Method for screening and identifying potassium-rich tobacco
An identification method and potassium-rich technology, applied in the field of tobacco heredity and variety selection, can solve the problems of blindness, unusability, and heavy workload, and achieve the effects of accurate experimental results, improved screening efficiency, and strong operability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
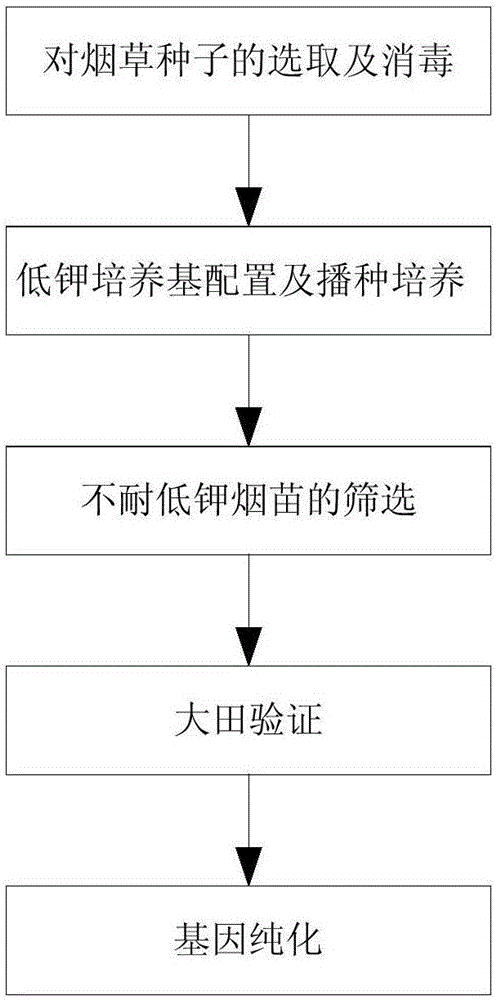
[0035] Example 1 Utilize the different grades of low-potassium-resistant plants screened out by low-potassium medium and their performance in the field
[0036] 500 mutant materials of "China Tobacco 100" were selected as the research objects. "China Tobacco 100" is a high-yield, nitrogen-tolerant genotypic tobacco variety. The low-potassium medium is used to screen plants that are not tolerant to low-potassium. After transplanting into field experiments, potassium-rich tobacco variants can be obtained, and then cultivated Potassium tobacco genotype varieties. Such as figure 1 As shown, the "China Tobacco 100" tobacco potassium-rich screening and identification method specifically includes the following steps:
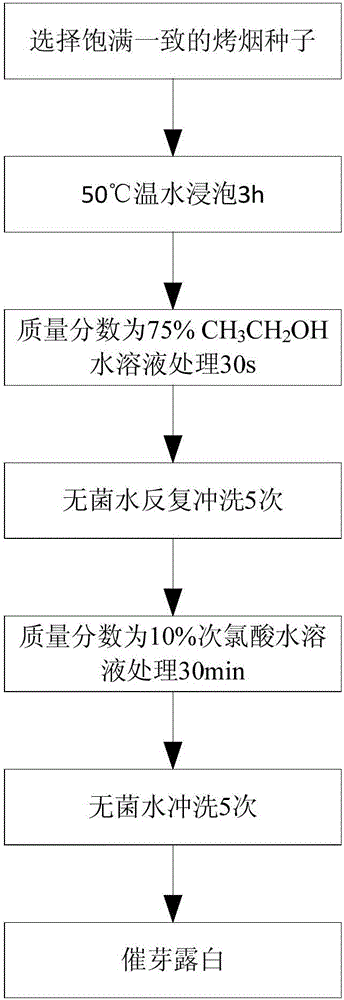
[0037] (1) Selection and disinfection of tobacco seeds
[0038] Such as figure 2 As shown, the process of selecting and disinfecting tobacco seeds is as follows: first select plump and consistent "China Tobacco 100" flue-cured tobacco seeds, and then soak them in ...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Example 2 Potassium Absorption Kinetics of NHX1 Tobacco and Response to Low Potassium
[0076] Guo Zhaokui, Heilongjiang Institute of Tobacco Science, transformed the yeast NHX1 gene into tobacco, and found that compared with the untransformed tobacco leaves, the potassium content of the transformed NHX1 tobacco leaves increased by 27.4% on average, and the potassium content of the material with the highest potassium content increased compared with the control tobacco. 42.3%.
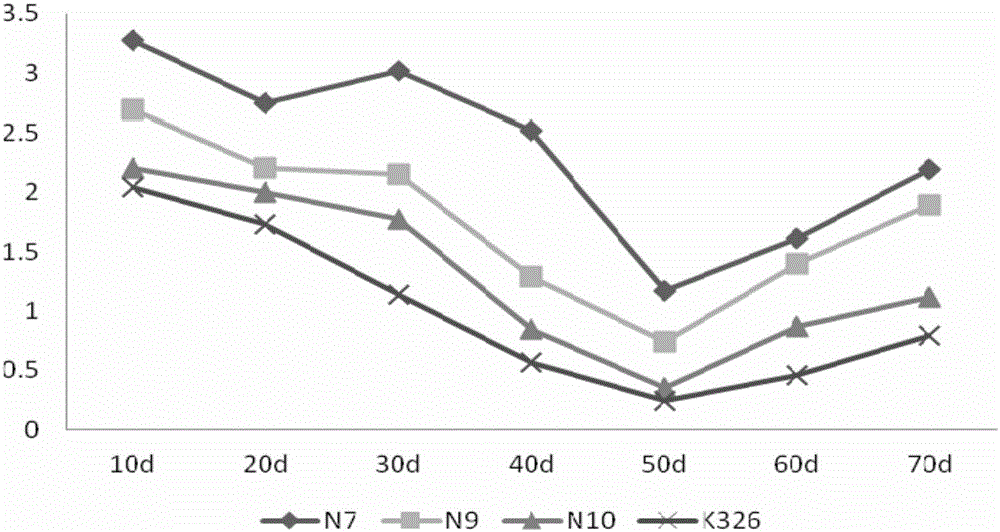
[0077] The NHX1-transformed tobacco lines N7, N9, N10 and K326 were compared and tested, and the changes of tobacco leaf potassium content with leaf age in the field test of NHX1-transferred tobacco lines N7, N9, N10 and K326 were as follows: image 3 As shown, the kinetic parameters of potassium uptake are shown in Table 6; later, N7, N9, N10 and K326 transgenic NHX1 tobacco lines were moved to low-potassium hydroponic conditions for cultivation. Potassium responses are shown in Table 7.
[00...
Embodiment 3
[0086] Example 3 Response of Nongda 202 and NHX1 Tobacco to Low Potassium
[0087] Under the same field cultivation and management conditions, the potassium content of the middle tobacco leaves of Nongda 202 and NHX1 tobacco at the mature stage were compared, and the comparison results are shown in Table 8; After culturing for 30 days, the responses of the two types of tobacco to normal potassium and low potassium were tested, and the response results are shown in Table 9.
[0088] Table 8 Comparison results of potassium content in middle tobacco leaves of Nongda 202 and NHX1
[0089]
[0090] Table 9 Response results of Nongda 202 and NHX1 tobacco to normal potassium and low potassium
[0091]
[0092] It can be seen from Table 8 that compared with Nongda 202, the potassium content of NHX1-transformed tobacco was higher. It can be seen from Table 9 that compared with Nongda 202, the transgenic NHX1 tobacco had a higher rate of yellowing under low potassium conditions,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com