A kind of soil oxidation-solidification stabilization repair agent and its application method
A technology for remediating chemicals and soil, applied in the environmental field, can solve the problems of no oxidation effect, difficult to deal with organic-heavy metal composite polluted soil, and metal sulfides cannot be stabilized, and achieves good curing effect, simple components, Easy-to-use effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
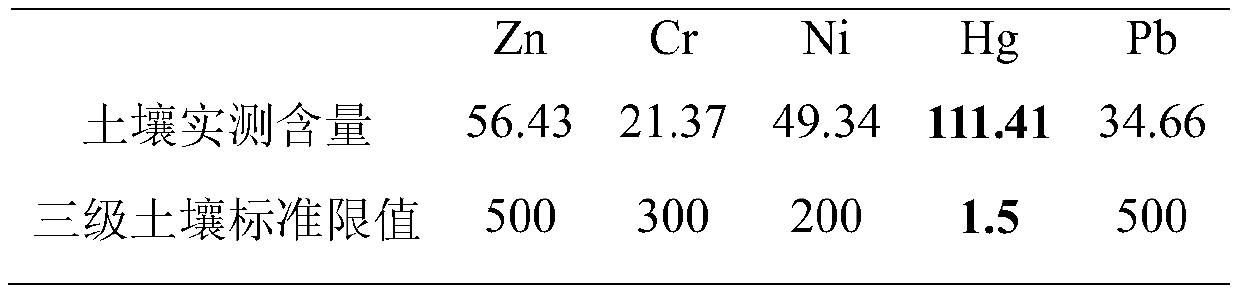
[0026] Take the polluted soil of a PVC production enterprise, and measure the content of various heavy metals and total natural organic matter (NOM) in the soil. The measurement results of heavy metals are shown in Table 1. It can be found that the mercury content therein exceeds the limit value of 1.5 mg / kg for the mercury content in the third-grade soil in the "Soil Environmental Quality Standard" (GB15618-1995), and the organic matter content of the soil is 6 g / Kg simultaneously.
[0027] Table 1 The content of heavy metals in the soil and the standard limit of the third grade soil mg / kg
[0028]
[0029] The oxidation-curing stabilizing and repairing agent used in this embodiment selects micron-sized zero-valent iron, sodium disilicate and calcium oxide.
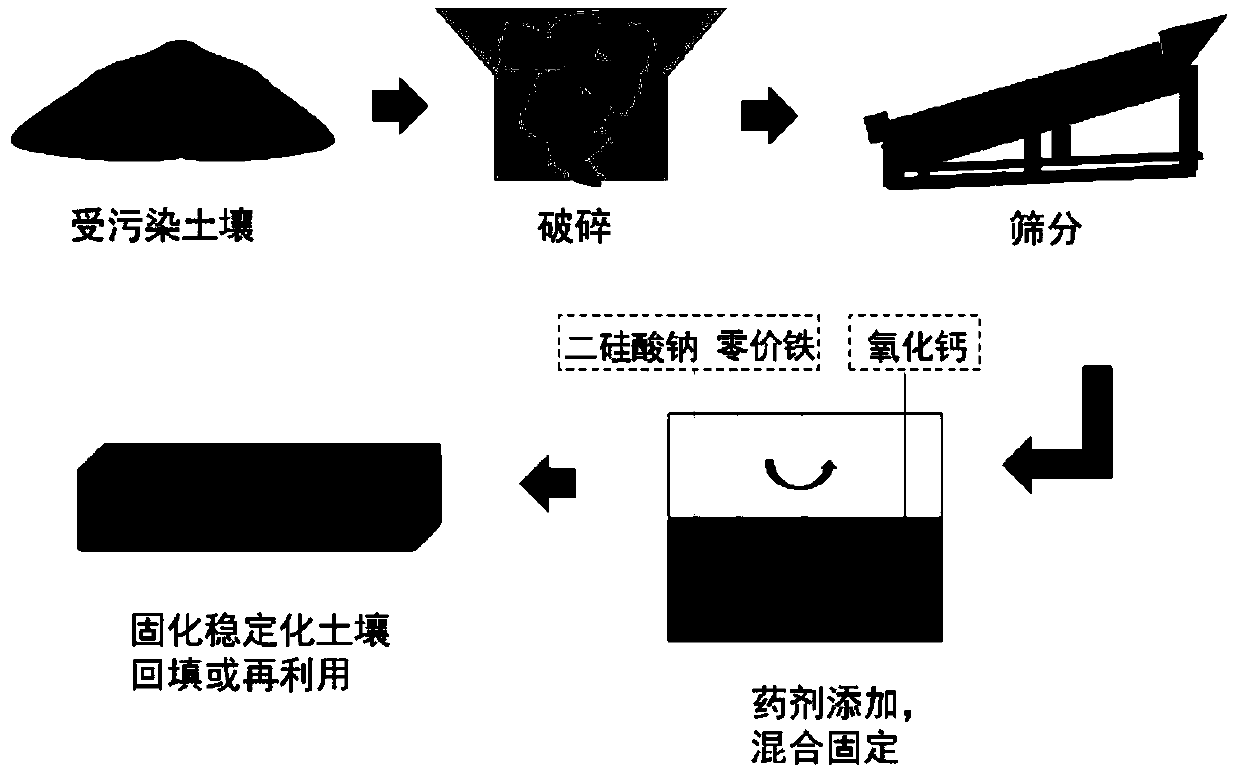
[0030] First, crush the retrieved heavy metal-contaminated soil, put it into a plastic cylinder, add a solution of 10mmol / L sodium disilicate and an appropriate amount of micron zero-valent iron, and stir fully while ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] The oxidation-solidification stabilizing remediation agent used in this embodiment selects nano-scale zero-valent iron, sodium disilicate and calcium oxide to remediate arsenic-contaminated soil.
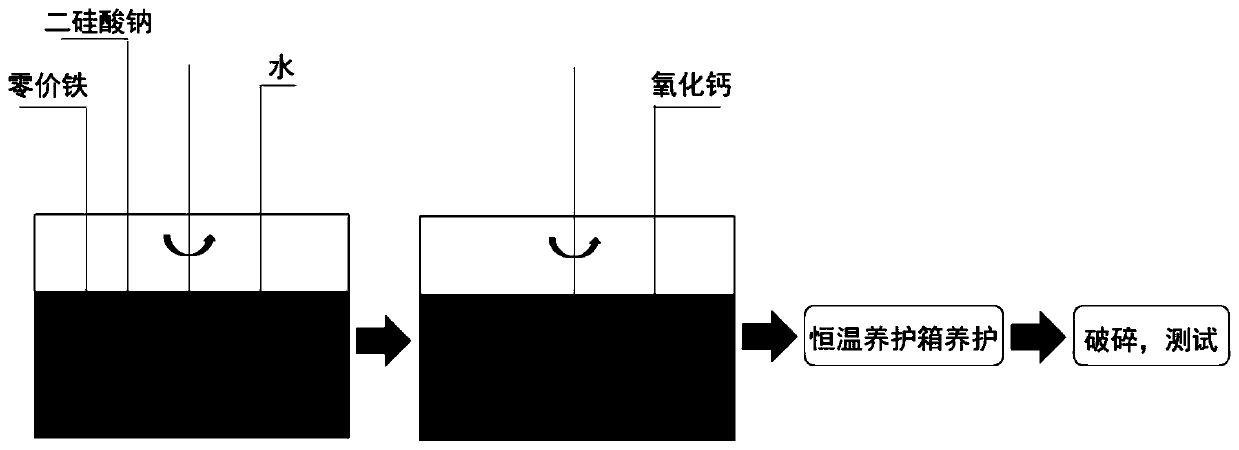
[0034] First, crush the heavy metal-contaminated soil retrieved, put it into a plastic cylinder (take a part first to test its total organic carbon content (TOC)), add 20mmol / L sodium disilicate solution and an appropriate amount of nanometer zero-valent iron, and add While fully stirring, the soil becomes muddy. Continue to stir continuously, and carry out proper aeration. After half an hour, add calcium oxide gradually, and then stir for 10 minutes. See the experimental device and brief process figure 2 . Afterwards, the mud is placed in a constant temperature curing box at 60°C and relative humidity <25% for digestion and molding until the mud is completely dry and has a certain strength. Digest and shape for 36 hours, then cool down naturally for crushing. At the end ...
Embodiment 3
[0039] The oxidation-solidification stabilization and remediation agent used in this embodiment selects micron-sized zero-valent iron, sodium disilicate and calcium oxide to remediate chromium-contaminated soil.
[0040] First, crush the retrieved heavy metal-contaminated soil, put it into a plastic cylinder, add a solution of 15mmol / L sodium disilicate and an appropriate amount of micron zero-valent iron, and stir fully while adding, the soil becomes muddy. Continue to stir continuously, and carry out proper aeration. After half an hour, add calcium oxide gradually, and then stir for 15 minutes. See the experimental device and brief flow figure 2 . Afterwards, the mud is placed in a constant temperature curing box at 60°C and relative humidity <25% for digestion and molding until the mud is completely dry and has a certain strength. Digest and shape for 36 hours, then cool down naturally for crushing.
[0041] After the soil treated with solidification and stabilization ha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com