Three-dimensional printing method
A technology of three-dimensional printing and printed body, applied in the field of additive manufacturing, which can solve the problems of low molding accuracy, inability to manufacture complex and fine structures, and structural damage.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
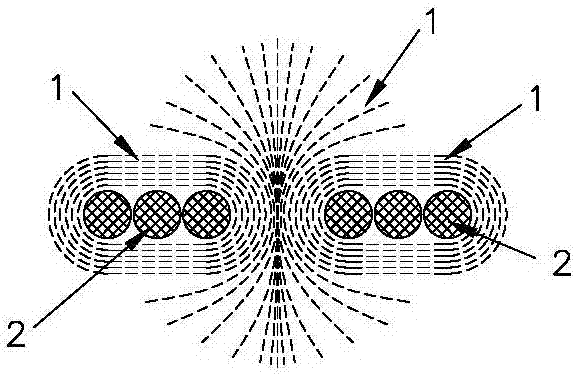
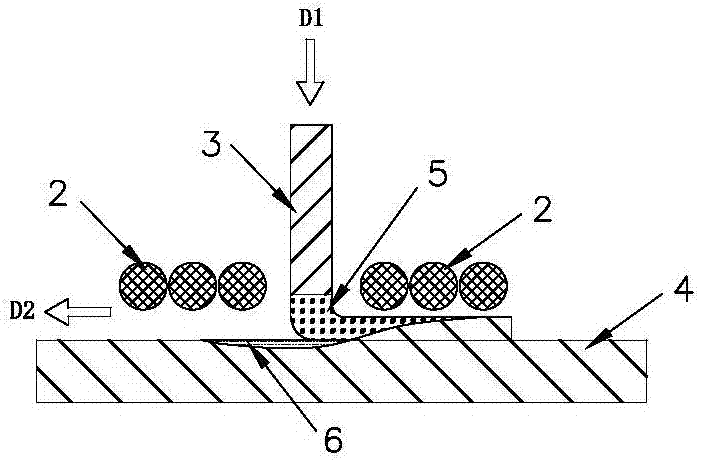
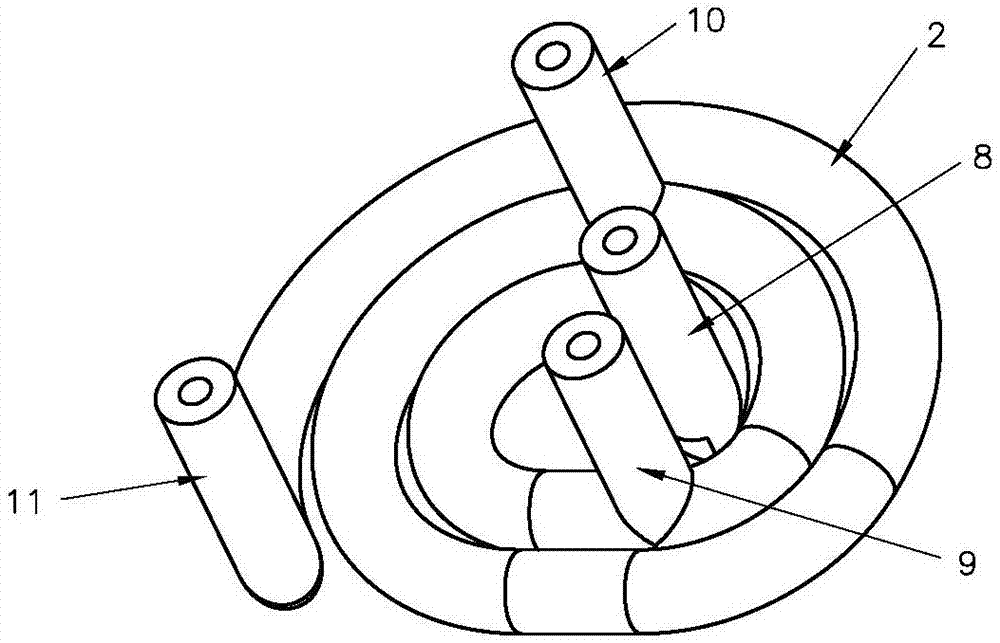
[0093] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 4 The first preferred specific embodiment of a three-dimensional printing method of the present invention is shown: a three-dimensional printing method, the main process of which is: placing the molten raw material (that is, the molten raw material 5) into the three-dimensional printing device used In the forming area, the molten raw material is accumulated in the forming area and transformed into a printed body, and the molten raw material is accumulated on the basis of the printed body (ie, printed body-4) until the object to be printed is formed, and the accumulated printed body constitutes the object to be printed; Wherein: in the process of accumulating molten raw materials, the position where the molten raw materials are placed is determined by the shape and structure of the object to be printed, that is, determined by the computer model data corresponding to the object to be printed; the three-dimensional printing device described The ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com