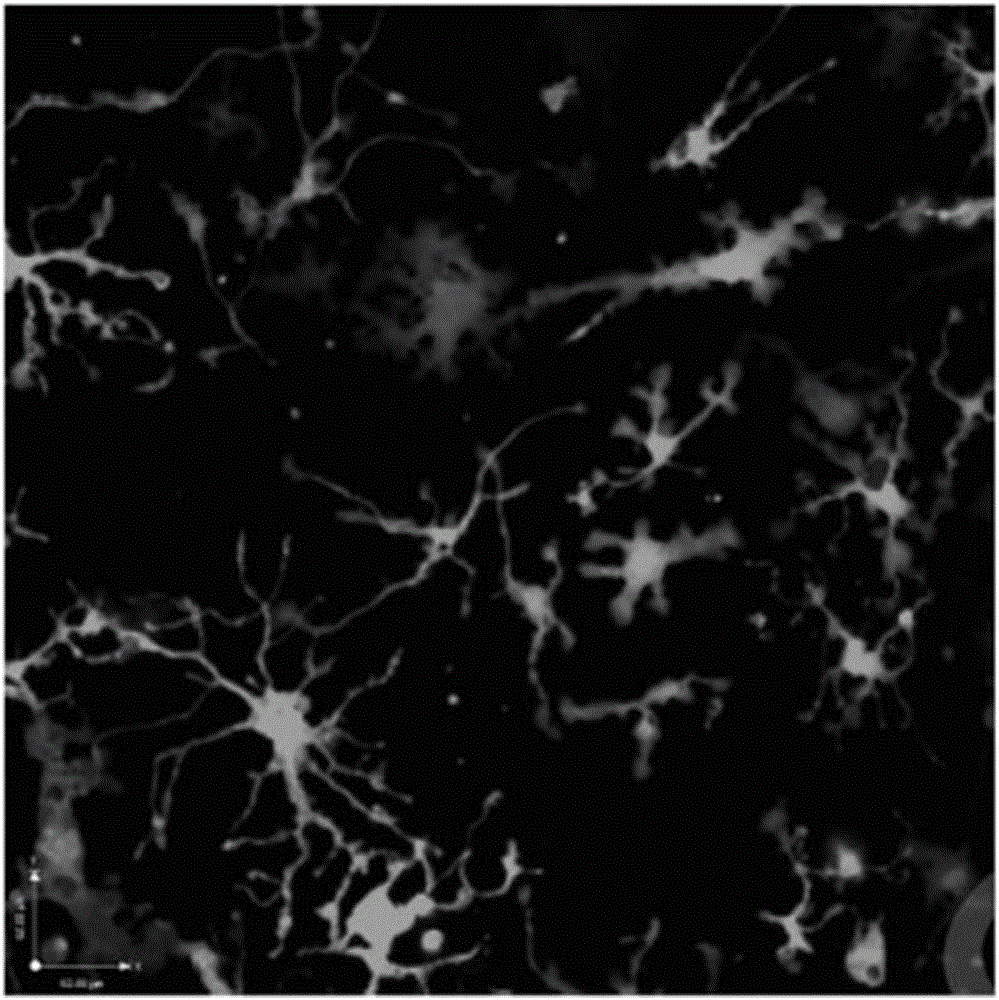
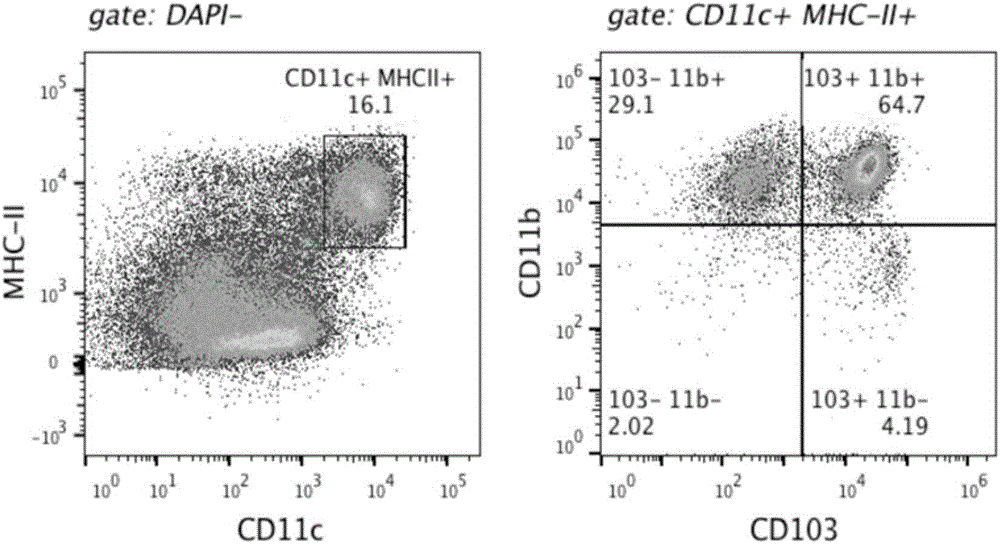
Separation method of mouse intestinal lamina propria primary dendritic cells
A technology of dendritic cells and lamina propria, applied in the field of isolation of primary dendritic cells in the lamina propria of the mouse intestine, can solve problems such as difficulty in achieving satisfactory results, easy death, and excessive cell damage, and shorten the potential Toxic action time, reduce mechanical damage, and increase cell productivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] 1. Put mice in routine CO 2 After execution, the abdominal wall and peritoneum were cut longitudinally with scissors to expose the abdominal viscera. The scissors intercepted the entire small intestine from the duodenum to the ileocecal, and put it in balanced salt solution A for temporary storage;
[0033] 2. Cut the small intestine into 4 segments on average (each segment is about 10-12cm long), ligate one end of the intestinal segment with silk thread, turn the intestinal segment to the surface of the thin tube with a polyethylene thin tube (so that the inner surface of the intestinal tube is exposed), and fix it with silk thread ligation (Such as figure 1 ), put into the 15ml test tube that 12ml balanced salt solution B is housed;
[0034] 3. After manually shaking the test tube for 2 minutes, replace it with a new 12ml balanced salt solution B, and shake it for another 2 minutes. Repeat this for a total of 3 times to wash away impurities such as fecal residue on t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com