Polyethylenimine-tannic acid/hydrolyzed polyacrylonitrile ultrathin composite membrane, and preparation and application thereof
A technology for hydrolyzing polyacrylonitrile and polyethyleneimine, which is applied in the field of composite membranes, can solve the problems of insufficient membrane stability and no literature reports on pervaporation, and achieves the effects of simple preparation method, good performance and good separation performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1: the preparation of polyethyleneimine-tannic acid / hydrolyzed polyacrylonitrile ultra-thin composite film, the steps are as follows:
[0030] 1) Preparation of hydrolyzed polyacrylonitrile ultrafiltration membrane: put the polyacrylonitrile ultrafiltration membrane into a sodium hydroxide solution with a molar concentration of 1.5mol / L for heat treatment for 1 hour, rinse with distilled water and dry to obtain a hydrolyzed polyacrylonitrile ultrafiltration membrane ;
[0031] 2) Preparation of polyethyleneimine solution: at room temperature, prepare a polyethyleneimine solution with a mass volume concentration of 2 g / L, and adjust the pH to 8 with an HCl solution with a molar concentration of 0.5 mol / L to obtain solution A;
[0032] 3) Preparation of tannic acid solution: at room temperature, prepare a tannic acid solution with a mass volume concentration of 2 g / L, and adjust the pH to 8 with a NaOH solution with a molar concentration of 0.5 mol / L to obtain ...
Embodiment 2
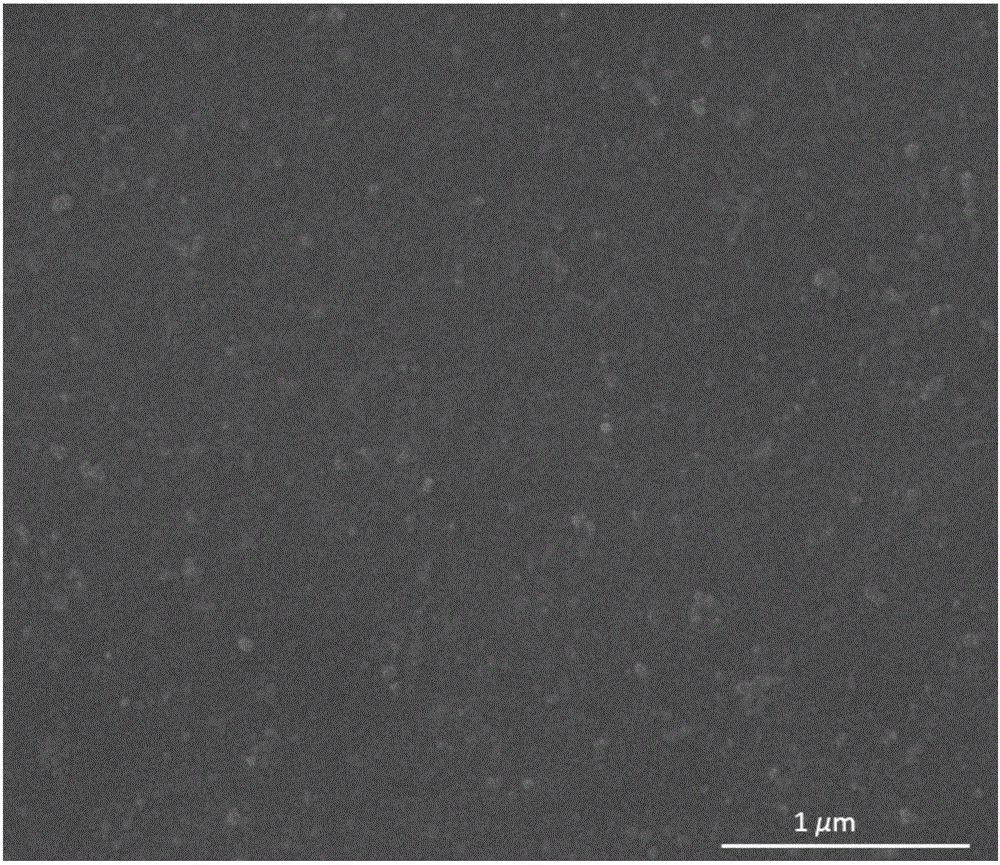
[0035] Embodiment 2: the preparation of polyethyleneimine-tannic acid / hydrolyzed polyacrylonitrile ultra-thin composite film, the steps are basically the same as in Example 1, the difference is only: the mass volume of polyethyleneimine solution in step 2) The concentration was 4g / L; the number of times of alternate immersion in step 4) was 3 times; finally, a polyethyleneimine-tannic acid / hydrolyzed polyacrylonitrile ultrathin composite film with a film thickness of about 300nm was obtained. image 3 The scanning electron microscope image of the surface of the polyethyleneimine-tannic acid / hydrolyzed polyacrylonitrile ultra-thin composite membrane obtained in Example 2 shows that the surface of the membrane is smooth, and the pores on the surface of the ultrafiltration membrane are completely covered. Used for pervaporation ethanol dehydration, flux 1930g / m 2 h, separation factor 280.
Embodiment 3
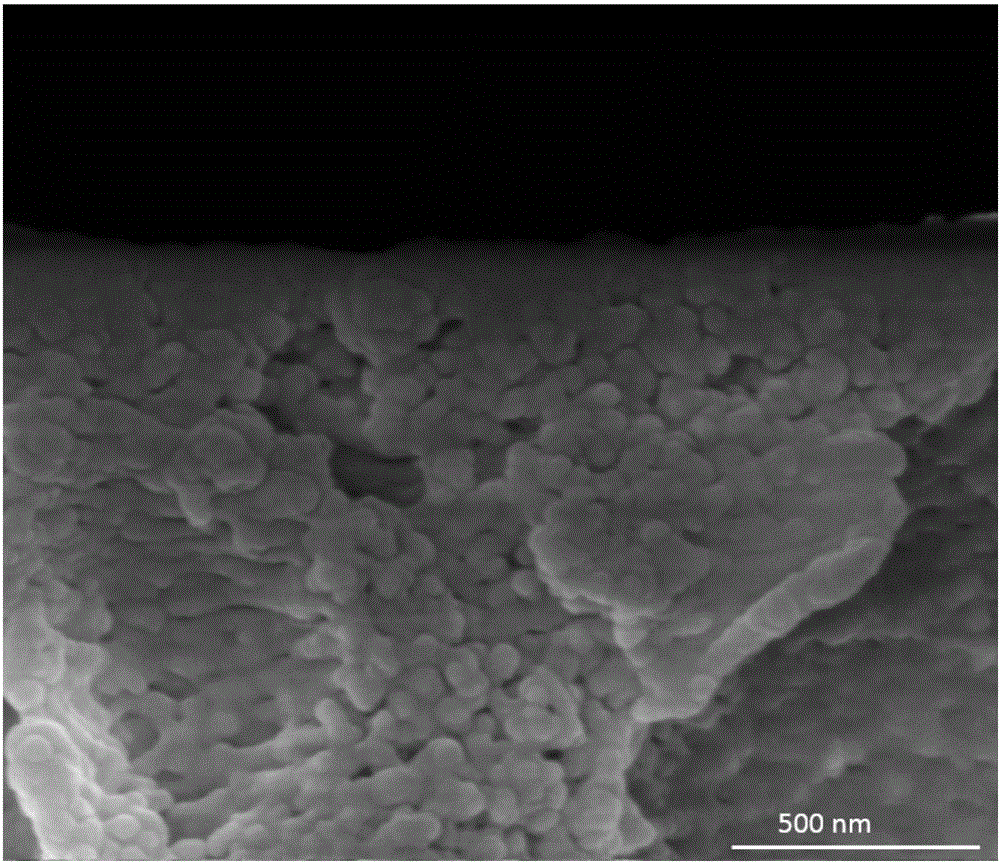
[0036] Embodiment 3: polyethyleneimine-tannic acid / hydrolyzed polyacrylonitrile ultrathin composite film, step is basically the same as embodiment 1, and difference is only: step 2) and 3) in polyethyleneimine solution and single The pH of the nic acid solution was adjusted to 10; finally, a polyethyleneimine-tannic acid / hydrolyzed polyacrylonitrile ultrathin composite film with a film thickness of about 280nm was obtained. Figure 4 The cross-sectional scanning electron microscope image of the polyethyleneimine-tannic acid / hydrolyzed polyacrylonitrile ultra-thin composite membrane obtained in Example 3 shows that the separation layer is closely combined with the supporting layer below, and the interface has no obvious boundaries, indicating that the interlayer is well bonded , without defects, the thickness of the film is about 260nm. Used for pervaporation ethanol dehydration, flux 1493g / m 2 h, Separation factor 807.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mass volume concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Osmotic flux | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Film thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com