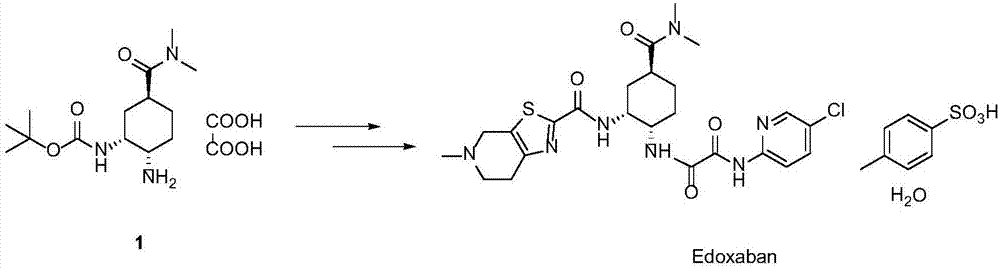
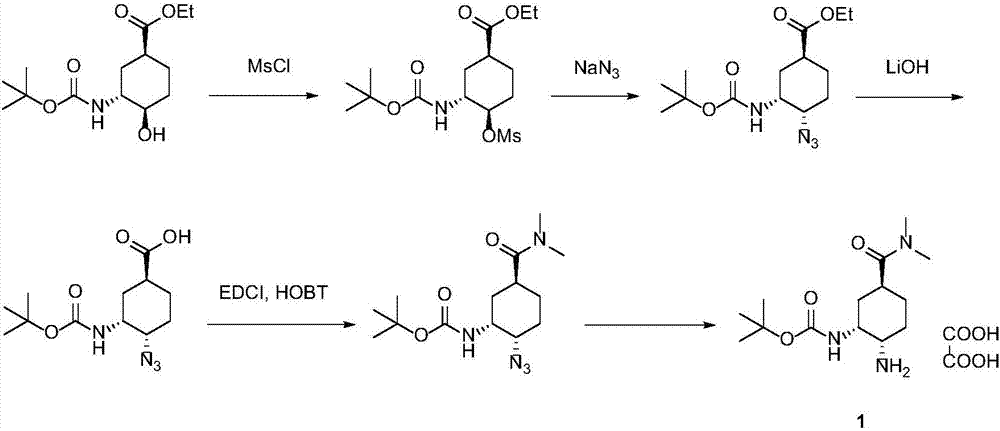
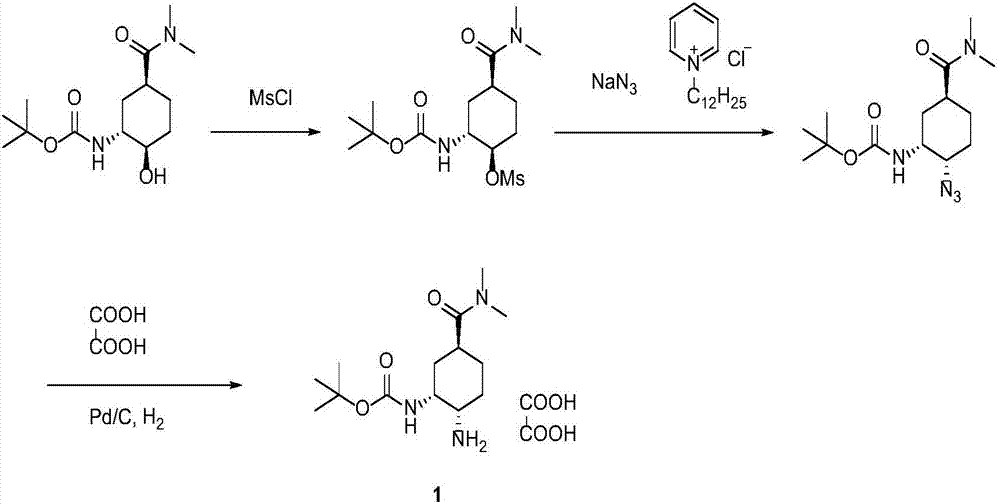
Synthesis method of edoxaban intermediate and intermediate product
A technology of edoxaban and a synthesis method, applied in chemical instruments and methods, preparation of organic compounds, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problem of high production risk of sodium azide, low diastereoselectivity, azide The problem of low chemical yield and other problems can be achieved to reduce the risk of industrial production, reduce production costs, and achieve the effect of high reaction conversion rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] The preparation of embodiment 1 compound 3a:
[0037]
[0038] Add 200mL water, 200mL dichloromethane, 2.0g NaBr, 4.2g NaHCO to the reaction flask 3 27.3 g of compound 2a (ie compound 2 when R is C1 alkoxy) was stirred until dissolved. The mixture was cooled to -5~0°C, then, a solution of 30 mg TEMPO reagent and 68 g NaClO (12% w / w active chlorine content) was added dropwise while maintaining the temperature at -5~0°C. The mixture was stirred at this temperature until all starting material was consumed (controlled by HPLC). Then, 100 mL of 10% aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution was added, and the mixture was stirred for about half an hour. The organic layer was collected, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered, and the filtrate was concentrated to dryness under reduced pressure to obtain 24.9 g of white solid compound 3a (that is, R was C1 alkane). Compound 3) in the case of an oxy group has a melting point of 80-82° C. and a yield of 92%.
[0039] [α] 20...
Embodiment 2
[0043] The preparation of embodiment 2 compound 3b:
[0044]
[0045] Add 200mL water, 200mL dichloromethane, 2.0g NaBr, 4.2g NaHCO to the reaction flask 3 , 28.7 g of compound 2b (ie, compound 2 when R is C2 alkoxy) stirred the mixture until dissolved. The mixture was cooled to -5~0°C, then, a solution of 30 mg TEMPO reagent and 68 g NaClO (12% w / w active chlorine content) was added dropwise while maintaining the temperature at -5~0°C. The mixture was stirred at this temperature until all starting material was consumed (controlled by HPLC). Then, 100 mL of 10% aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution was added, and the mixture was stirred for about half an hour. The organic layer was collected, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered, and the filtrate was concentrated to dryness under reduced pressure to obtain 27.4 g of white solid compound 3b (that is, R was C2 alkane). Compound 3) in the case of an oxy group has a melting point of 42-44° C. and a yield of 96%.
[00...
Embodiment 3
[0050] The preparation of embodiment 3 compound 3c:
[0051]
[0052] Add 200mL water, 200mL dichloromethane, 2.0g NaBr, 4.2g NaHCO to the reaction flask 3 30.1 g of compound 2c (ie compound 2 when R is C3 alkoxy) was stirred until dissolved. The mixture was cooled to -5~0°C, then, 30mg TEMPO reagent and 68g NaClO (12% w / w active chlorine content) solution were added dropwise while maintaining the temperature at -5~0°C. The mixture was stirred at this temperature until all starting material was consumed (controlled by HPLC). Then, 100 mL of 10% aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution was added, and the mixture was stirred for about half an hour. The organic layer was collected, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered, and the filtrate was concentrated to dryness under reduced pressure to obtain 27.1 g of white solid compound 3c (that is, R was C3 alkane). Compound 3) in the case of an oxy group has a melting point of 61-63° C. and a yield of 91%.
[0053] [α] 20 D (C...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com