Method for preparing highly corrosion-resistant sintered NdFeB magnet
A NdFeB, high corrosion-resistant technology, applied in the direction of magnetic objects, inductance/transformer/magnet manufacturing, magnetic materials, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient diffusion at low temperature, uneven distribution of diffusion elements, and insufficient depth of diffusion layer, etc. , to achieve the effect of eliminating the heat treatment diffusion process, increasing the diffusion temperature, and improving the microstructure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
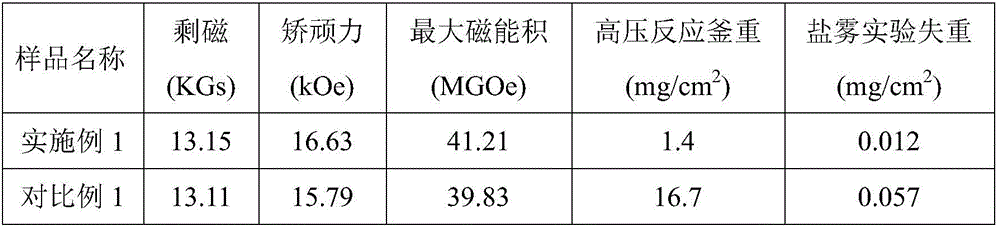
[0032] Example 1: 6mm thick sintered magnet surface covered with Al 2 o 3 grain boundary diffusion heat treatment
[0033] Step 1. Fe and Pr with a purity of 99.9% 22.5 Nd 77.5 、Dy 80 Fe 20 , Fe 81.4 B 18.6 Other raw materials according to (Pr, Nd) 12.5 Dy 1.0 Fe bal Nb 0.1 B 6.0 (bal: refers to the proportion of the above ingredients removed, and the remaining proportion) for proportioning. Use a vacuum induction furnace to smelt and throw the strips to make alloy thin strips, which are crushed by hydrogen to make coarse powder, and then jet milled to make fine magnetic powder with an average particle size of 5um;
[0034] Step 2. The prepared NdFeB magnetic powder is oriented and pressed under 1.8T magnetic field and 16MPa; then oil-cooled and isostatic pressed under 225MPa to make a green body, and the holding time is 30S.
[0035] Step 3. Put the green body into the RVS-10G vacuum sintering furnace for vacuum low-temperature pre-sintering. The sintering temperat...
Embodiment 2
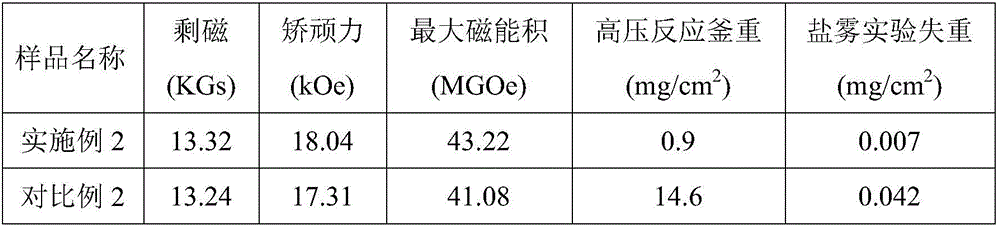
[0044] Example 2: 5mm thick sintered magnet surface covered with TiO 2 grain boundary diffusion heat treatment
[0045] Step 1. Fe and Pr with a purity of 99.9% 22.5 Nd 77.5 、Dy 80 Fe 20 , Fe 81.4 B 18.6 Other raw materials according to (Pr, Nd) 12.8 Dy 1.0 Fe bal co 0.3 Nb 0.2 B 6.0 Make a ratio. Melt in a vacuum induction furnace and throw the strips to make thin alloy strips, crush them with hydrogen to make coarse powders, and then go through jet mills to make fine magnetic powders with an average particle size of about 4um.
[0046] Step 2. The prepared magnetic powder is oriented and pressed under 2.0T magnetic field and 16MPa; then it is oil-cooled and isostatically pressed under 250MPa to form a green body, and the holding time is 25S.
[0047] Step 3. Put the green body into the RVS-10G vacuum sintering furnace for vacuum low-temperature pre-sintering. The sintering temperature is 870°C, the holding time is 3.5h, and the vacuum degree is 1.0×10 -2 Pa, ai...
Embodiment 2 and comparative example 2
[0053] Table 2 Example 2 and Comparative Example 2 magnet corrosion resistance and magnet magnetic performance comparison
[0054]
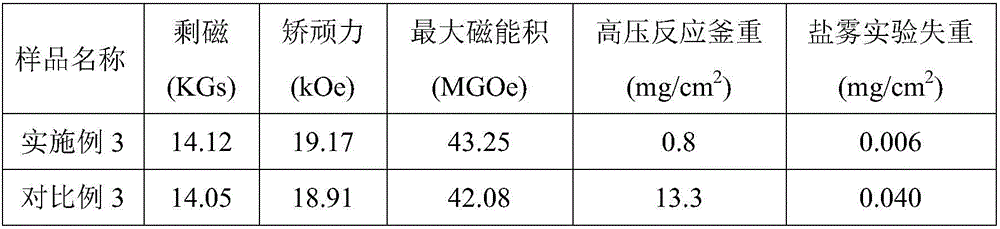
[0055] The above results show that for the sintered NdFeB magnets of the same composition, the grain boundary diffusion metal oxide (TiO 2 ) can significantly improve its corrosion resistance, and at the same time ensure the magnetic properties of the magnet, and have a small increase.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com