Method of conservation and recovery of haematococcus pluvialis cell
A technology of Haematococcus pluvialis and a preservation method is applied in the field of preservation and recovery of Haematococcus pluvialis cells, and can solve the problems such as the recovery survival rate of only 66.13%, the complicated operation technology preservation equipment, and the limitation of the efficiency and scale of preservation. , to achieve the effect of inhibiting the proliferation of bacteria and miscellaneous algae, high recovery survival rate, and simple method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
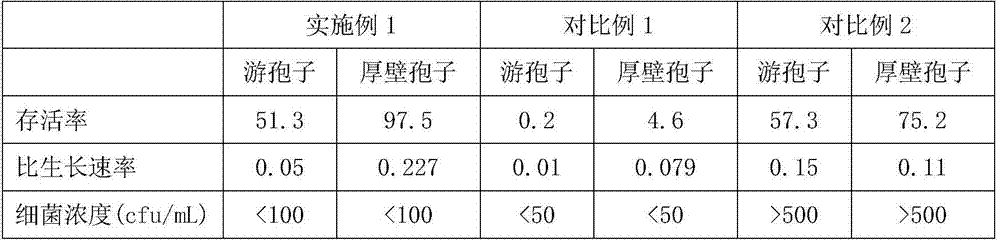
[0024] Haematococcus pluvialis NIES-144 strain (commercially available), respectively: 1) in total nitrogen BBM medium (commercially available) at 50 μE / m 2 The green zoospores obtained by cultivating algal strains for 5 days under / s light;
[0025] 2) In nitrogen-free BBM medium at 300μE / m 2 The chlamydospores obtained by cultivating algal strains for 10 days under / s light;
[0026] The green zoospores and thick-walled spores obtained above were left to settle and concentrate, and then placed in the fresh-keeping room of the refrigerator at 5 degrees Celsius for cold acclimation for 24 hours; then transferred to the refrigerator at -20 degrees Celsius to freeze into ice and continue to freeze for 60 days; After storage, take it out and let it thaw at room temperature.
[0027] Afterwards, dilute the above-mentioned concentrated algae liquid with the BBM medium containing 4mmol / L sodium nitrate to a cell density of 0.449g / L, and place it at 200μE / m 2 / s light, and pass 1%...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Haematococcus pluvialis SCCAP K-0084 algal strain (commercially available), in nitrogen-free BBM medium at 300 μE / m 2 Cultivate the algal strain under the light of / s for 10 days to obtain chlamydospores. After standing and settling, the concentrated algae liquid with a cell density of 60g / L was obtained. The concentrated algae liquid was placed in the fresh-keeping room of the refrigerator at 5 degrees Celsius for 24 hours of cold acclimation; after that, it was packed in In multiple sample bags, after subpackaging, place them in refrigerators at -5, -20, and -80 degrees Celsius to freeze into ice, and continue to freeze for 60 days. Then take it out and let it melt at room temperature, dilute and melt it with BBM medium containing 4mmol / L sodium nitrate, concentrate the algae liquid to a cell density of 0.5g / L, and place it at 200μE / m 2 / s light, and pass 1% CO 2 air culture. After culturing under light for 48 hours, use a fluorescent microscope to observe and count...
Embodiment 3
[0044] In nitrogen-free BBM medium at 300 μE / m 2 Cultivate the algae strain under the light of / s for 10 days to obtain the thick-walled algae liquid. After standing and settling, the concentrated algae liquid with a cell density of 40g / L was obtained, which was placed in the fresh-keeping room of the refrigerator at 5 degrees Celsius for 24 hours of cold acclimation; transfer to a freezer at -5°C to freeze into ice. After 3, 38 and 75 days of frozen storage, take out a bag of frozen algae and thaw at room temperature; then dilute the thawed and concentrated algae liquid with BBM medium containing 4mmol / L sodium nitrate to a cell density of 0.5g / L , placed in 200μE / m2 / s light, and passed through 1% CO 2 air culture. Sampling at regular intervals to monitor cell growth. The experiment in which only cold-acclimated cells were used as inoculation materials without freezing was used as a control. The results showed that the survival rates of recovered cells after 3, 38 and 75 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com