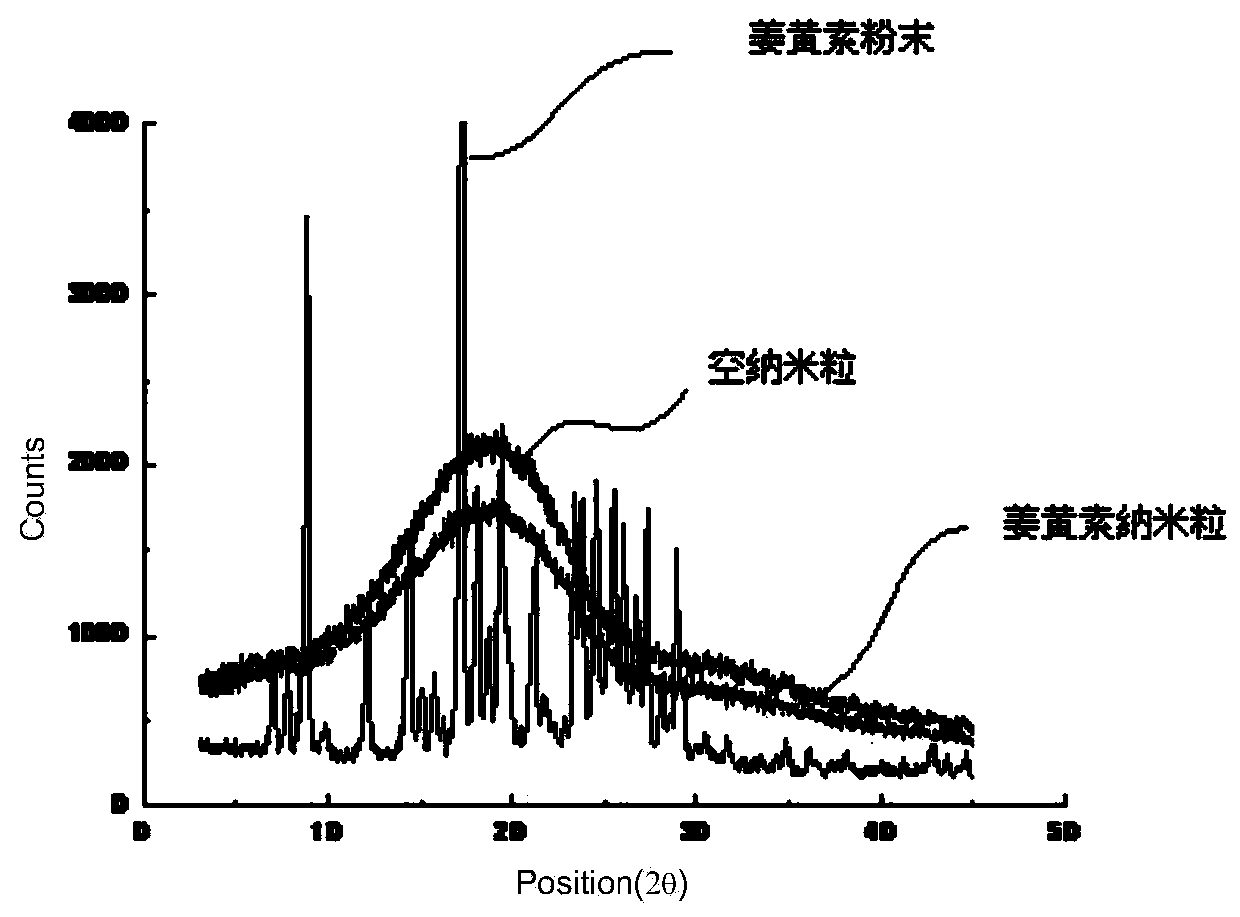
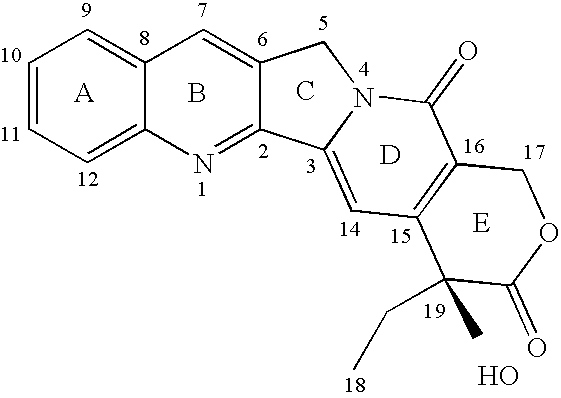
Method for preparing curcumin lipid nano-particle suspension or nano-particles
ActiveCN103768012AHigh encapsulation efficiencySmall particle sizeAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryLipid formationOrganic solvent
The invention relates to a method for preparing a curcumin lipid nano-particle suspension or nano-particles, and belongs to the technical field of medicinal preparations. The method for preparing the curcumin lipid nano-particle suspension or nano-particle aims to solve existing problems of difficult operation, poor encapsulation rate and large particle diameter, and comprises the following steps: dissolving 1 part by weight of curcumin and 5-20 parts by weight of amphoteric degradable high-molecular polymer into an organic solvent to form a lipid phase solution; dissolving 5-20 parts by weight of surfactant in water to form an aqueous phase solution; injecting the lipid phase solution and the aqueous phase solution into a micro-passage of a passage reactor to mix the lipid phase solution and the aqueous phase solution into particles, wherein the aqueous phase flow velocity is 0.65-0.75mL / min, and the lipid phase flow velocity is 0.2-0.5mL / min; removing the organic solvent to obtain the curcumin lipid nano-particle suspension. The method has the effects of being simple in process, easy to operate, high in drug encapsulation rate, small in particle diameter and high in uniformity.
Owner:浙江佳泰科技有限公司
Composition containing nanoparticles containing water-soluble basic drug encpsulated therein
A drug and a biodegradable polymer having at least one carboxyl group are encapsulated into nanoparticle which is formed by a block copolymer having a hydrophilic segment and a hydrophobic segment. This invention thus provides a drug-encapsulated nanoparticle which shows an increased in vivo drug-stability.
Owner:NANOCARRIER
Process of preparing microspheres for sustained release having improved dispersibility and syringeability
ActiveUS20090269414A1Easy to mass produceHigh encapsulation efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsEmulsionMicrosphere
Disclosed is a process of preparing sustained release microspheres, containing a biodegradable polymer as a carrier and a drug, using spray drying. The process comprises preparing a solution, suspension or emulsion containing a biodegradable polymer, a drug and a solvent; spray drying the solution, suspension or emulsion; and suspending spray-dried microspheres in an aqueous solution containing polyvinyl alcohol to remove the residual solvent and increase the hydrophilicity of the microsphere surface. The process enables the preparation of microspheres having high drug encapsulation efficiency, almost not having a toxicity problem due to the residual solvent, and having good syringeability. The microspheres prepared according to the present invention release an effective concentration of a drug in a sustained manner for a predetermined period when administered to the body, and are thus useful in the treatment of diseases.
Owner:DAEWOONG PHARM CO LTD +1
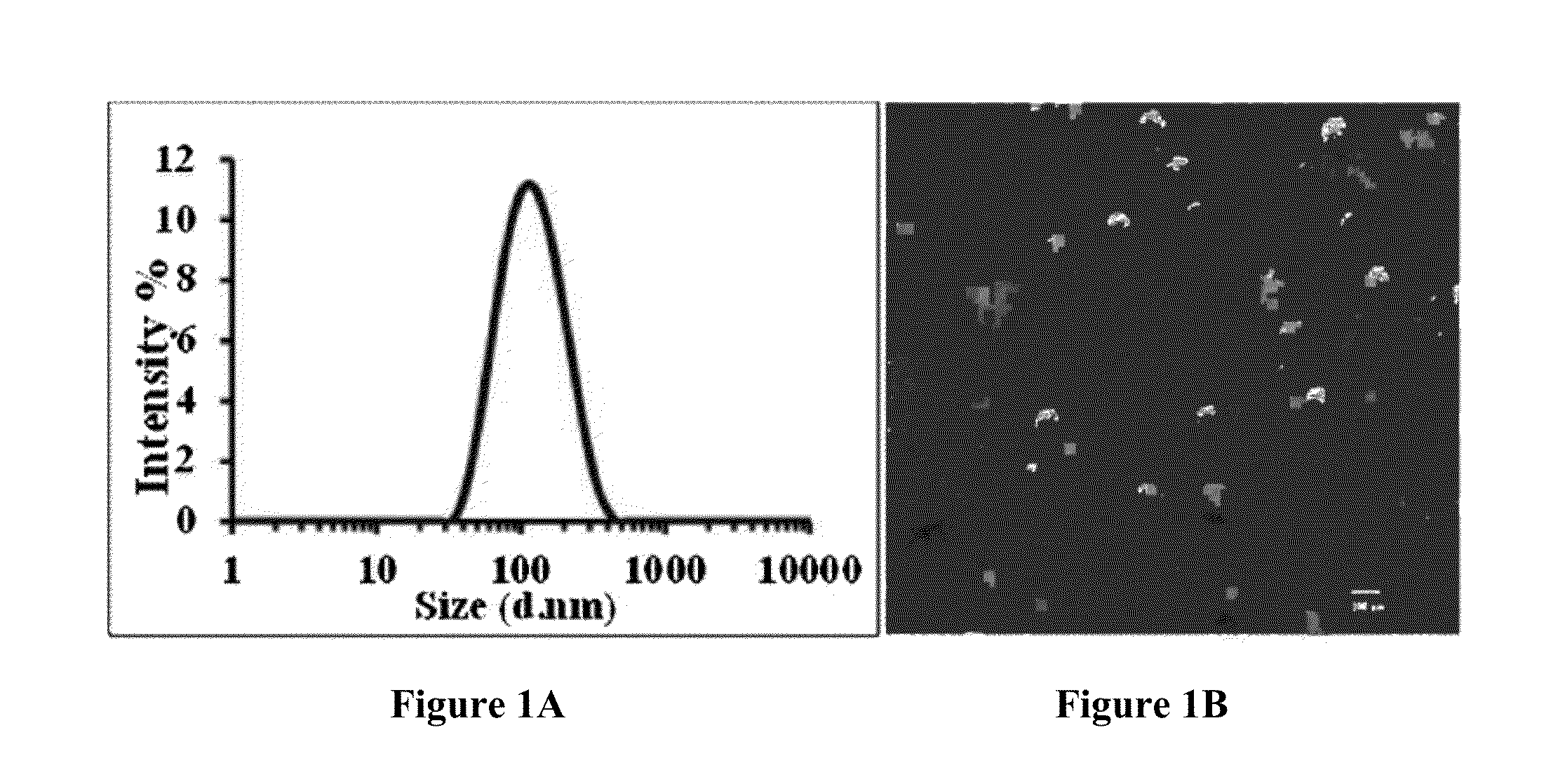
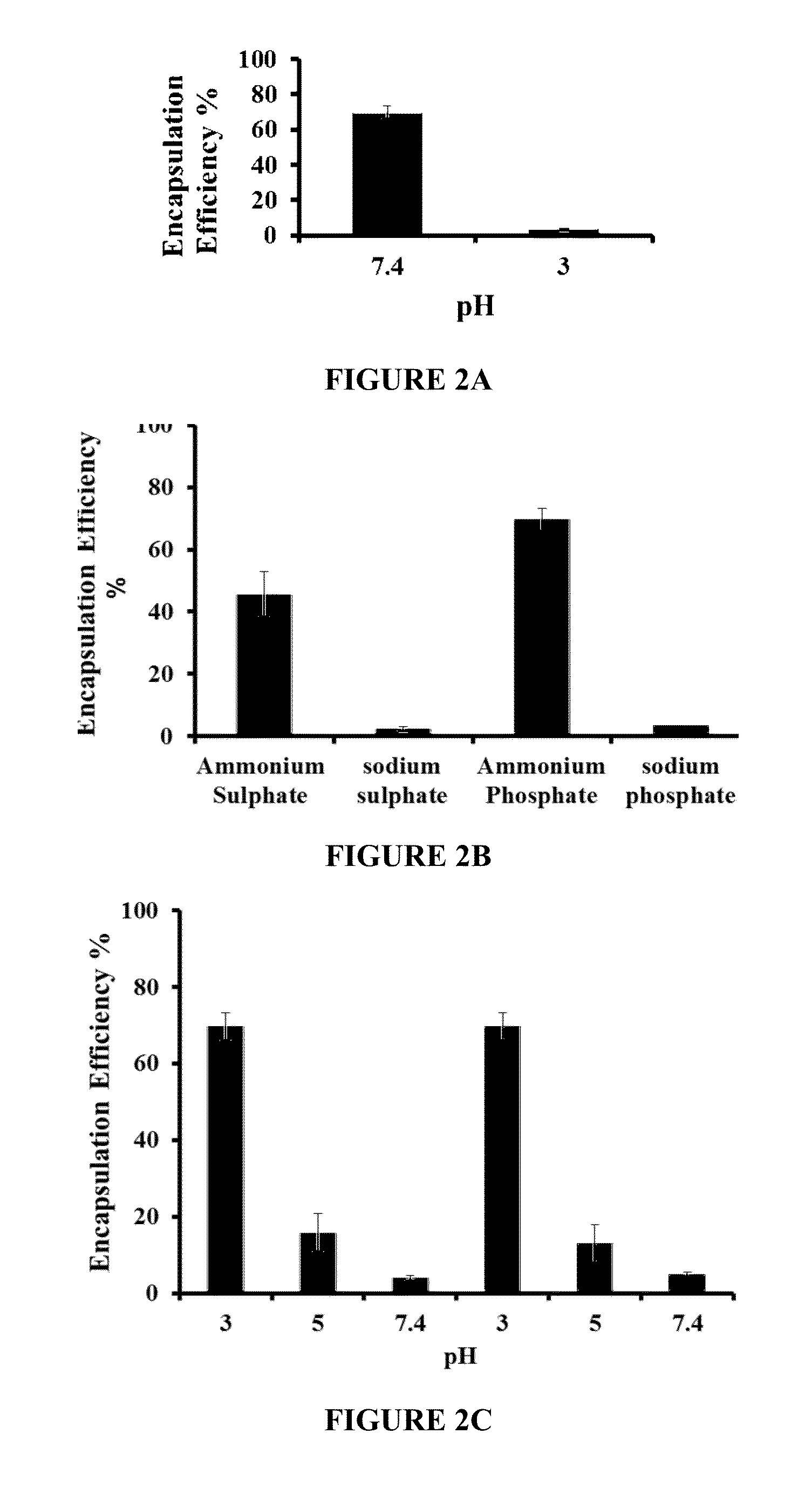
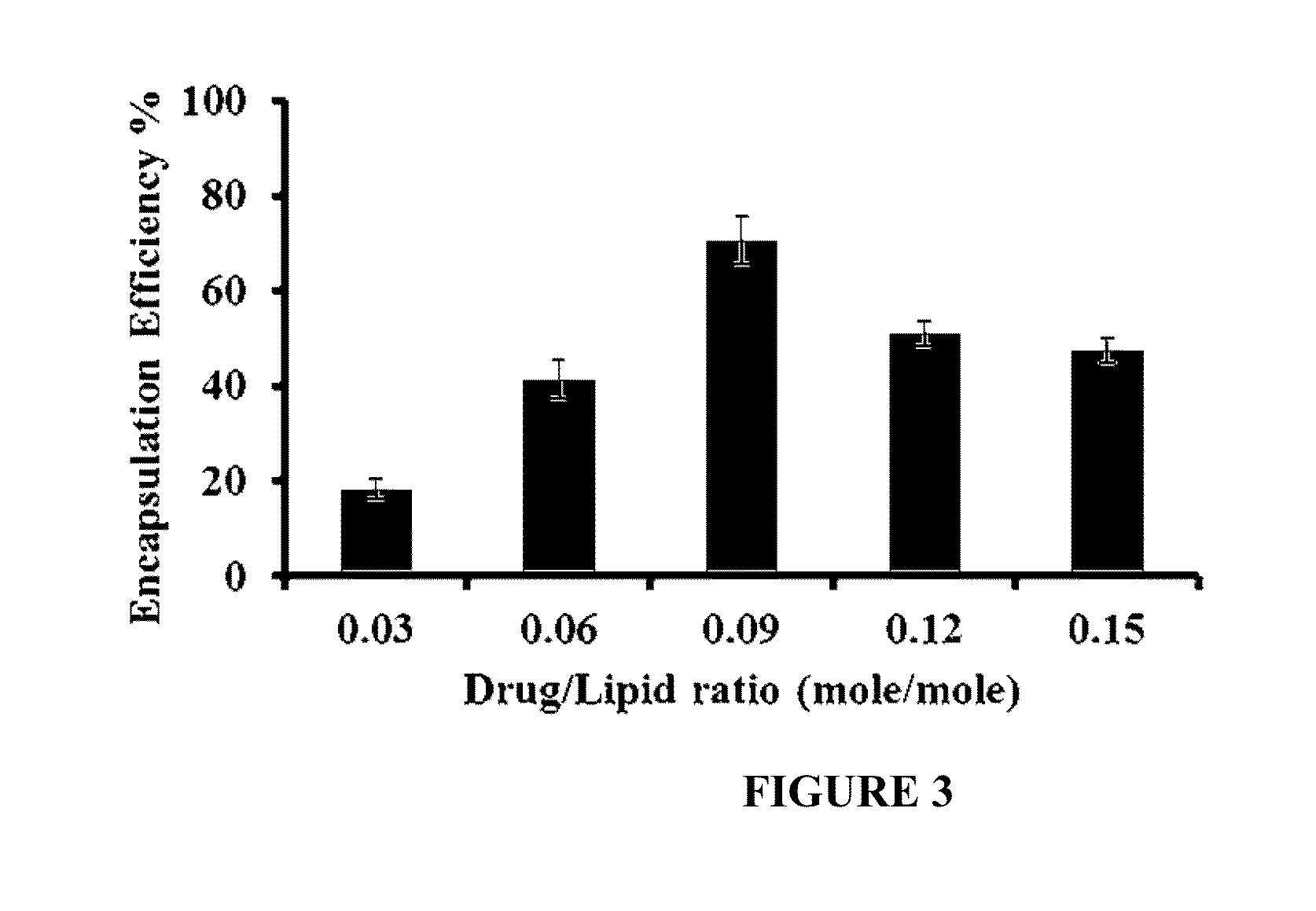
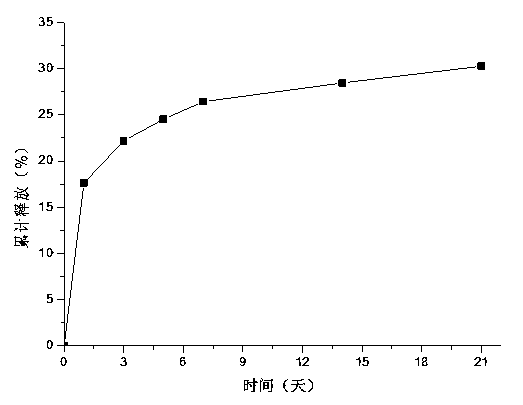
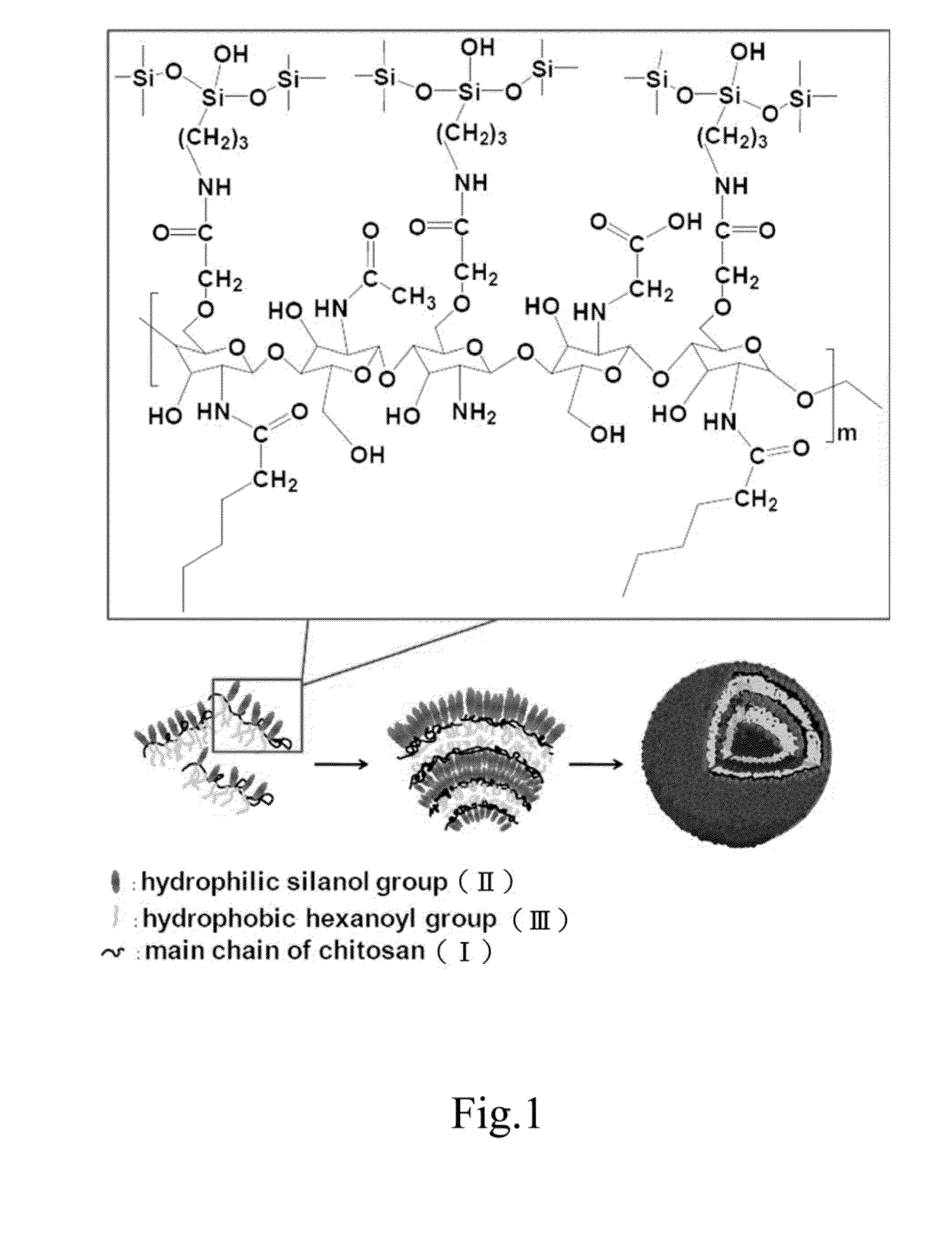
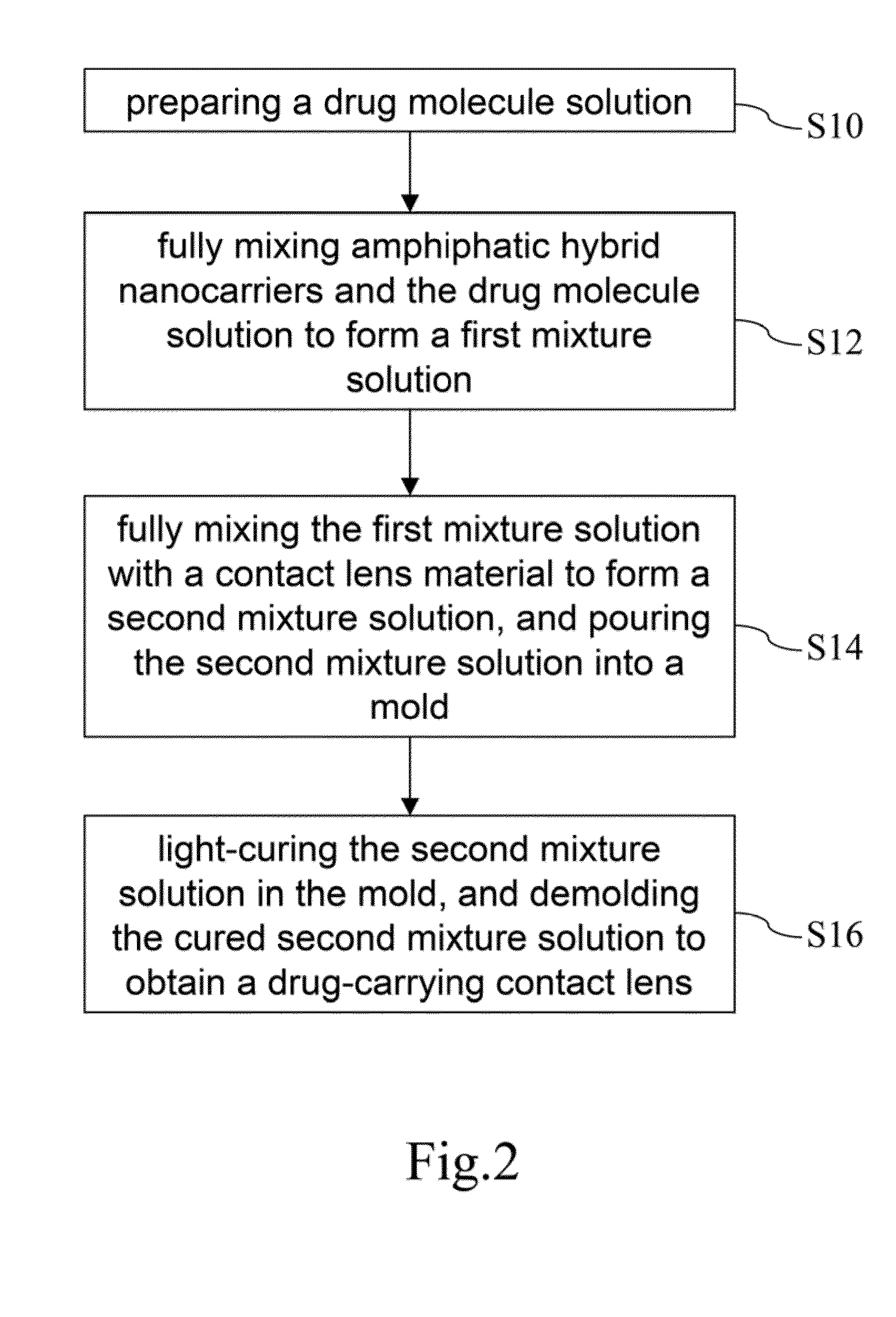
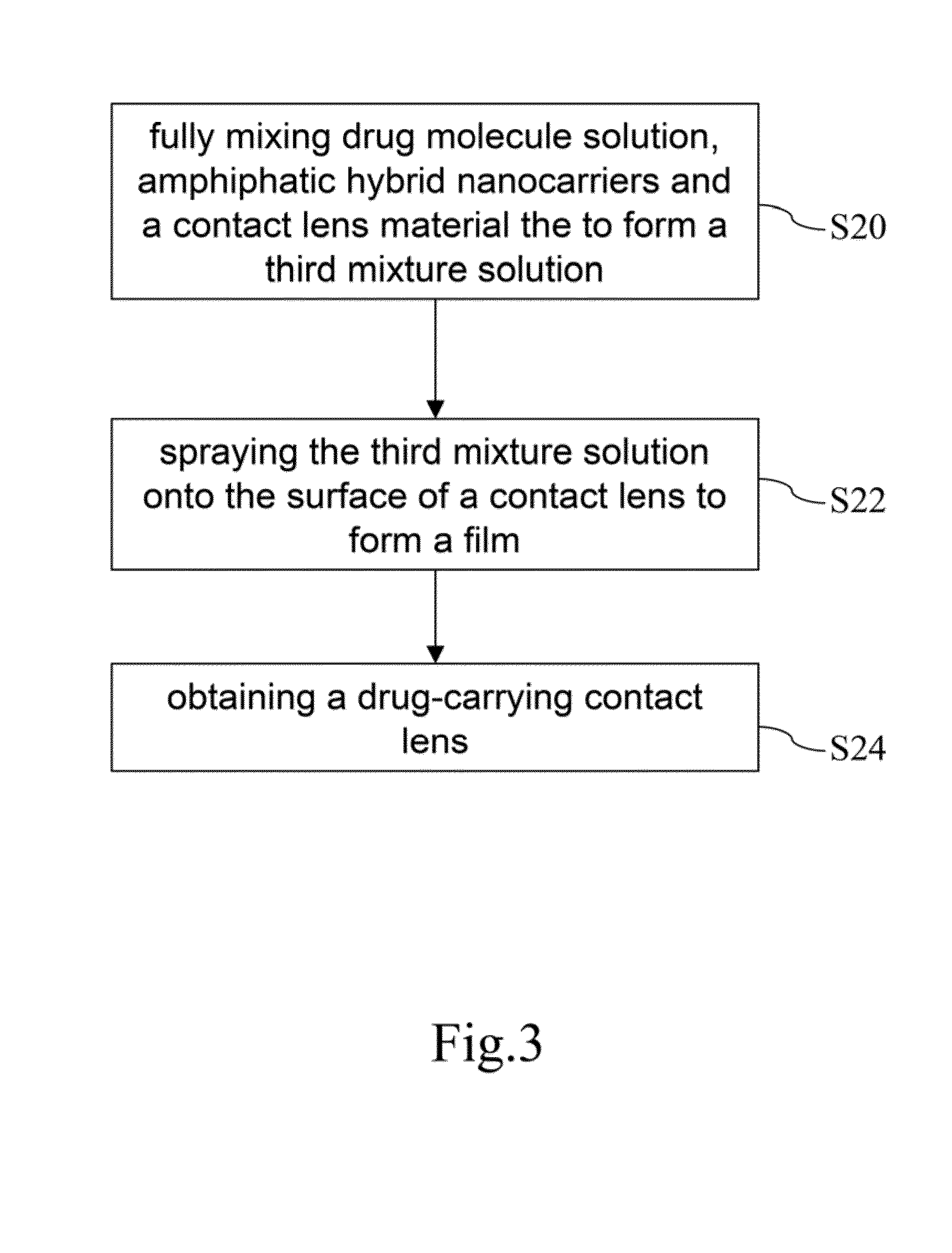
Drug-carrying contact lens and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS8623400B2Good biocompatibilityImprove rendering capabilitiesBiocideOptical articlesSide effectNanocarriers
The present invention discloses a drug-carrying contact lens and a method for fabricating the same. The drug-carrying contact lens comprises a contact lens containing at least one amphiphatic hybrid nanocarrier carrying drug molecules. According to the heat or light sensitivity of the drug molecule, the present invention respectively fabricates an encapsulation-type drug-carrying contact lens and a drug-soaking type drug-carrying contact lens. The present invention uses a highly-biocompatible amphiphatic hybrid nanocarriers having superior drug encapsulation capability to wrap the drug molecules. Thereby, the drug molecules are uniformly distributed in the contact lens and can be gradually and locally released to the eye of the user wearing the contact lens. Therefore, the present invention can prevent or cure ocular diseases with the loss and side effects of the drug being reduced.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Liposomal drug encapsulation
Provided herein are novel methods of making liposomally encapsulated drugs using reverse pH gradients and optimizing internal buffer compositions. Further provided herein are liposome compositions including an active pharmaceutical ingredient and uses thereof to treat a variety of diseases (e.g. cancer, inflammatory, neurological and cardiovascular diseases).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Preparation method of drug bearing microsphere/chitosan/sodium alginate injectable aquogel
The invention discloses a preparation method of a drug bearing microsphere / chitosan / sodium alginate injectable aquogel. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: dissolving chitosan into a water solution of dilute acetic acid to obtain a solution 1; dissolving sodium alginate into hot deionized water to obtain a solution 2; dissolving Tris into deionized water to obtain a solution 3; dissolving anhydrous calcium chloride into deionized water to obtain a solution 4; uniformly mixing the solutions 1, 2 and 3 to obtain a mixed solution, and freezing and storing the mixed solution; dispersing preliminarily-prepared drug bearing microspheres into the mixed solution, and injecting the mixed solution on a defected part to initially form the aquogel; then, injecting the solution 4 to obtain a cured aquogel. The aquogel prepared by the using preparation method disclosed by the invention is rapid in forming, good in biocompatibility, high in drug encapsulation efficiency and little in brust release in an in-vitro drug release process; the preparation method is simple in process, easy in acquisition of raw materials, low in cost and easy for realization of industrialization.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Drug-carrying contact lens and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20130011460A1Good biocompatibilitySuperior drug encapsulation capabilityBiocideOptical articlesSide effectNanocarriers
The present invention discloses a drug-carrying contact lens and a method for fabricating the same. The drug-carrying contact lens comprises a contact lens containing at least one amphiphatic hybrid nanocarrier carrying drug molecules. According to the heat or light sensitivity of the drug molecule, the present invention respectively fabricates an encapsulation-type drug-carrying contact lens and a drug-soaking type drug-carrying contact lens. The present invention uses a highly-biocompatible amphiphatic hybrid nanocarriers having superior drug encapsulation capability to wrap the drug molecules. Thereby, the drug molecules are uniformly distributed in the contact lens and can be gradually and locally released to the eye of the user wearing the contact lens. Therefore, the present invention can prevent or cure ocular diseases with the loss and side effects of the drug being reduced.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
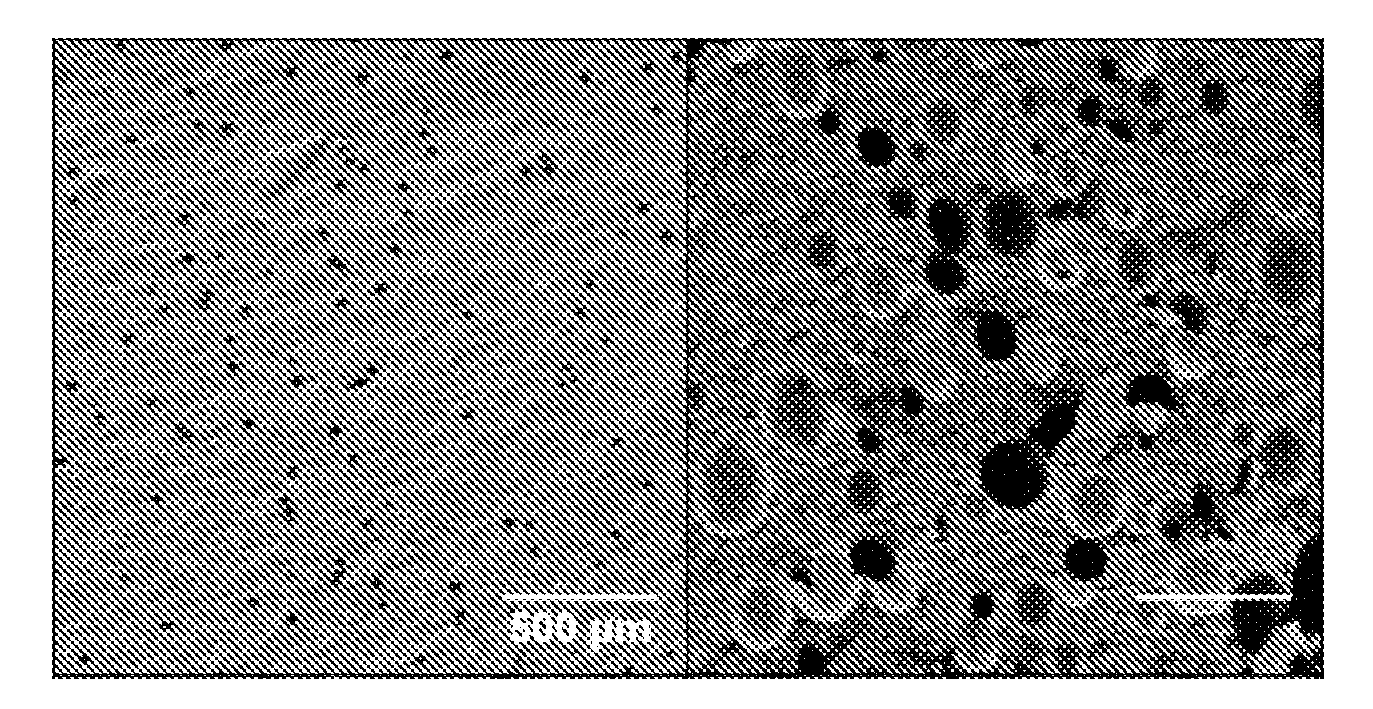
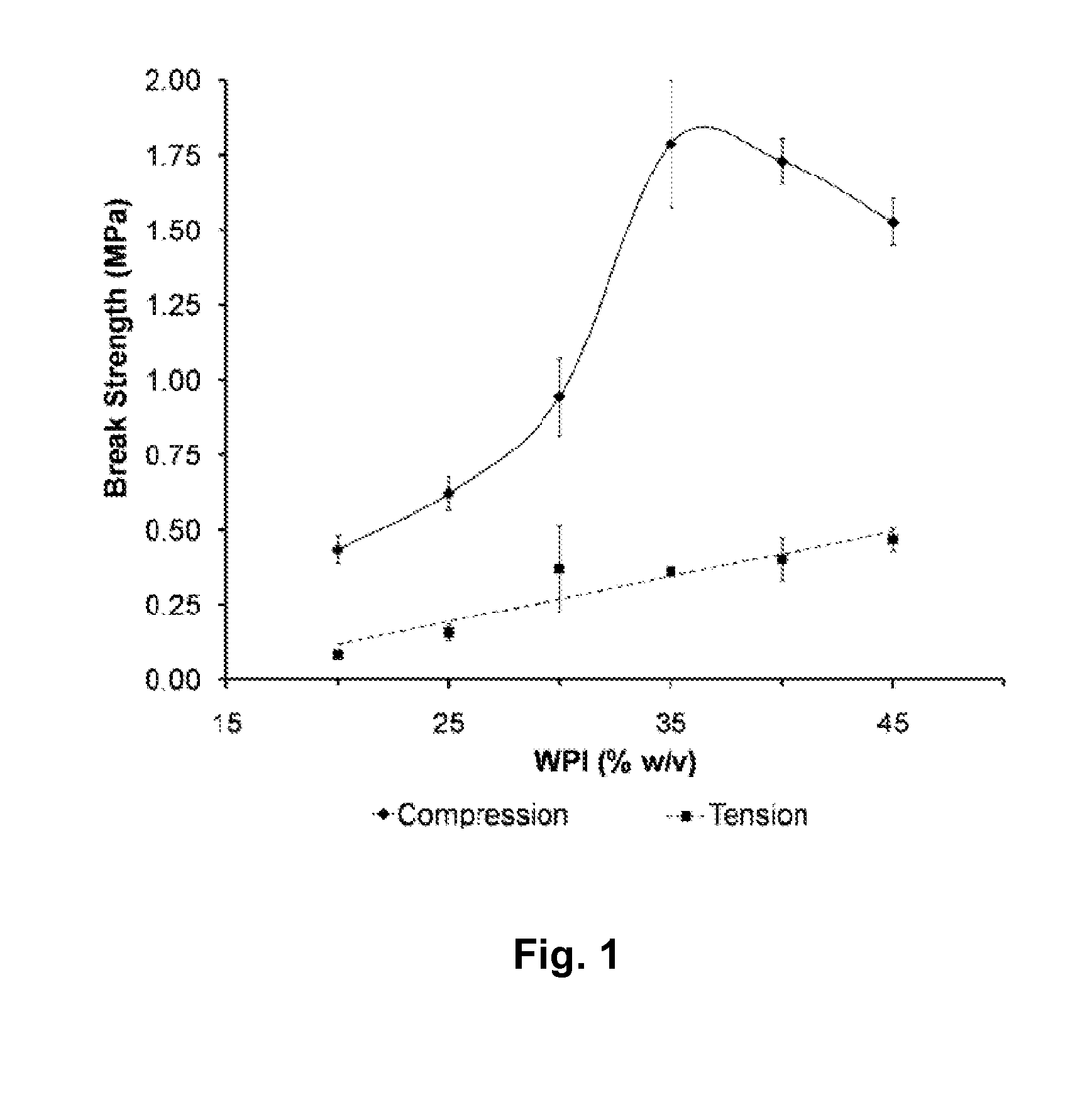
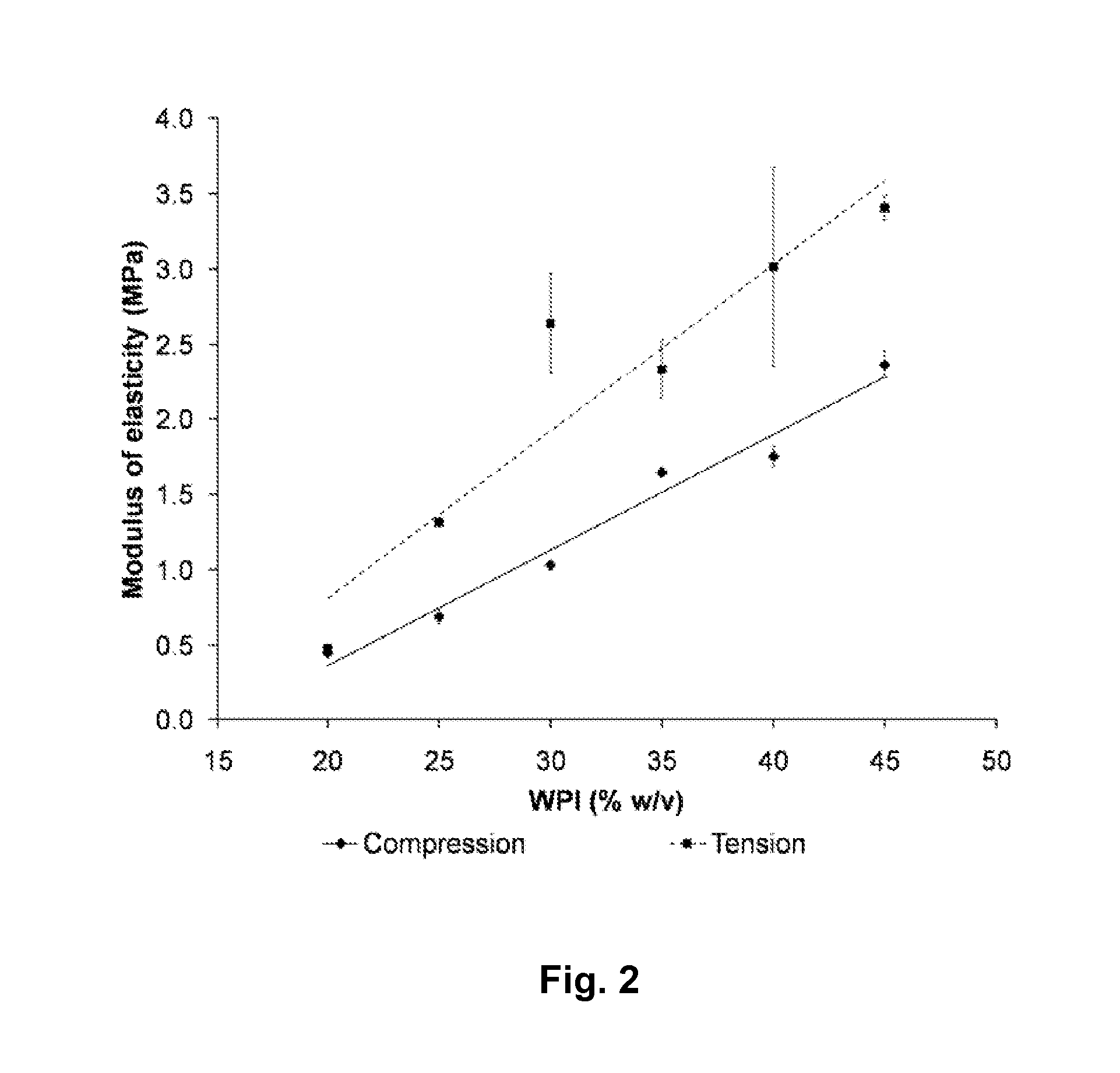
Whey Protein Isolate Hydrogels and Their Uses
A biodegradable hydrogel has been made based on high concentrations of whey protein isolate (WP1). WP1 gels of different compositions were fabricated by thermally inducing gelation of high-concentration suspensions of protein, and characterized for compressive strength and modulus, hydration swelling and drying properties, mechanical behavior change due to polysaccharide additives, and intrinsic pore network structure. The gels were shown to be compatible with bone cells and could be used as bone tissue scaffolds. In addition, WP1 fibers were produced by electrospinning. Several additives could be incorporated into the WPI gels, including structural additives, growth factors, amino acids, etc. The WP1 hydrogels can be made with glycerol to increase flexibility and stability. The hydrogels could be used for tissue regeneration, food protection, controlled-release applications (including drug encapsulation, dietary supplement release, attractant release in lures, nutrient release to plants (fertilizers), column packing for compound separation, and membrane development.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
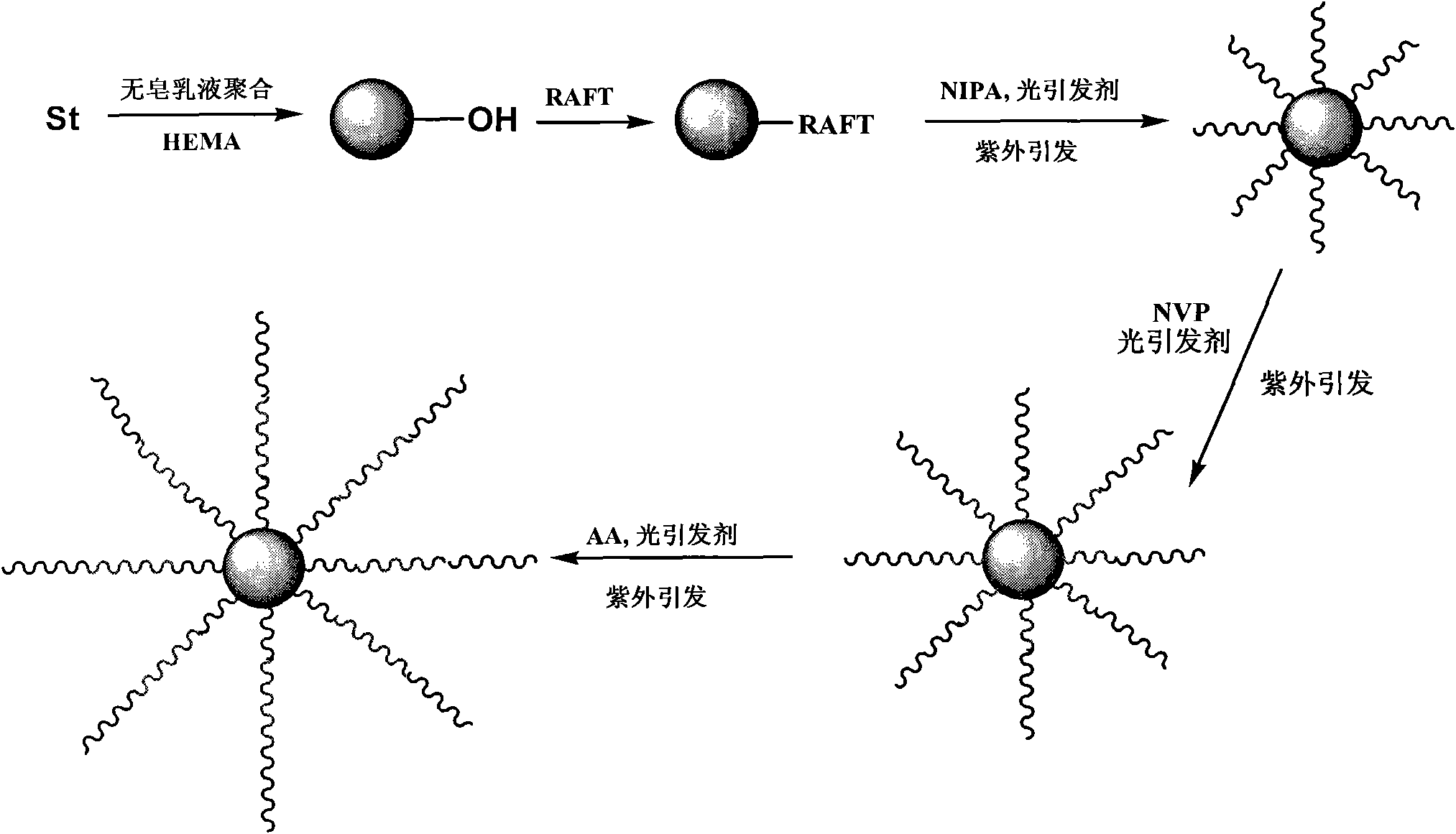
Methods for preparing multiple environment-responding type hairy polymer micro-spheres and photo-initiation RAFT (Reversible Addition-Fragmentation chain Transfer) polymerization thereof
The invention relates to methods for preparing a multiple environment-responding type hairy polymer micro-spheres and photo-initiation RAFT (Reversible Addition-Fragmentation chain Transfer) polymerization thereof. The hairy structure of the surface of the hairy polymer micro-spheres prepared by the invention is a polyN-isopropyl acrylamide, polyN-vinyl pyrrolidone, polyacrylic acid homopolymerization-type, diblock-type or triblock-type polymer brush. The hairy polymer micro-spheres have the advantages of controllable structure, temperature sensitivity and pH sensitivity, and can be used for protein renaturation, chemical valves, drug encapsulation and catalyzer loading and other aspects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
PH-sensitive pentablock linear polymer based on PDEAEMA and micelle
ActiveCN104650307AQuick releaseControlled releasePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsEmulsion deliveryMolecular materialsDrug encapsulation
The invention belongs to the technical field of high polymer materials for biological medicines and discloses a pH-sensitive pentablock linear polymer based on PDEAEMA, a preparation method of the polymer and a micelle system obtained based on the polymer and the application of the micelle system. The polymer has the structure shown in a formula described in the specification, wherein x is equal to 45, y is equal to 19-37, and z is equal to 15-19. A symmetrical pentablock linear polymer is designed and synthesized, the drug encapsulation amount of the polymer can be obviously improved, the pH response range of the self-assembly micelle can be well regulated by virtue of the intermediate layer PDEAEMA so that the drug loading micelle can rapidly respond the change of the pH value in a tumor environment, the drug release can be effectively controlled, and burst release of the drug is avoided. A thick pH responsive intermediate layer is formed in the micelle formed by the polymer, the encapsulation capacity is improved, the drug release performance is improved, the particle size of the micelle after drug release is reduced, the drug discharge is facilitated, and the polymer can be widely applied to the field of medicines.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
ATP responding type drug-releasing nano gel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107349176AImprove securityImprove targetingOrganic active ingredientsAerosol deliveryHigh concentrationDrug encapsulation
The invention relates to an ATP responding type drug-releasing nano gel and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of medicine. The nano gel is composed of carboxymethyl chitosan, DNA 1 with carboxyl modified terminals, DNA 2 with carboxyl modified terminals, and an ATP aptamer. Amino groups of carboxymethyl chitosan react with carboxyl groups of terminals of single chain DNA 1 and DNA2 to form stable amide bonds; because the ATP aptamer can carry out complementary base pairing with single chain DNA 1 and DNA2, the ATP aptamer can be used as a gel crosslinking agent, which can realize the crosslinking of nano gel; through physical embedding, doxorubicin hydrochloride is embedded in the GC segment of nucleic acid, the drug encapsulation is realized; and a novel ATP responding type drug-releasing nano gel drug delivering system is prepared. The system can respond to the high concentration ATP in tumor cell and competitively combines with the gel crosslinking agent (ATP aptamer); thus the complementarily paired nucleic acid chains are broken, the gel skeleton is broken, and drugs are released. The provided nano gel can improve the safety and targeting property of a tumor drug delivery system to a certain degree.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Instrument and method for ultrasound mediated drug delivery
InactiveUS20140135681A1Prevention and therapyIncreases mechanical indexUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasonic radiationMechanical index
A method and instrumentation for ultrasound mediated delivery of drugs to diseased tissue use ultrasound beams with frequency and focusing that provides an ultrasound radiation force acting on the drug and surrounding fluid, which produces a convection of drugs and compensates for the lack of a pressure gradient. To manipulate drug encapsulations and also stimulate transport of drugs across biological membranes, like the cell membrane or the blood brain barrier, the method and instrumentation use low frequency beams with high mechanical index. The method and instrumentation additionally uses ultrasound heating of the tissue to increase blood flow and manipulate thermally sensitive particles.
Owner:SURF TECH AS
Magnetism/temperature/pH tri-responsive nanogel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109745285AEasy to operateMild experimental conditionsOrganic active ingredientsAerosol deliveryCross-linkRelease time
The invention discloses a magnetism / temperature / pH tri-responsive nanogel medicine carrying system capable of carrying combined chemotherapy drug of the breast cancer, namely paclitaxel, and disclosesa preparation method of magnetic nanogel. The preparation method comprises the steps that Fe3O4 nano particles are prepared by adopting a chemically modified coprecipitation method, polyacrylic acid(PAA) and N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM) are taken as monomers, divinylbenzene (DVB) is taken as a cross-linking agent, Fe3O4 is taken as a nuclear body material, and the magnetic nanogel is prepared by adopting a miniemulsion co-polymerization method. The preparation method of the magnetic nanogel has the advantages that the magnetic nanogel loaded with the paclitaxel is synthesized through the miniemulsion polymerization method, the operation is simple, the experiment conditions are mild, and the synthesized nanogel is regular in appearance and uniform in dispersion, and has good temperaturesensibility and pH-sensitivity. Test results show that drug encapsulation efficiency is high, and the slow-release time is as long as 14 days.
Owner:JINLING INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com