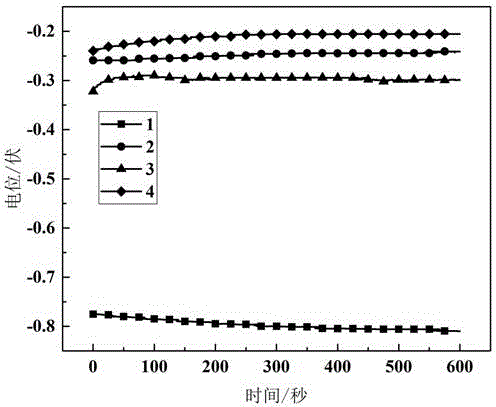
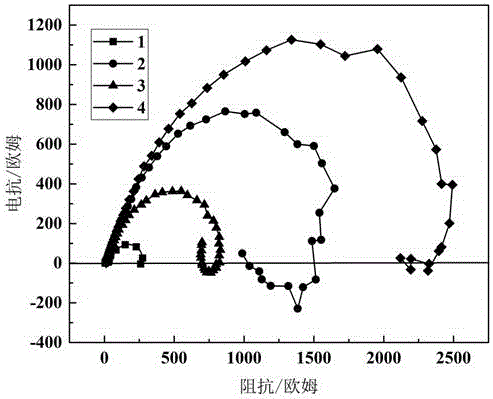
Method for improving corrosion resistance of neodymium-iron-boron magnet by carrying out grain boundary diffusion on Al-Cu alloy
A technology of grain boundary diffusion and neodymium iron boron, applied in the direction of magnetic materials, magnetic objects, permanent magnet manufacturing, etc., can solve the problem of damaging the magnetic properties of magnets, and achieve the effect of reducing magnetic properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1: 48SH magnet surface coated with Al 82.9 Cu 17.1 (atomic percent) powder grain boundary diffusion heat treatment
[0029] Select 48SH commercial sintered NdFeB magnets and process them into a square sample with a size of 4×4×4mm, which is recorded as sample No. 1.
[0030] According to the alloy composition ratio Al 82.9 Cu 17.1 (Atomic percentage) Weigh Al and Cu with a purity greater than 99.99%, put Al and Cu in an electric arc furnace, and evacuate to 5×10 -3 Pa, first melt the oxygen-absorbing Ti block to exhaust the oxygen in the residual cavity, and then repeatedly smelt each sample 4 times to ensure that the components are evenly distributed.
[0031] The smelted button-shaped ingot is polished with a grinding wheel, and then polished with fine sandpaper to remove the surface oxide skin, and ultrasonically cleaned in alcohol. Use pliers to roughly break into small pieces, according to the ball-to-material ratio of 10:1, the rotation speed is 300r / ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2: 48SH magnet surface coated with Al 89 Cu 11 (atomic percent) powder grain boundary diffusion heat treatment
[0034] Select 48SH commercial sintered NdFeB magnets and process them into a square sample with a size of 4×4×4mm, which is recorded as sample No. 1.
[0035] According to the alloy composition ratio Al 89 Cu 11 (Atomic percentage) Weigh Al and Cu with a purity greater than 99.99%, put Al and Cu in an electric arc furnace, and evacuate to 5×10 -3 Pa, first melt the oxygen-absorbing Ti block to exhaust the oxygen in the residual cavity, and then repeatedly smelt each sample 5 times to ensure that the components are evenly distributed.
[0036] The smelted button-shaped ingot is polished with a grinding wheel, and then polished with fine sandpaper to remove the surface oxide skin, and ultrasonically cleaned in alcohol. Use pliers to roughly break into small pieces, according to the ball-to-material ratio of 10:1, the rotation speed is 200r / min, an...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3: 48SH magnet surface coated with Al 75 Cu 25 (atomic percent) powder grain boundary diffusion heat treatment
[0039] Select 48SH commercial sintered NdFeB magnets and process them into a square sample with a size of 4×4×4mm, which is recorded as sample No. 1.
[0040] According to the alloy composition ratio Al 75 Cu 25 (Atomic percentage) Weigh Al and Cu with a purity greater than 99.99%, put Al and Cu in an electric arc furnace, and evacuate to 5×10 -3 Pa, first melt the oxygen-absorbing Ti block to exhaust the oxygen in the residual cavity, and then repeatedly smelt each sample 4 times to ensure that the components are evenly distributed.
[0041]The smelted button-shaped ingot is polished with a grinding wheel, and then polished with fine sandpaper to remove the surface oxide skin, and ultrasonically cleaned in alcohol. Use pliers to roughly break into small pieces, according to the ball-to-material ratio of 10:1, the speed is 400r / min, and the ball...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com