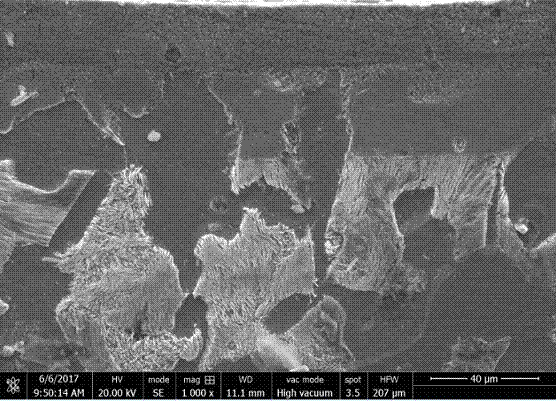
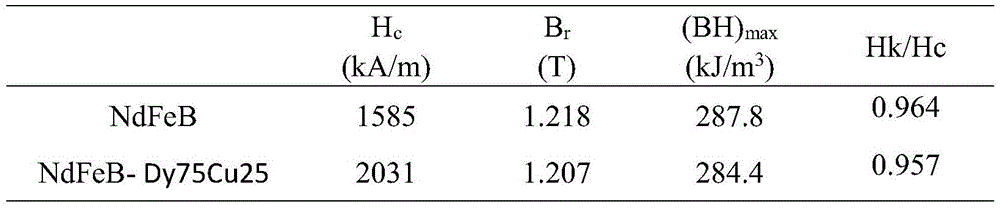
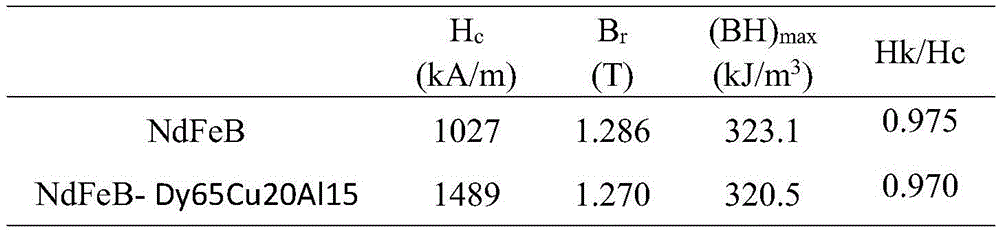
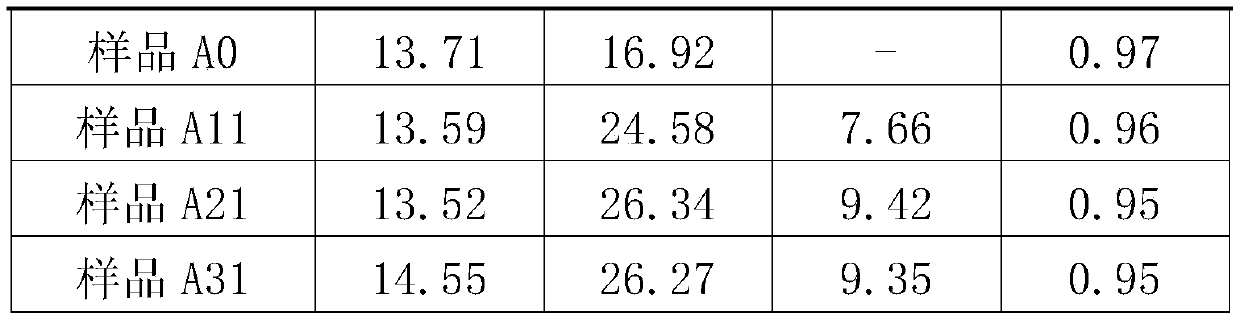
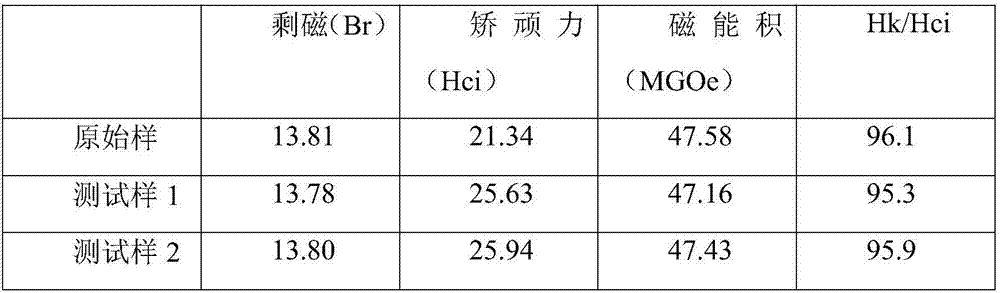
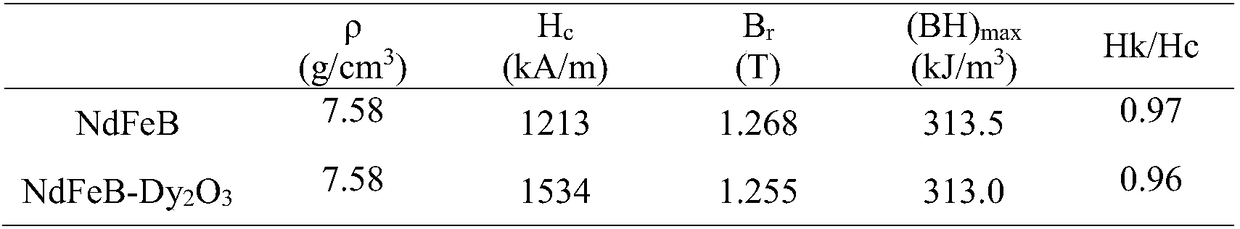
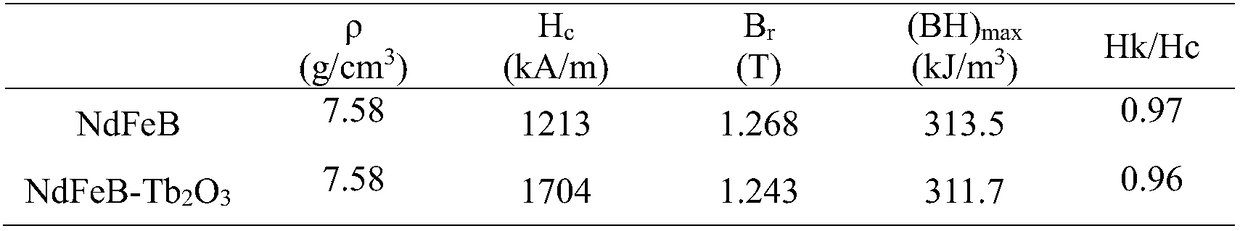
Patents
Literature
72results about How to "Increased Diffusion Depth" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Grain boundary diffusion method for improving properties of sintered NdFeB magnets
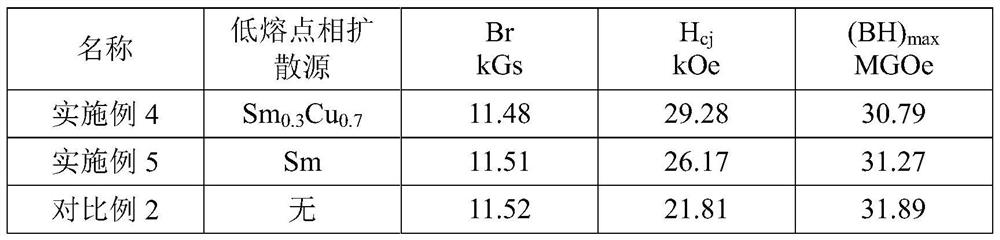
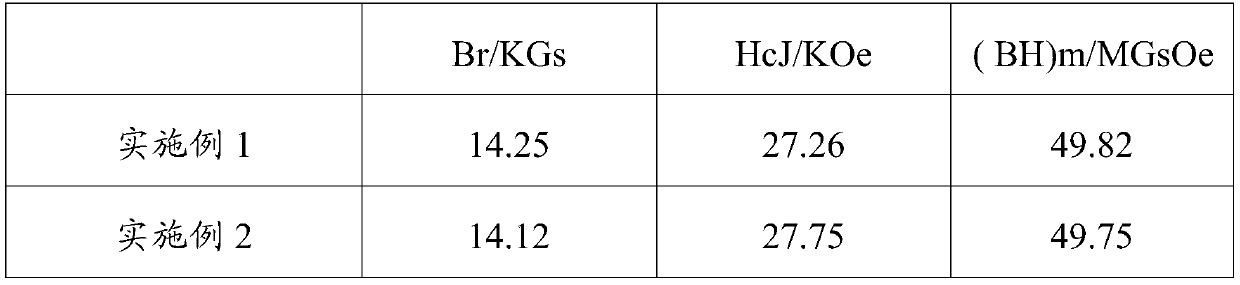
ActiveCN104388951AIncreased diffusion kinetic energyLow melting pointInorganic material magnetismRare-earth elementDiffusion methods
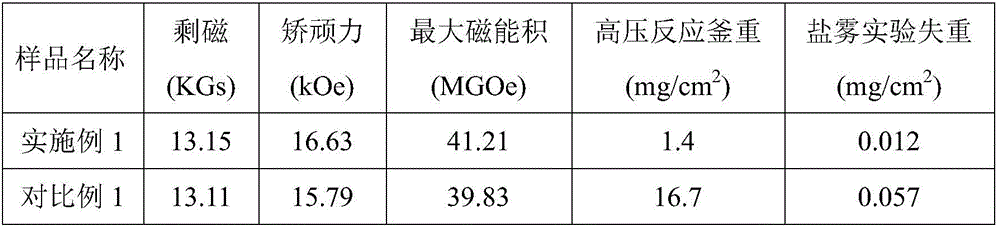
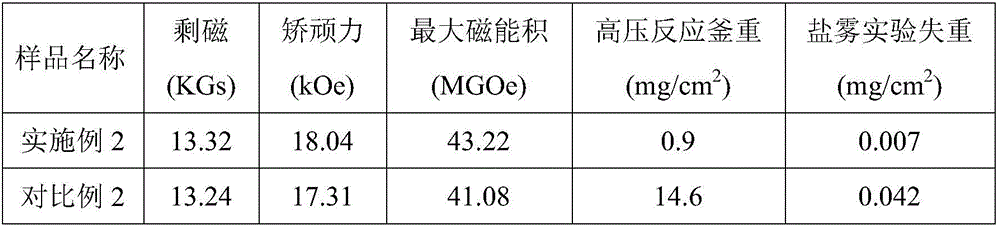
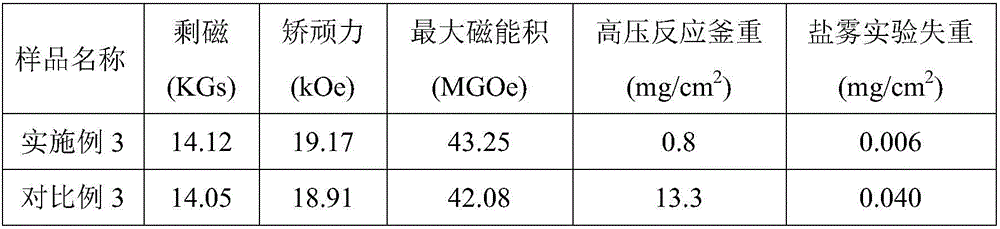
The invention relates to a grain boundary diffusion method for improving properties of sintered NdFeB magnets. The grain boundary diffusion method comprises the following steps of stacking sintered NdFeB magnets and diffusion alloy sheets together and placing in a hot-pressing furnace; vacuumizing the hot-pressing furnace until the vacuum degree reaches a set value, heating the hot-pressing furnace, and when the temperature of the hot-pressing furnace reaches a set value, beginning to exert a pressure and maintaining the pressure and putting the diffused sample into a high-vacuum furnace for annealing, wherein the diffusion alloy sheets are low-melting-point eutectic diffusion alloys and are represented by R-TM, R is one or more of Sc, Y, La, Ce, Pr or Nd and TM is one or more of Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu and Zn. Compared with the prior art, the sintered NdFeB magnets modified by the pressure diffusion method, which is provided by the invention, have the advantages of large diffusion depth of a diffusion agent, uniform distribution of grain boundary phases, high coercivity and the like, especially, low-melting-point diffusion alloys designed by the invention are free of expensive heavy rare earth element dysprosium and thus the cost of the raw materials is relatively low, the diffusion temperature is low and the energy consumption in the diffusion process is small.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Crystal boundary diffusion method for improving coercive force and thermal stability of neodymium-iron-boron magnet
InactiveCN107093516ADiffusion rate is fastInhibit growthInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureRare earthHeat treated
The invention discloses a crystal boundary diffusion method for improving the coercive force and the thermal stability of a neodymium-iron-boron magnet, and belongs to the field of rare earth permanent magnet materials. According to the method, a quaternary alloy Dy-Ni-Al-Cu with a low melting point is used as a diffusion source and melted and prepared into a rapid-hardening strip, after coarse breaking, the strip casting is laid around the neodymium-iron-boron magnet, and by the adoption of a heat treatment method, the rapid-hardening strip diffuses and enters the magnet along the crystal boundary. After the processing, the coercive force of the magnet is significantly improved, and the magnetic energy product is improved to a certain extent; meanwhile, since the temperature of the diffusion treatment is low, energy consumption can be reduced, the cost can be lowered, and Nd2Fe14B crystal grains can be prevented from growing up; compared with a coating and magnetron sputtering method, the crystal boundary diffusion method omits a powder preparing and coating process in a coating technology and a thin film preparing process in a magnetron sputtering technology. After the technology processing of the crystal boundary diffusion method, the neodymium-iron-boron magnet with the high coercive force and the high thermal stability is finally obtained.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for improving magnetic properties of sintered neodymium-iron-boron thin-sheet magnet
ActiveCN105632748AImprove diffusion efficiencyIncreased Diffusion DepthInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementHigh volume manufacturing
The invention discloses a method for improving magnetic properties of a sintered neodymium-iron-boron thin-sheet magnet. According to the method, the surface of the sintered neodymium-iron-boron thin-sheet magnet is coated with powder containing rare earth elements to form a surface coating layer, and diffusion treatment and aging treatment are carried out to allow the rare earth elements in the coating layer to enter the interior of the sintered neodymium-iron-boron thin-sheet magnet, wherein the powder containing the rare earth elements is a mixture of powder of rare earth oxide and powder of hydrogen storage alloy hydride. The method has the advantages that oxidation-reduction reaction is carried out between the rare earth elements and the hydrogen storage alloy hydride, the rare earth elements are reduced, hydrogen is released from the hydrogen storage alloy hydride during diffusion treatment, thus, the diffusion efficiency of the rare earth elements is remarkably reduced, the diffusion depth of the rare earth elements is increased, the content difference of the rare earth elements at different positions in the sintered neodymium-iron-boron thin-sheet magnet is reduced, the coercive force is obviously increased, and residual magnetism reduction is ensured not to be obvious; and moreover, mass production can be achieved, and the final squareness of the sintered neodymium-iron-boron thin-sheet magnet cannot be affected.
Owner:NINGBO YUNSHENG +1
Method for obtaining high-magnetism sintered neodymium iron boron by means of hot isostatic pressure
ActiveCN105655075ALow melting pointImprove liquidityInorganic material magnetismRare earthSlow cooling
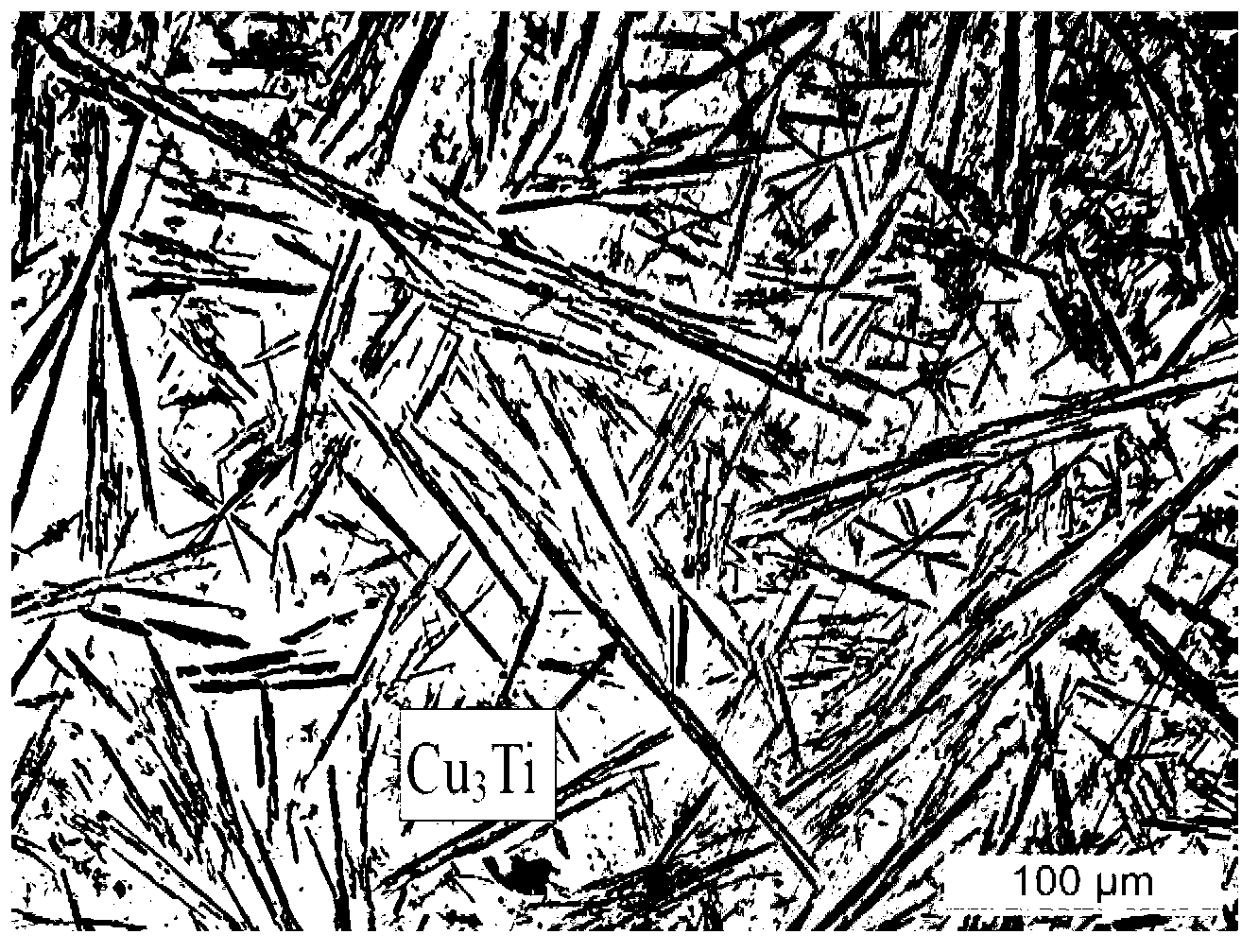
The invention provides a method for obtaining high-magnetism sintered neodymium iron boron by means of hot isostatic pressure and belongs to the technical field of rare earth magnetic materials. According to the method, a sintered neodymium iron boron body and a low-melting-point diffusion alloy piece are stacked together, pressure is exerted in a hot isostatic pressure machine and kept for carrying out diffusing heat treatment and annealing heat treatment, diffusing heat treatment temperature ranges from 700 DEG C to 900 DEG C, the temperature is preserved for 3-5 h, annealing heat treatment is carried out for 2-10 h at the temperature of 400 DEG C-600 DEG C, and slow cooling is carried out to obtain the sintered neodymium iron boron body diffused uniformly. In the hot isostatic pressure diffusing heat treatment process, the low-melting-point diffusion alloy piece is melted to liquid to wrap the surface of neodymium iron boron, diffusion kinetic energy of the melted diffusion alloy is increased due to pressure, diffusion of elements such as Dy, Cu, Al and Ni in a crystal boundary can be accelerated, and the depth of a diffusion layer is increased. A diffusion source is melted into liquid, and the processes of fine powder manufacturing and surface coating can be omitted. The neodymium iron boron body after the hot isostatic pressure is diffused has the advantages of being large in diffusion depth, uniform in crystal boundary phase distribution, clear in boundary, high in coercivity and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Preparation method of high-performance neodymium-iron-boron magnet
InactiveCN110164644AImprove uniformityImprove controllabilityInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsOxideControllability
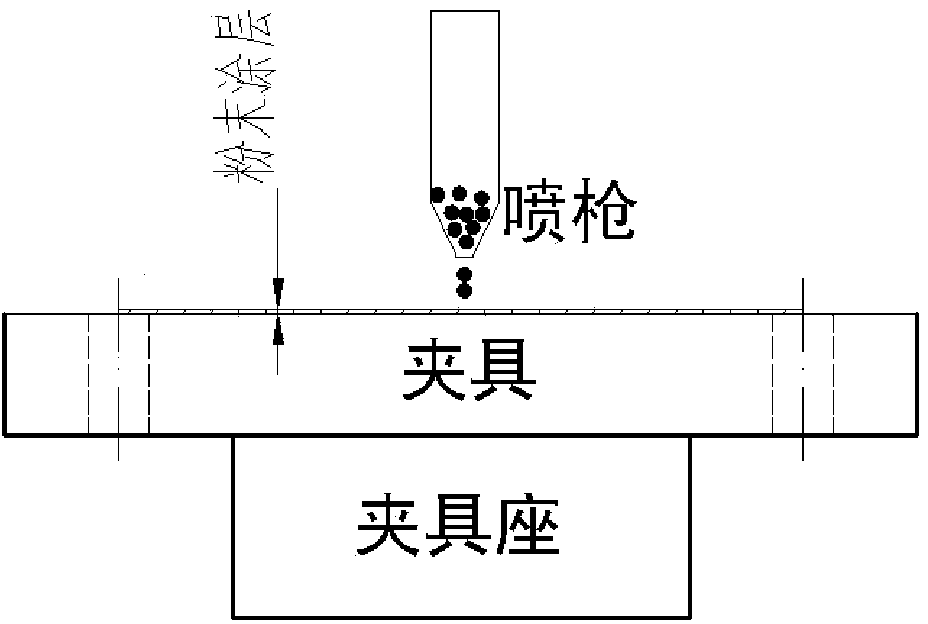
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-performance neodymium-iron-boron magnet. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing R1-Fe-B-M sintered magnet blank, configuring volatile oil solvent suspension containing alloy powder of heavy rare earth or low melting point metal, hydride, fluoride or oxide and heating, cleaning the blank and immersing the blank into thesuspension at the angle of 5-45 degrees and then taking out and sintering so as to obtain the magnet. The preparation method has the advantages that the high-temperature volatile organic solvent is applied and volatilization is quite quick so as to greatly improve uniformity and controllability, omit the conventional dip-coating or spray-drying process in the past, save energy, greatly improve the production efficiency, increase the material utilization rate reduce the cost and have higher uniformity of diffusion; and the introduction of impurities such as C is greatly reduced by the use of the volatile solvent.
Owner:ZHEJIANG INNUOVO MAGNETICS
Method for improving magnetic performance of sintered neodymium-iron-boron magnet
InactiveCN109898063AImprove coercive forceIncreased Diffusion DepthVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingRare-earth elementNeodymium iron boron
The invention relates to a method for improving magnetic performance of a sintered neodymium-iron-boron magnet. The method is suitable for sintered neodymium-iron-boron magnets with various components. The method comprises low-melting-point metal or alloy grain boundary repairing, heavy rare earth element grain boundary diffusion and corresponding heat treatment technologies. According to the method, the character of the low melting point of an alloy is utilized, the surface-layer discontinuous grain boundary rare earth phase of the magnet is preferably diffused and repaired, a continuous low-melting-point rare earth phase is obtained and serves as a channel for rapid diffusion of heavy rare earth elements, the diffusion depth of the heavy rare earth elements in the magnet is effectively improved, the usage amount of the heavy rare earth elements is reduced, the coercivity of the magnet is improved, and wide application value is achieved.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing nanometer surface coating
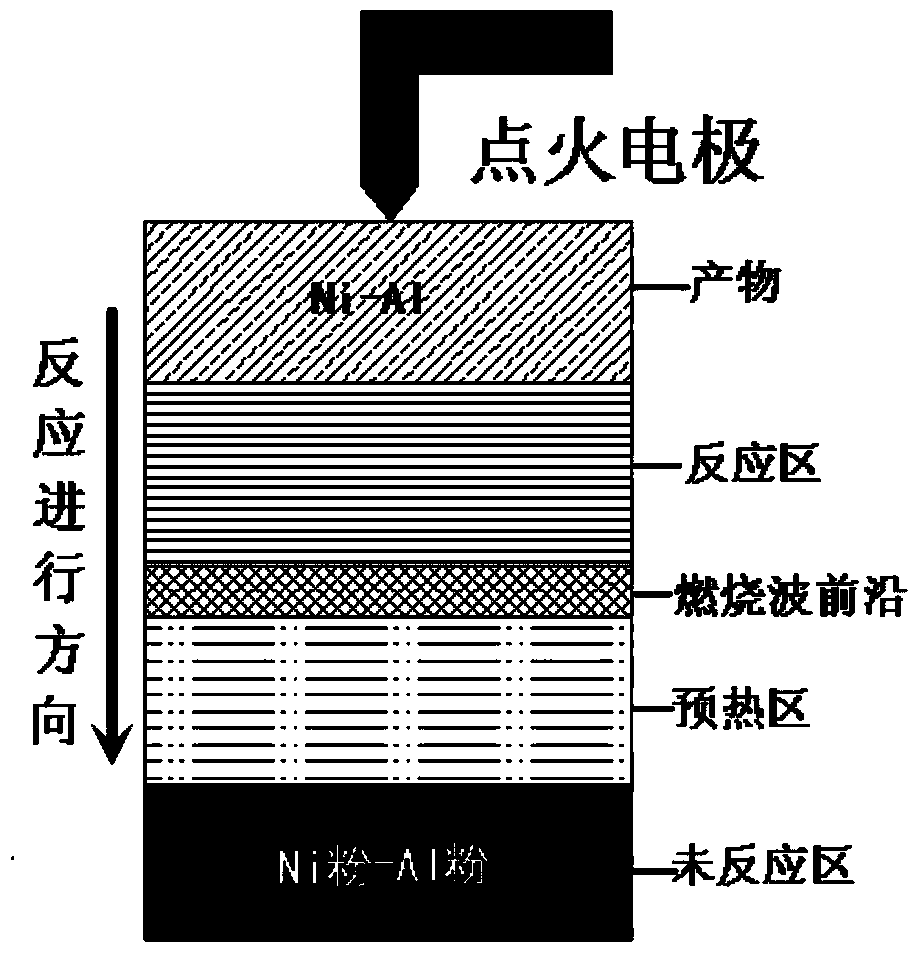
InactiveCN103469200AIncreased Diffusion DepthImprove adhesionMetallic material coating processesPeeningEnergy consumption
A disclosed method for preparing a nanometer surface coating comprises the following steps: 1) performing ball milling on a self-propagation reaction metal mixed powder, coating on the surface of a metal plate; 2) igniting the metal mixed powder coating on the surface of the metal plate to make the metal mixed powder coating have a self-propagation reaction; and 3) performing shot blasting on the metal mixed powder coating subjected to the self-propagation reaction, to obtain the nanometer surface coating after the self-propagation reaction and shot blasting are finished. According to the method, shot blasting is performed on the coating after the self-propagation reaction is carried out for a certain time, so that the coating metal powder is increased in diffusion depth in the metal surface, and the bonding force between the coating and the matrix metal is increased; by shot blasting, the density of the coating is improved substantially, and shot blasting has surface nanocrystallization effect; the prepared coating has high density and high viscosity; and the preparation method of the invention is simple in equipment, low in energy consumption and low in cost.
Owner:CHONGQING ACADEMY OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing sintered rare earth-based magnet using melting point depression element and sintered rare earth-based magnet prepared thereby
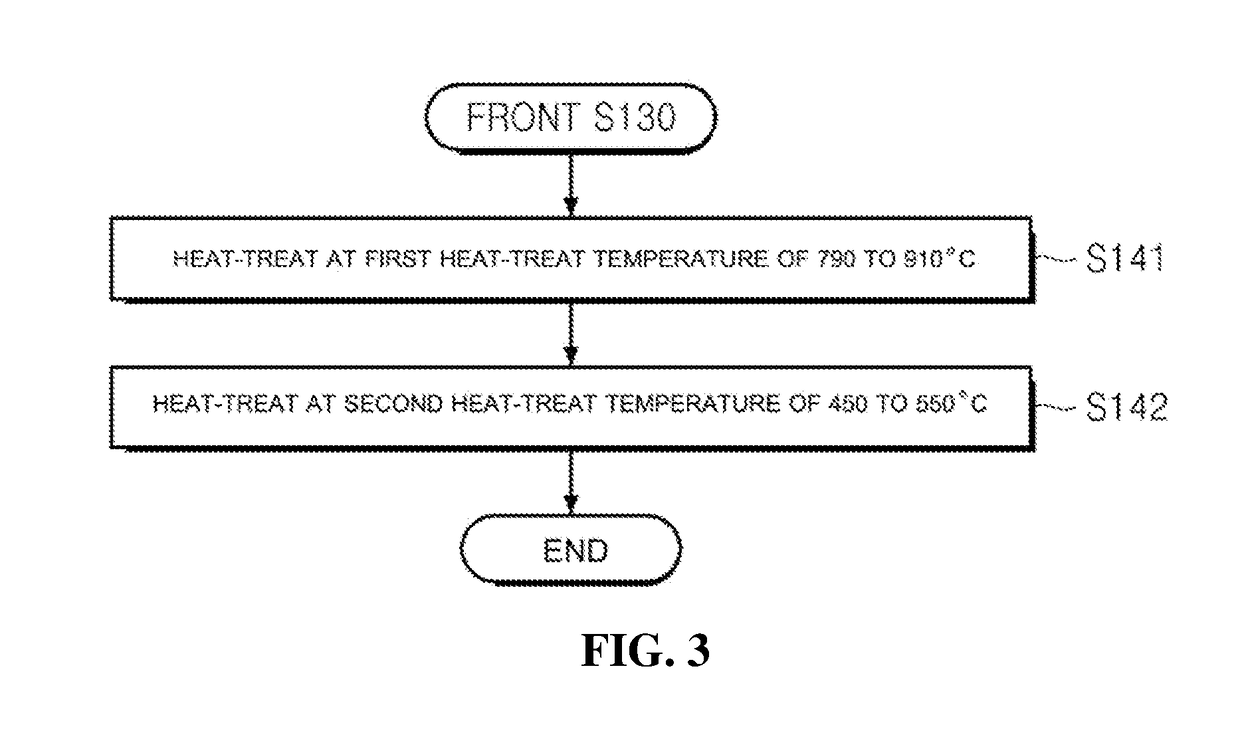
InactiveUS20180218835A1Improve coercive forceIncreased Diffusion DepthInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementSintered magnets
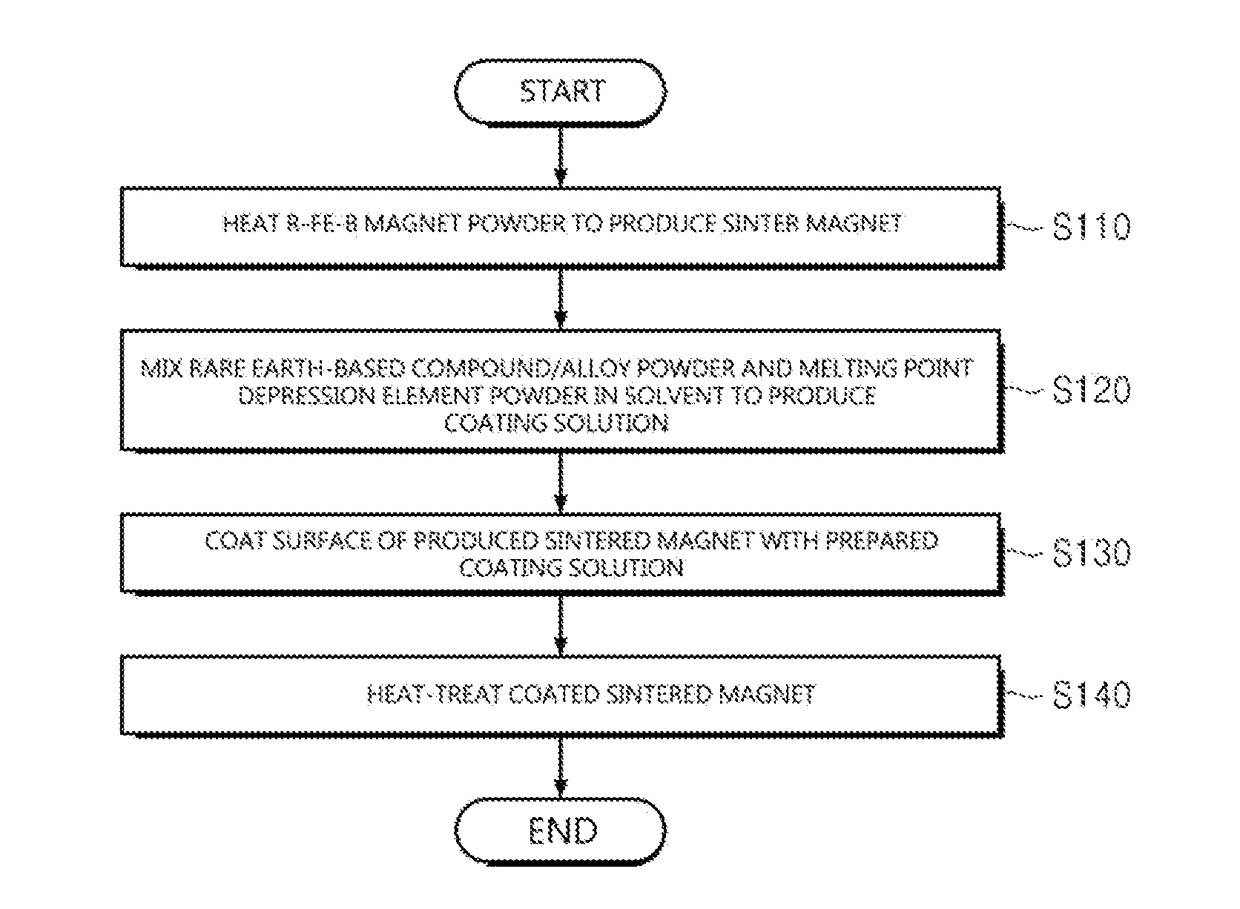
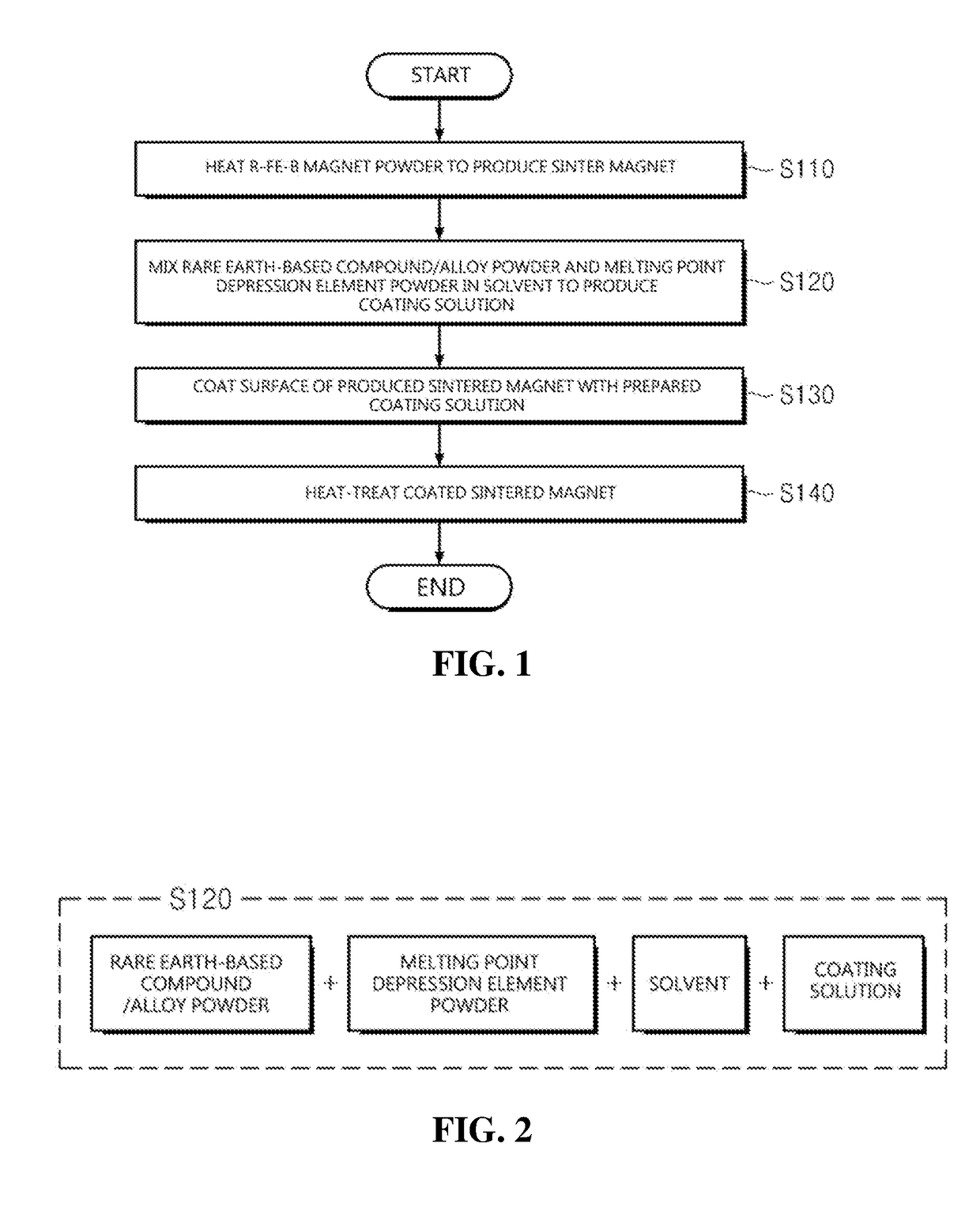
A method for preparing a sintered rare earth-based magnet using a melting point depression element and a sintered rare earth-based magnet prepared by the same are disclosed. The method for preparing a sintered rare earth-based magnet according to the present invention includes the steps of: heating an R—Fe—B based magnet powder to a predetermined temperature to produce a sintered magnet, in which R is a rare earth element or a combination of rare earth elements; coating the surface of the produced sintered magnet with a coating solution prepared by mixing a heavy rare earth powder and a melting point depression element powder in a solvent; and heat-treating the coated sintered magnet.
Owner:IND UNIV COOP FOUND SUNMOON UNIV
Method for obtaining high-magnetism sintered NdFeB by hot isostatic pressing low-temperature sintering
A method for obtaining a high-magnetism sintered NdFeB by hot isostatic pressing low-temperature sintering belongs to the technical field of a rare-earth magnetic material. The method comprises the steps of performing half-density sintering on sintered NdFeB magnetic power, covering surrounding of half-density sintered NdFeB with a low-melting point diffusion alloy source, placing the NdFeB in a glass tube, performing vacuum glass tube sealing, and performing hot isostatic pressing low-temperature sintering and tempering to prepare the high-density and high-magnetism sintered NdFeB magnet. Inthe hot isostatic pressing low-temperature sintering process, the glass tube is a molten state, a layer of glass package sleeve is formed on a surface of a sample, and the sintering density of the half-density NdFeB magnet reaches 7.5g / cm<3> or above by air pressure acting on each surface of the glass package sleeve; meanwhile, the diffusion element diffusing along a boundary is accelerated underthe effect of air pressure, the depth of a diffusion layer is increased, and the thickness of the sample reaches 1.5 centimeter or above; the NdFeB magnet subjected to hot isostatic pressing low-temperature sintering has the advantages of large diffusion depth, uniform boundary phase distribution, clean boundary, fine crystal grain, high density, high coercivity and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Passivated solar cell with printed metal electrodes and preparation method thereof
PendingCN109713065AExtended tailShallow tailFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationCrystalline siliconMetal electrodes
The invention relates to a passivated solar cell with printed metal electrodes and a preparation method thereof. The passivated solar cell comprises an N-type crystalline silicon substrate, and the back surface of the N-type crystalline silicon substrate sequentially comprises an n+ doped polycrystalline silicon layer, a back passivated antireflection film and n+ metal electrodes from inside to outside. A doped polycrystalline silicon band tail layer is formed at one side, close to the n+ doped polycrystalline silicon layer, of the N-type crystalline silicon substrate. The band tail of the doped polycrystalline silicon layer in the metal contact region is prolonged, and the diffusion depth of doped atoms in crystalline silicon is increased, thereby reducing the recombination of the metal contact region. The band tail of the doped polycrystalline silicon layer in the non-metal contact region remains shallower, and the recombination of the non-metal contact region is reduced. The methodis simple in process, and the n+ doped polycrystalline silicon layers of the first region and the second region can be completed through one-time doping. The related technological processes are industrialized and suitable for large-scale production. Metal contact recombination and resistance loss can be obviously reduced, and open-circuit voltage and conversion efficiency of the cell are improved.
Owner:TAIZHOU ZHONGLAI PHOTOELECTRIC TECH CO LTD
Multi-layer in-situ agent injection method for contaminated site
ActiveCN108380660AAchieve uniformityIncrease profitContaminated soil reclamationContaminationMaterials science
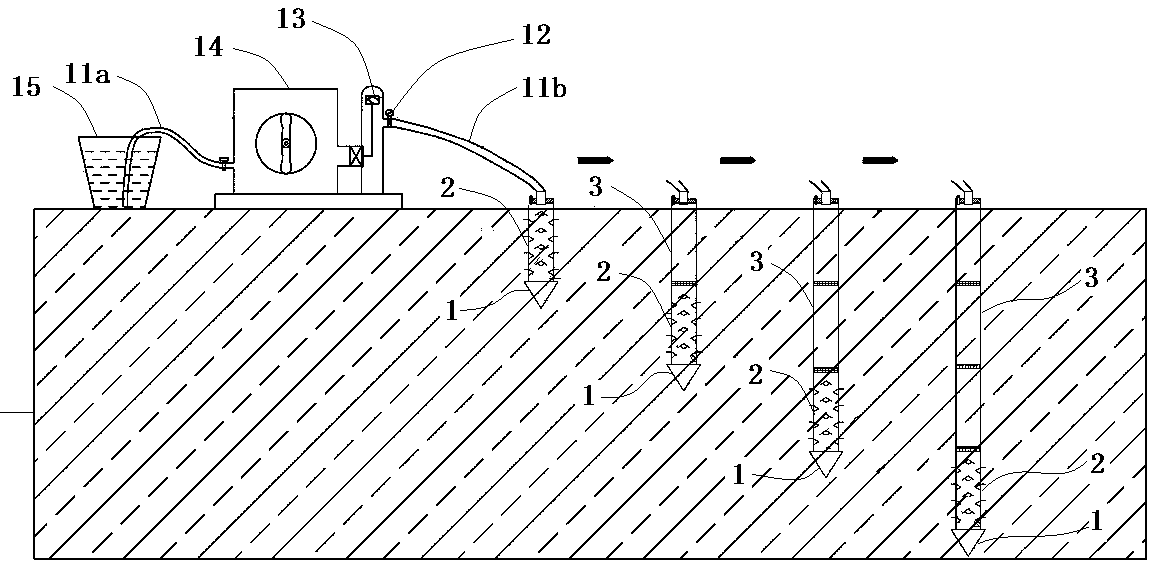
The invention discloses a multi-layer in-situ agent injection method for a contaminated site. The multi-layer in-situ agent injection method comprises the following steps that (1) an agent injection steel pipe is pressed to the first-stage depth in a soil body; a pipe sealing cover is arranged at an upper port of the agent injection steel pipe, a closed cavity is formed, and a remediation agent ispumped into the agent injection steel pipe to achieve remediation within the first-stage depth range; (2), the pipe sealing cover is dismantled, the agent injection steel pipe is lengthened through aconnecting pipe group and pressed to the second-stage depth in the soil body, the dismantled pipe sealing cover is closely installed at an upper port of the connecting pipe group, and the remediationagent is pumped into the agent injection steel pipe to achieve agent injection remediation within the second-stage depth range; and (3), repeated operation is conducted according to the step (2), andagent injection remediation within all stages of the depth range is completed in sequence by lengthening the agent injection steel pipe. The multi-layer in-situ agent injection method for the contaminated site has the advantages that the multi-layer in-situ agent injection method is convenient and easy to operate, and by lengthening the agent injection steel pipe through the connecting pipe group, multi-layer fixed-depth injection within the contamination depth range can be achieved from the shallower to the deeper.
Owner:SHANGHAI GEOTECHN INVESTIGATIONS & DESIGN INST
Sintered neodymium-iron-boron magnet with high coercivity and low remanence temperature sensitivity, and preparation method
ActiveCN106205992ALow melting pointImprove liquidityInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRemanenceThermal insulation
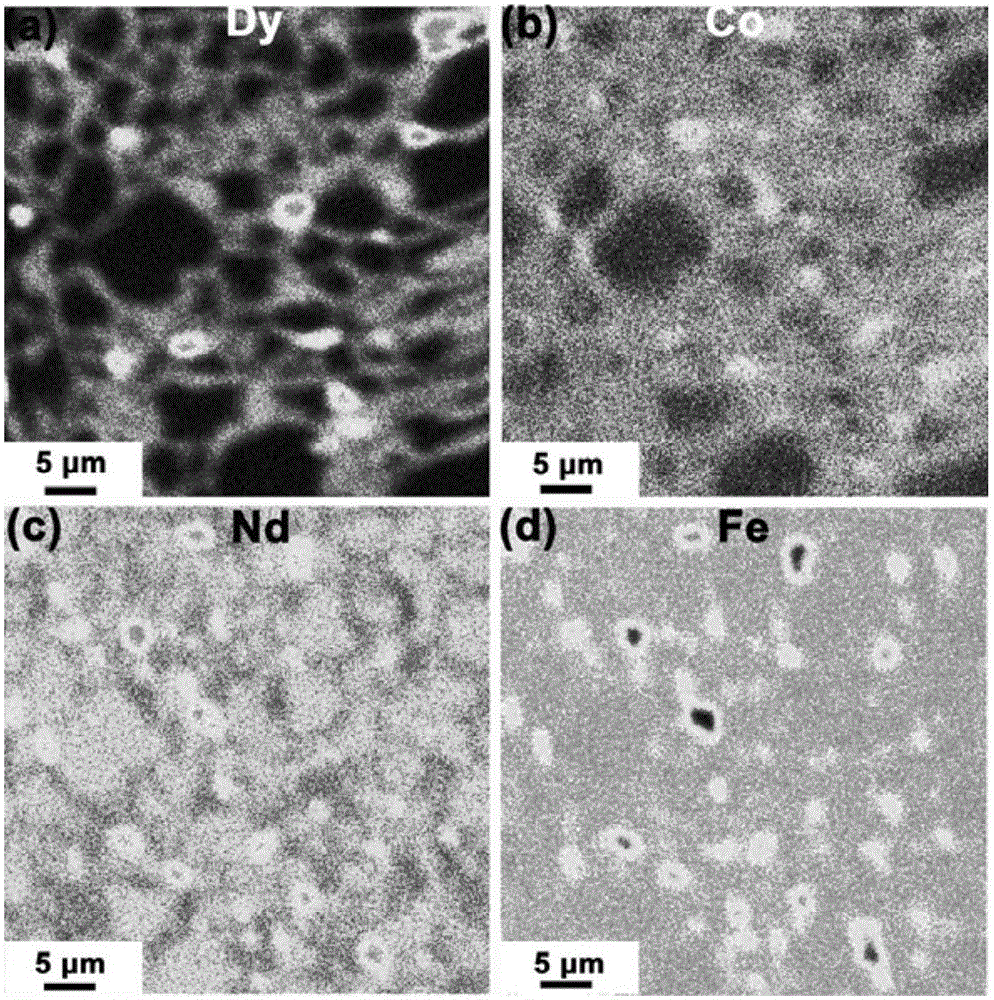
The invention relates to a preparation method for a sintered neodymium-iron-boron magnet with high coercivity and low remanence temperature sensitivity. The preparation method comprises the steps of taking a Dy-Co alloy diffusion sheet as a diffusion source for the sintered neodymium-iron-boron magnet; performing thermal insulation at a temperature which is higher than the Dy-Co alloy melting point; and enabling the melted Dy-Co alloy liquid to be diffused to the interior of the neodymium-iron-boron magnet along grain boundary to form a Dy-rich and Co-rich composite shell-shaped structure on the edges of crystal particles. Due to the presence of the Dy-rich and Co-rich composite shell-shaped structure, the coercivity and remanence temperature stability of the sintered neodymium-iron-boron magnet can be greatly improved; compared with the prior art, the Dy-rich and Co-rich composite shell-shaped structure prepared by the method can improve the coercivity and the remanence temperature stability as well; and the sintered neodymium-iron-boron magnet which is diffused and modified by a crystal boundary diffusion process provided by the invention has the advantages of high diffusion depth of a diffusant, uniform grain boundary phase distribution, high coercivity, low magnet remanence temperature sensitivity coefficient and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for improving corrosion resistance of neodymium-iron-boron magnet by carrying out grain boundary diffusion on Al-Cu alloy
InactiveCN106783124AReduce magnetismAvoid ingredientsSolid state diffusion coatingMagnetic materialsCu elementRare earth
The invention discloses a method for improving the corrosion resistance of neodymium-iron-boron magnet by carrying out grain boundary diffusion on Al-Cu alloy, belonging to the field of rare earth magnetic materials. According to the method, an Al-Cu alloy ordinary ingot which has a low melting point and high potential is directly used as a surface diffusion source of the neodymium-iron-boron magnet after being coarsely crushed and ball-milled, and an Al-Cu-rich thin layer is formed at the crystal boundary of the neodymium-iron-boron magnet after diffusing heat treatment and annealing heat treatment are carried out, so that the neodymium-iron-boron magnet with high corrosion resistance is obtained. According to the method, Al-Cu alloy is taken as the diffusion source, thus avoiding the phenomenon that the residual magnetism of the magnet is reduced since Al and Cu elements are not directly added into the ingot, and the non-magnetic Al and Cu enter a principal phase so as to generate a magnetic dilution effect; the corrosion resistance and magnetic property of the magnet also can be improved since the grain boundary diffusion can improve the chemical stability of a grain boundary phase, optimize a microstructure, improve the distribution of the grain boundary phase, and increases the density of the magnet.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Coercive-force-enhanced NdFeB thermal deformation magnet as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104347217AImprove coercive forceImprove temperature stabilityInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureRare-earth elementThermal deformation
The invention discloses a coercive-force-enhanced NdFeB thermal deformation magnet as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The magnet comprises a crystallized ribbon-like mixture forming nanocrystalline quick-quenched ribbons, and heavy rare earth oxide doped between the nanocrystalline quick-quenched ribbons, wherein the crystallized ribbon-like mixture comprises the following main components (in percentage by weight): 21-31% of neodymium, 5.5-6% of boron, 0.2-0.8% of gallium, 0-22.3% of M, and the balance of ferrum and other unavoidable trace impurities, wherein M is one or more of praseodymium, dysprosium, terbium, copper and cobalt; the total mass of neodymium, praseodymium, dysprosium and terbium in the crystallized ribbon-like mixture is 29-31% that of the crystallized ribbon-like mixture; the heavy rare earth oxide is 0.1-6% of the total mass of the crystallized ribbon-like mixture. The influence of addition of the heavy rare earth element into the NdFe magnet on the magnetization strength, the maximum energy product and the production cost is effectively improved; the stabilities of the coercive force and the temperature are improved; the production cost and the application cost of the heavy rare earth element are reduced.
Owner:宁波金鸡强磁股份有限公司
Zirconium-containing copper silver titanium solder alloy
InactiveCN102699567AReduce manufacturing costExcellent brazeabilityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaTitaniumUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses a zirconium-containing copper silver titanium solder alloy. The zirconium-containing copper silver titanium solder alloy comprises the following components by mass percent: 10-45% of Ag, 1-4% of Ti, 0.5-5% of Zr and Cu for the rest. A vacuum melting and argon shield casting mode is adopted, silver and copper are molten at first and then titanium and zirconium are added. The zirconium-containing copper silver titanium solder alloy can be used for directly soldering copper alloys, iron steel, ceramics and diamonds. The zirconium-containing copper silver titanium solder alloy has the advantages as follows: the cost is low; a connector is high in mechanical strength, has smooth surface, is stable in quality and is good in uniformity after the copper alloys are soldered by the zirconium-containing copper silver titanium solder alloy; and the joint clearances can be fully filled up. The zirconium-containing copper silver titanium solder alloy can replace the conventional copper silver titanium solder and is suitable for large-scale industrial application.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for preparing highly corrosion-resistant sintered NdFeB magnet
InactiveCN106782973AImprove bindingIncreased diffusion kinetic energyInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureRare earthGrain boundary
The invention provides a method for preparing a highly corrosion-resistant sintered NdFeB magnet. The method comprises the following steps: performing orientation pressing on sintered NdFeB magnetic powder in a 1.5-2.0T oriented magnetic field under the pressure of 16MPa, performing cold press molding on a pressed shape in an oil-cooled isostatic pressing machine so as to obtain a green body; performing low-temperature vacuum pre-sintering on the green body in a vacuum sintering furnace at the temperature of 850-890 DEG C for 3-3.5 hours so as to obtain a magnet; taking the magnet as a substrate, and covering a non-rare-earth compound layer on the surface of the substrate by adopting a magnetron sputtering method; performing high-temperature sintering in the vacuum sintering furnace for 2-3 hours, performing secondary tempering treatment, filling inert gases of 20-22MPa for applying pressure in the temperature treatment process, thereby obtaining the highly corrosion-resistant sintered NdFeB magnet. According to the magnetron sputtering manner, a diffusion source is attached to the surface of the magnet, grain boundary diffusion is completed in the sintering process, the base bonding force is improved, and the diffusion depth and corrosion resistance are improved.
Owner:EARTH PANDA ADVANCE MAGNETIC MATERIAL
Neodymium-iron-boron magnet and preparation method and application thereof
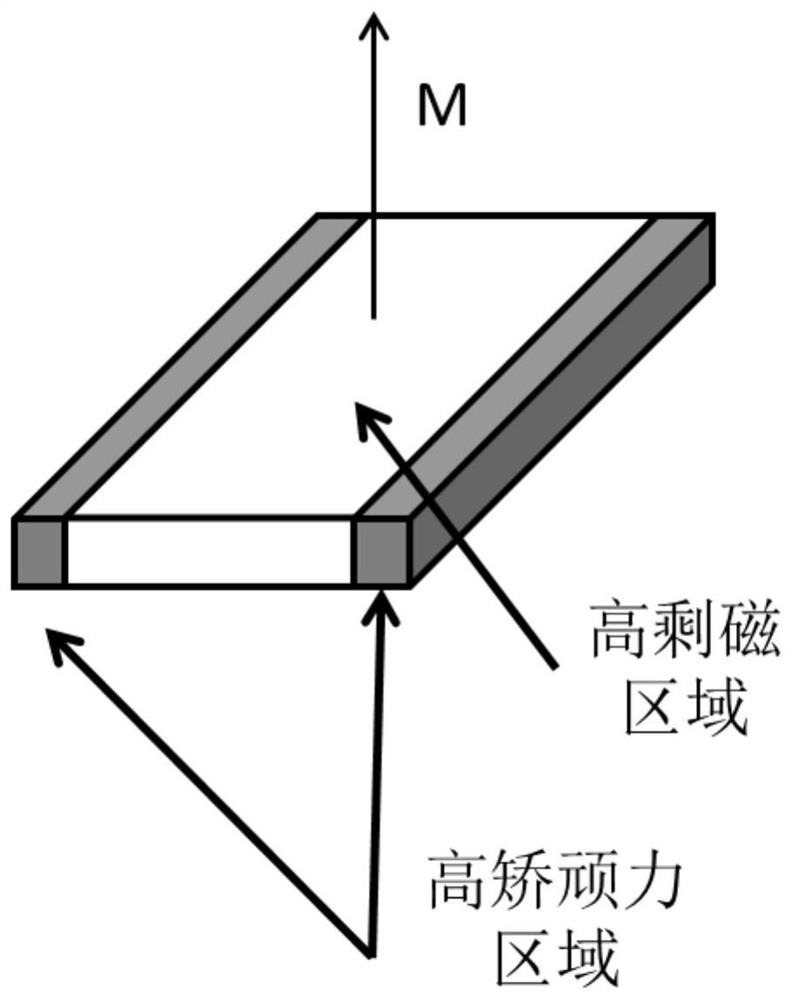
ActiveCN111653404AImprove high temperature demagnetization resistanceReduce fluxTransformersVacuum evaporation coatingRare-earth elementRemanence
The invention provides a neodymium-iron-boron magnet and a preparation method and application thereof. The neodymium-iron-boron magnet is represented by a chemical formula R1-R2-Fe-M-B, and the neodymium-iron-boron magnet has a composite structure of a high-coercivity region and a high-remanence region, wherein R1 is a rare earth element at least containing Nd, R2 is a heavy rare earth element atleast containing Dy and / or Tb, and M is a transition metal element at least containing Co. The magnet can adopt a small amount of Dy / Tb, the high-temperature demagnetization resistance of the magnet is greatly improved, the reduction of the magnetic flux of the magnet is inhibited, and the magnet is suitable for an embedded high-speed motor. The method for preparing the magnet can also greatly improve the utilization rate and the production efficiency of the material, and has mass production feasibility.
Owner:YANTAI ZHENGHAI MAGNETIC MATERIAL CO LTD
Method for improving performance of rare-earth permanent magnetic material by high temperature compressive stress
ActiveCN106952721AImprove magnetismImprove coercive forceInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsDiffusionRare earth
The invention discloses a method for improving the performance of a rare-earth permanent magnetic material by high temperature compressive stress. The method for improving the performance of the rare-earth permanent magnetic material by high temperature compressive stress at least comprises the following steps: attaching heavy rare-earth compounds to the surface of the sintered magnet; and obtaining the magnet through heating and applying compressive stress at high temperature. According to the invention, the problems of the limitation of the magnet specification and dimension and the inconsistency of the heavy rare-earth diffusion in the traditional process can be overcome by improving the diffusion depth of magnet, therefore, the diffusion effect is enhanced, the magnet can obtain better magnetic performance, the equipment investment is simple, the cost is lower, and the invention is suitable for large-scale promotion.
Owner:宁波金鸡强磁股份有限公司
Method for preparing high magnetic sintered NdFeB by hot isostatic pressing and low temperature sintering
ActiveCN108511179AAvoid damageImprove adhesionInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementHigh density
The invention relates to a method for preparing high magnetic sintered NdFeB by hot isostatic pressing and low temperature sintering and belongs to the technical field of rare earth magnetic materials, wherein sintered NdFeB magnetic powder is subject to semi-densified sintering, wherein the density is of 85% to 95%; then, a turbid liquid containing a heavy rare earth compound and having a viscosity of 100 to 500 mpa.s is coated on the periphery of the semi-densified sintered NdFeB; vacuum glass tube sealing is carried out, low temperature sintering is carried out at 700-900 DEG C through hotisostatic pressing, and tempering is carried out at 400-500 DEG C so as to prepare the high-density and high-magnetic sintered NdFeB magnet. Coatings of Dy2S3, Dy2O3, Tb2O3, DyF3 or DyH3 have good adhesion to the semi-densified sintered NdFeB magnet. During the hot isostatic pressing and low temperature sintering process, the heavy rare earth elements diffuse along the grain boundary and pores. Under the gas pressure in all directions, the diffusion rate is faster, thereby effectively increasing the diffusion depth and diffusion uniformity as well as effectively increasing the sintering density of the magnet and refining the grain size.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method for improving performance of sintered NdFeB magnet
InactiveCN110211797AImprove coercive forceIncreased Diffusion DepthInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementMagnet
The invention discloses a method for improving performance of a sintered NdFeB magnet. According to the method, a metal oxide is reduced with hydrogen under a high temperature by means of the characteristic of low-melting metal oxide, low-melting metal is sequentially obtained according to a reduction sequence, a discontinuous crystal boundary rare-earth phase of a magnet surface layer is preferably diffused and recovered, a continuous low-melting point rare-earth phase is obtained and is used as a rapid diffusion passage of a heavy rare-earth element, the diffusion depth of the heavy rare-earth element in the magnet is effectively improved, the dosage of the heavy rare-earth element is reduced, the improvement of magnet coercivity is achieved, meanwhile, the dosage of the heavy rare-earthelement is also remarkably reduced, the method is simple in process, is easy to implement and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for improving magnetic performance of samarium-cobalt permanent magnet material
ActiveCN112038083AValid entryImprove liquidityInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsMetallurgySamarium
The invention discloses a method for improving the magnetic performance of a samarium-cobalt permanent magnet material. The method comprises the steps: providing a samarium-cobalt permanent magnet asa base material, and the chemical formula of the base material as a powder orientation forming green body being Sm(CoxFeyCuzZrm)n, wherein x is larger than 0.5 and smaller than 0.9, y is larger than 0.01 and smaller than 0.1, z is larger than 0.01 and smaller than 0.1, m is larger than 0.01 and smaller than 0.1, and n is larger than 6 and smaller than 9; applying a low-melting-point phase diffusion source to the surface of the base material in a coating and / or cladding manner, and then performing vacuum and / or pressurized thermal diffusion treatment on the obtained base material; and carryingout sintering densification and aging treatment on the base material subjected to thermal diffusion treatment to prepare the samarium-cobalt permanent magnet material. According to the method providedby the invention, the magnetic performance of the samarium-cobalt permanent magnet material is effectively improved, and the application field of the samarium-cobalt rare earth permanent magnet material is expanded.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Grain boundary diffusion method suitable for large rare earth permanent magnet material
ActiveCN111063536AIncrease the diffusion coefficientIncreased Diffusion DepthInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsPhysicsThermal deformation
The invention discloses a grain boundary diffusion method suitable for a large rare earth permanent magnet material. A spark plasma sintering technology is used for carrying out grain boundary diffusion treatment on a magnet, and the comprehensive magnetic performance of the magnet is improved. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing an initial magnet through a sintering or hot pressing or thermal deformation process; (2) loading a grain boundary diffusion alloy source on the surface of the magnet through magnetron sputtering, electroplating, chemical vapor deposition, physicalvapor deposition, direct physical contact or bonding by a binder; and (3) putting the loaded initial magnet into a discharge plasma device, and carrying out grain boundary diffusion by using discharge plasma heating to raise the temperature, thereby obtaining the final magnet. By controlling the current, the plasma, the pressure and the like in the spark plasma sintering process, the diffusion coefficient of elements is remarkably increased, and the diffusion depth of the elements is increased. According to the grain boundary diffusion rare earth permanent magnet material prepared by the method, the magnetic performance is increased more remarkably, the grain boundary diffusion process can be suitable for large magnets and is not limited by the thickness of the magnets, and the industrialproduction and market requirements are met.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Little-defect clean Sn-Zn solder containing palladium and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN104191101AImprove cleanlinessGrain refinementWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaIndiumVegetable oil
The invention discloses little-defect clean Sn-Zn solder containing palladium. The solder comprises metal components including, by weight, 0.05-0.3% of Pd, 0.1-0.5% of Ga, 6-10% of In, 0.1-3.5% of Ag, 7-10% of Zn and the balance Sn. During preparation, the palladium is ground into powder for use after hydrogen absorption, and silver and tin are smelted into silver-tin intermediate alloy in proportion; remaining tin and the molten silver-tin intermediate alloy are placed in a furnace for melting, raw material zinc is added after temperature of molten liquid rises to 350-450 DEG C, heat preservation is carried out, and Sn-Zn-Ag intermediate alloy liquid is obtained; raw material indium and gallium are sequentially added, when the temperature of the molten liquid lowers to 250-350 DEG C, heat preservation is carried out, and Sn-Zn-Ag-In-Ga intermediate alloy liquid is obtained; palladium powder is added and is covered with a mixture of zinc chloride and vegetable oil after complete melting, heat preservation is carried out, and the mixture is poured to form cast ingot; the solder can be obtained after the cast ingot is extruded and drawn or rolled into a wire shape or a flaky shape. The solder has the advantages of being high in cleanliness, high wettability, little in soldering seam defect, low in melting point and the like.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU RES INST OF MECHANICAL ENG CO LTD
Preparation method of annular radiation orientation magnet
PendingCN111768965AGood heat resistanceImprove coercive forceInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementComputational physics
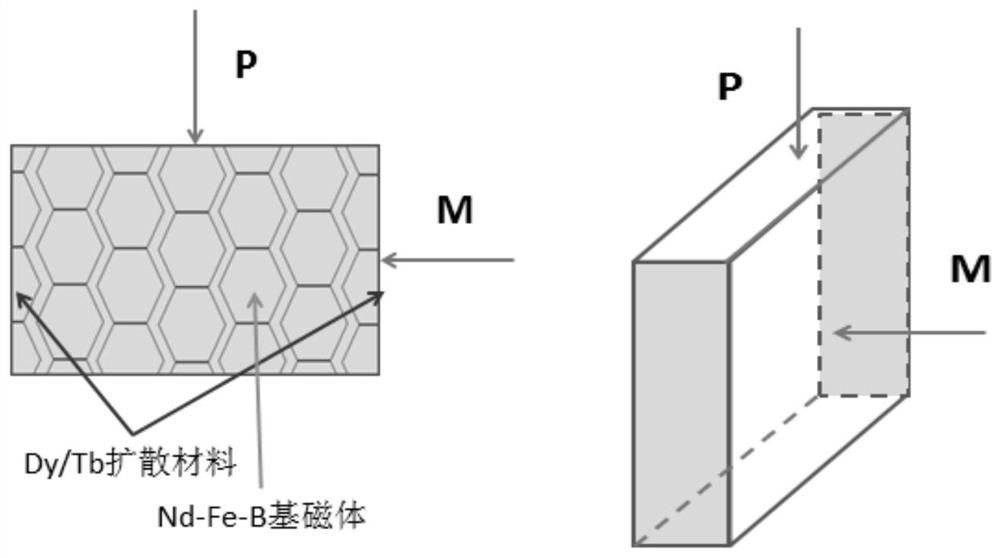
The invention provides a preparation method of an annular radiation orientation magnet. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a radiation ring neodymium iron boron blank; mixing HRx-My-Hz powder with an organic solvent to obtain a mixed solution, coating the surface of the radiation ring neodymium iron boron blank with the mixed solution, and then sintering; and carryingout heat treatment on the sintered radiation ring neodymium iron boron to obtain the annular radiation orientation magnet. Heavy rare earth elements are introduced into the radiation ring neodymium-iron-boron magnet through a diffusion method, the residual magnetism and coercive force of the annular radiation orientation magnet are improved, and the problem that the magnet cracks in the sinteringprocess is solved.
Owner:JIANGXI JLMAG RARE EARTH
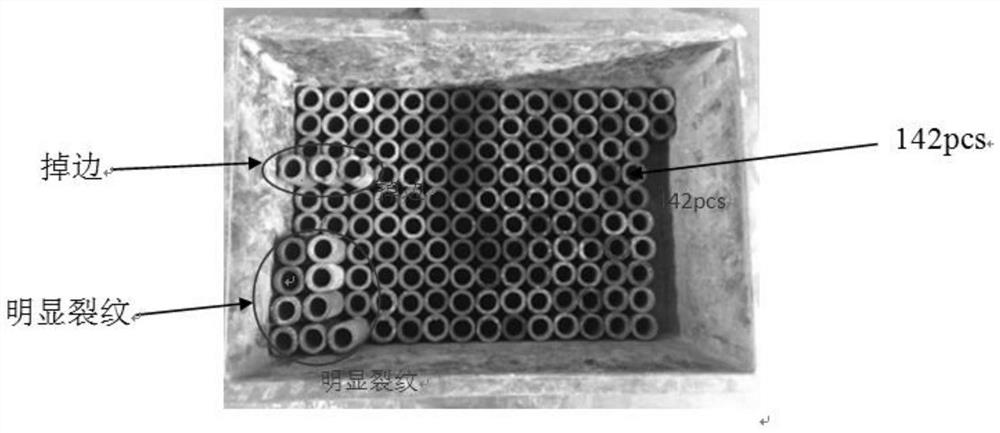
New method for welding ZL203 aluminum alloy on preset magnesium-based amorphous intermediate layer
The invention discloses a new method for welding a ZL203 aluminum alloy on a preset magnesium-based amorphous intermediate layer, and belongs to the field of welding of aluminum alloys. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: cutting and sawing a self-poured ZL203 aluminum copper alloy test sample to form a block with the length of 35mm, the width of 15mm and the thickness of 15mm; polishing a surface to the welded of the test sample, and removing an oxidation film on the surface; and in order to ensure stressing uniformity of a joint, welding an aluminum copper alloy in a butt joint mode. According to the optimal parameter of a diffusion welding process, the pressure is 0.5MPa, the temperature rise velocity is 25 DEG C / min, the welding temperature is 510 DEG C, and the heat preservation time is 20 minutes; and at the moment, the tensile strength of a ZL203 aluminum copper alloy joint reaches the maximum value 185MPa, and the strength of a ZL203 aluminum copper alloy body is 180 to 190MPa.
Owner:ZHENJIANG YINUOWEI SHAPE MEMORY ALLOYS
Nitrocarburized crankshaft member and steel for nitrocarburized crankshafts
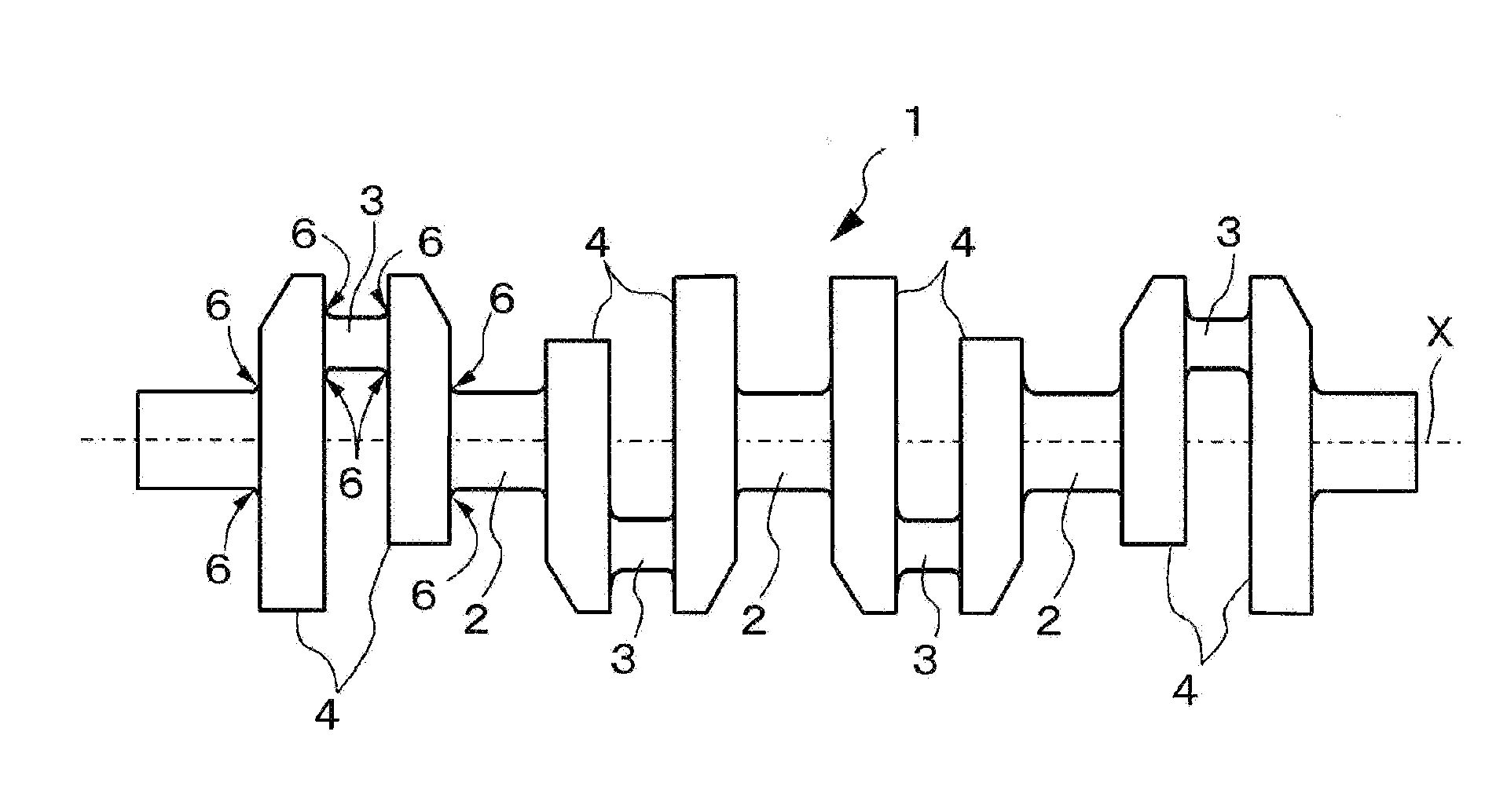
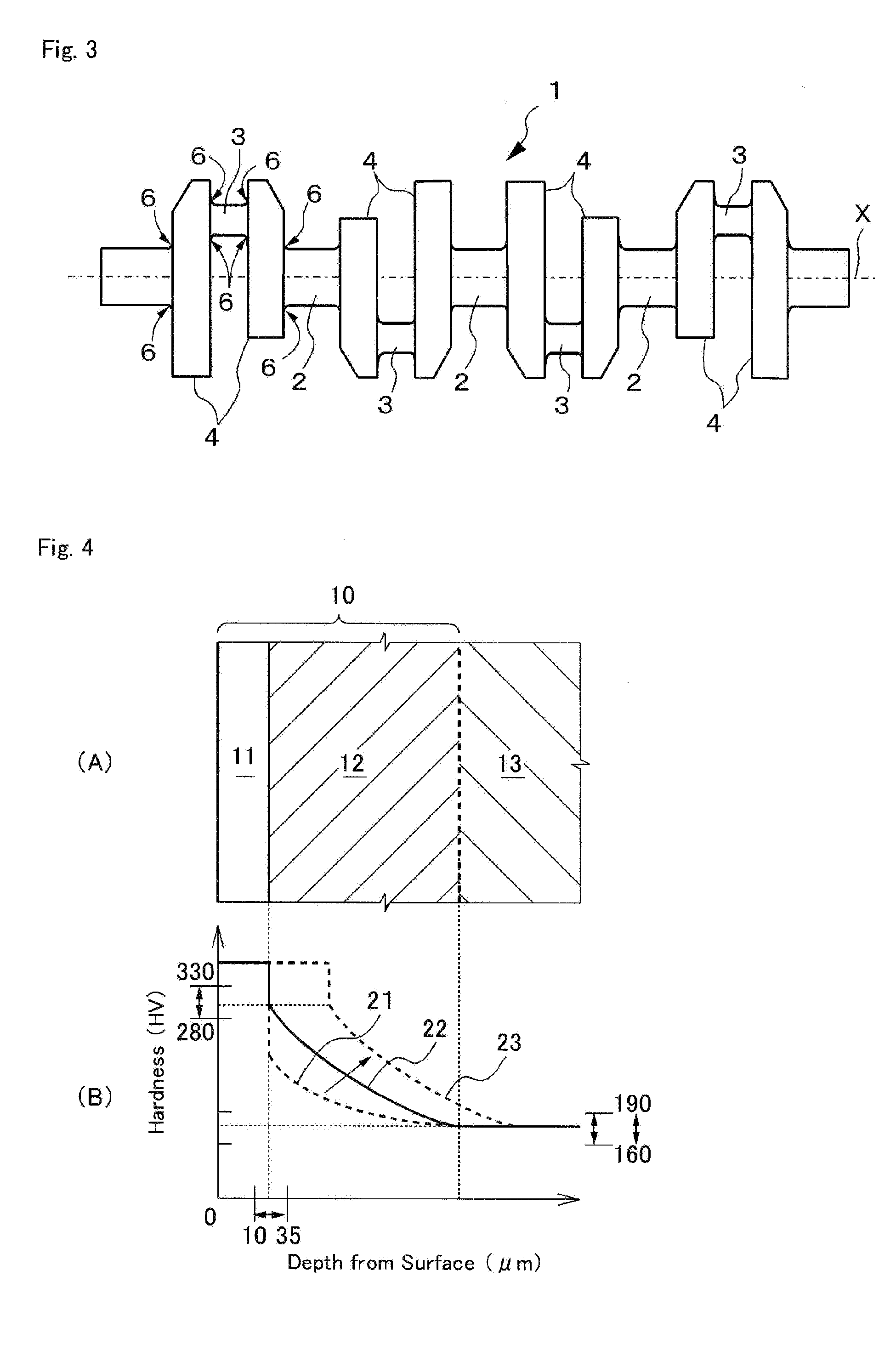
ActiveUS20110132138A1Good correctabilityImprove fatigue strengthCrankshaftsSolid state diffusion coatingNitrogenCrankshaft
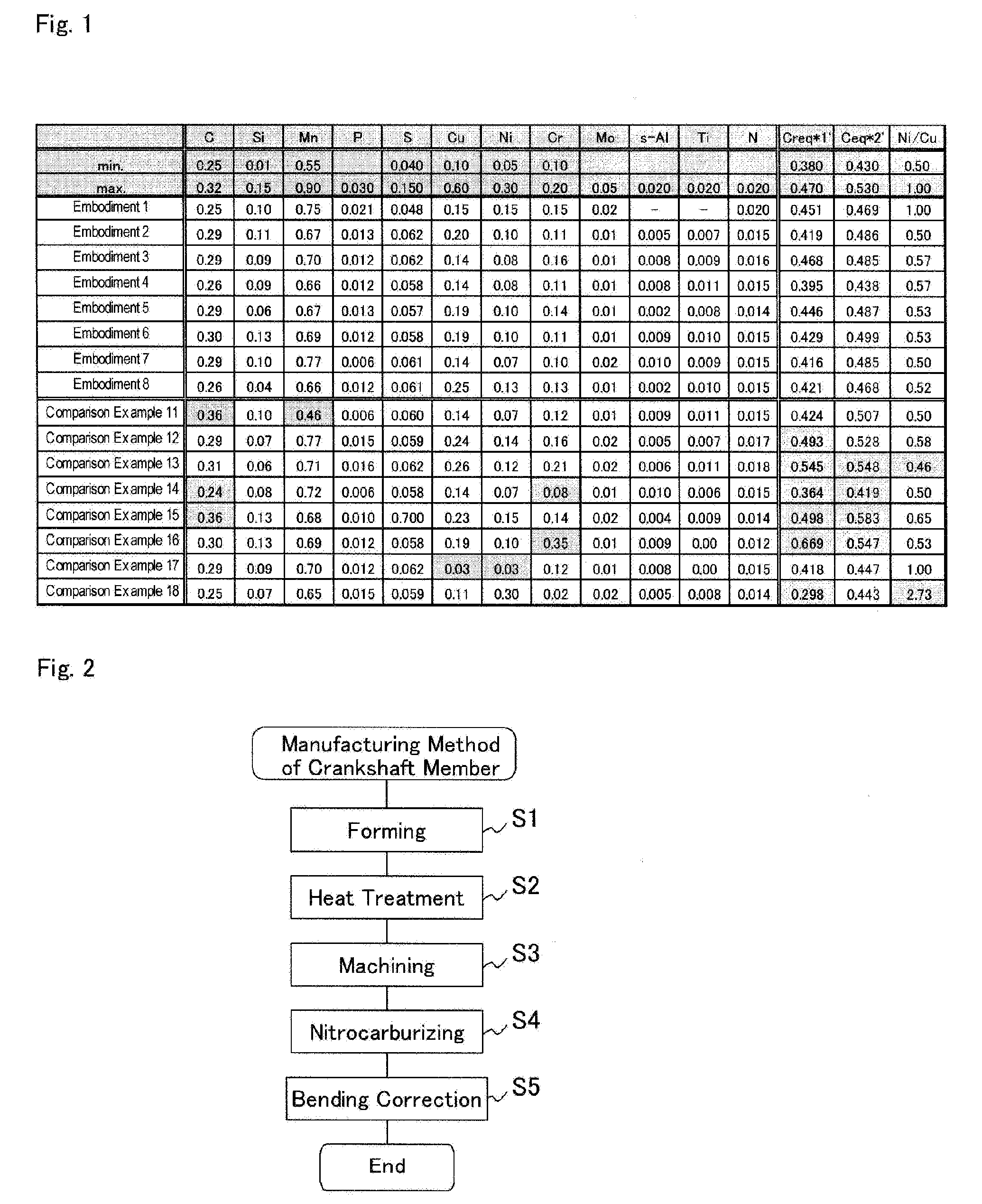
A nitrocarburized crankshaft member made of a steel that includes C in an amount by weight of 0.25 to 0.32% as a required element and an optional element that may be included, and Fe and inevitable impurities in a remaining portion. The steel-made crankshaft member mainly includes ferrite and perlite, wherein at least a portion of the steel surface thereof having a ferrite surface area of 50% or greater is imparted with a nitrocarburized hard layer. The nitrocarburized hard layer includes a surface compound layer suppressed to a thickness of 10 to 35 μm, and a nitrogen diffusion zone below the surface compound layer having a diffusion depth of 700 μm or greater. The steel includes C, Si, Mn, Cu, Ni, and Cr as the required elements and Mo, N, s-Al, and Ti as the optional elements.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD +1
Production method of high-transparency PMMA-PU gradient composite plate
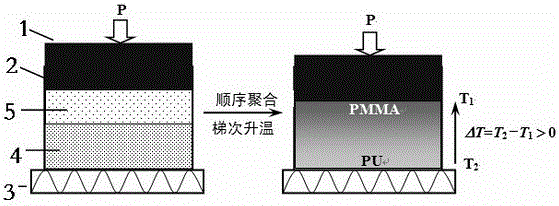
The invention discloses a production method of a high-transparency PMMA-PU gradient composite plate and belongs to the field of composites. The method comprises the following steps: (1) taking aliphatic isocyanate and polyether polyol as the raw materials and producing polyurethane (PU) prepolymer in a stainless steel mould; (2) uniformly mixing polymethyl methacrylate monomers (MMA), initiators and cross-linking agents, and adding the mixture into the PU prepolymer mould, applying pressure to an MMA monomer solution and the PU prepolymer via an upper pressing head of the mould to enable the MMA monomer solution to be diffused and permeated into the PU prepolymer to form a compositional gradient structure; and (3) controlling the temperature of a heating platform by using a gradient temperature increasing manner and building a temperature gradient field between the bottom of the mould and the upper pressing head to produce the high-transparency PMMA-PU gradient composite plate. The gradient composite plate has the characteristics of high transparency, high strength, impact resistance and heat stability and has potential application prospects in aviation transparent parts and bullet-proof transparent windows.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Neodymium iron boron permanent magnet material preparation method
InactiveCN110364352AImprove uniformityImprove consistencyInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsMaterials preparationHydrogen
The invention provides a neodymium iron boron permanent magnet material preparation method. Aluminum hydride is deposited on a neodymium iron boron magnet green body, the aluminum hydride releases reducing hydrogen during heating, oxidized heavy rare earth can be reduced at a high temperature, and grain boundary penetration effects can thus be improved. Aluminum is a low-melting-point metal, whenthe neodymium iron boron magnet is heated at a first sage, at a low temperature, on one hand, oil left on the surface of the neodymium iron boron green body in an isostatic pressing step is removed, and on the other hand, the low-melting-point aluminum is promoted to repair the surface grain boundary of the magnet. Dysprosium-iron alloy is then induced through second-stage heating to be quickly diffused with the well-repaired grain boundary low-melting point channel, the diffusion speed and the depth are enhanced, and the magnet can be completely dehydrogenated. Finally, through sintering, tempering and aging treatment, the neodymium iron boron permanent magnet material is obtained. The prepared neodymium iron boron permanent magnet material has the advantages of good uniformity, good consistency, deep diffusion of heavy rare earth, and the permanent magnet material performance is improved.
Owner:宁德市星宇科技有限公司
Electron beam surface alloying method for 45# steel
InactiveCN107385378AImprove corrosion resistanceImprove performanceMolten spray coatingThermal sprayingTurnover time
The invention discloses an electron beam surface alloying method for 45# steel. The electron beam surface alloying method comprises the steps of preset coating on the surface of the 45# steel and scanning through continuous electron beams, wherein the preset coating comprises the step that tungsten powder is sprayed on the surface of the 45# steel by plasma thermal spraying to form a spraying bonding layer; and scanning through continuous electron beams comprises the step that electron beam scanning is carried out on the surface of the 45# steel so as to obtain a surface alloying modification layer on the surface of the 45# steel. According to the electron beam surface alloying method, the continuous electron beam scanning technology is combined with the plasma thermal spraying, the novel medium-carbon steel-based composite material which takes a high-performance alloying element as a reinforced phase is prepared by adopting the unique advantages of the continuous surface treatment, so that the procedures are greatly simplified, the cost is reduced, the turnover time is shortened, and the surface performance of the 45# steel is improved and the service life of the 45# steel is prolonged by preparing the alloy layer with high hardness, high abrasion resistance and high corrosion resistance.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
R-T-B magnet material, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111210987AIncrease the amount of diffusionIncreased Diffusion DepthInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementTemperature resistance
The invention discloses an R-T-B magnet material, a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method of the R-T-B magnet material comprises the following steps: performing hydrogen activation treatment on a sintered body of the R-T-B magnet material in a gas atmosphere; and then performing grain boundary diffusion, wherein the gas atmosphere includes a mixed gas of an inert gas and hydrogen; a temperature of the hydrogen activation treatment is 100-300 DEG C, and time is more than 10 minutes; a ratio of amass volume concentration of the hydrogen to the mass volume concentration of the sintered body is 0.01-0.1%; and the volume ratio of the hydrogen to the inert gas is 0.1-5%. The R-T-B magnet material disclosed by the invention is relatively good in high-temperature resistance, demagnetization resistance and coercive force; rare earth elements or a large amount of cobalt elements are not added during smelting so that cost is relatively low; grain refinement can beavoided, and production difficulty is low; and the R-T-B magnet material with a length within 1 mm in anorientation direction can be obtained, and the magnet material is good in magnetic performance.
Owner:FUJIAN CHANGJIANG GOLDEN DRAGON RARE EARTH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com